Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0609–0672) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster I: Research
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: As primary myocardial involvement in systemic sclerosis (SSc) is associated with worse prognosis, research on diagnostic tools for recognition is essential. Troponin I was suggested as a more specific biomarker for myocardial involvement in SSc than the frequently used troponin T. The aim of this study is to evaluate the association between troponin I levels and primary myocardial involvement in SSc patients, and to evaluate the presence of subclinical myocardial involvement by comparing troponin I levels between SSc patients and healthy controls.
Methods: A cross-sectional observational study was performed, including four groups of each 20 SSc patients, fulfilling ACR/EULAR 2013 criteria, selected from the Leiden Combined Care in Systemic Sclerosis cohort: (1) patients with primary myocardial involvement, (2) patients with myositis, (3) patients with elevated troponin T and CK levels but without organ involvement, and (4) patients without any suggestions of organ involvement. Primary myocardial involvement was assessed independently by an experienced rheumatologist and an experienced cardiologist. Troponin I levels were measured in patient sera and 20 additional healthy donors using ELISA. Troponin I levels were compared between the different groups using Mann-Whitney U and Kruskal-Wallis tests.
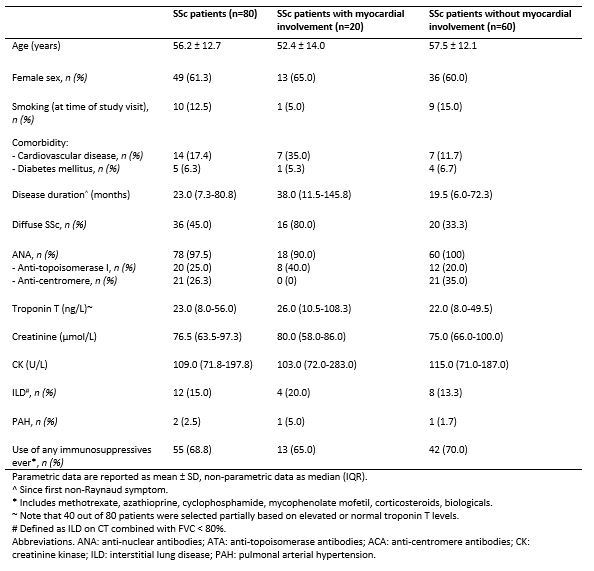
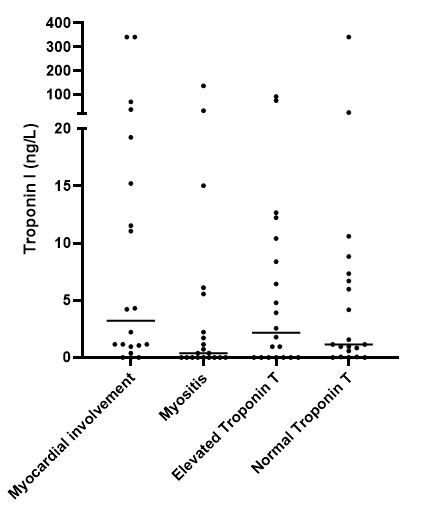
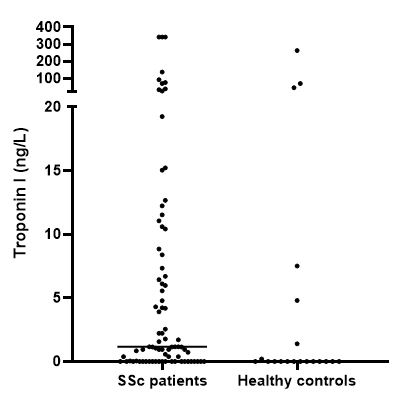
Results: The mean age of the 80 included patients was 56.2 ± 12.7 years, 61% of the study population was female. Troponin I levels were comparable between patients with and without myocardial involvement (2.7 [0.5 – 15.3] vs. 1.2 [0.1 – 6.6] ng/L; p = 0.117). Within the group of patients without myocardial involvement, SSc patients with myositis, SSc patients with elevated troponin T levels without organ involvement and SSc patients with normal troponin T levels without organ involvement, had median troponin I levels of 0.4 (0.0 – 4.7) ng/L, 2.2 (0.0 – 9.9) ng/L, and 1.2 (0.2 – 7.2) ng/L, respectively. No significant differences were found in median troponin I levels between the four different subgroups (p=0.131) (Figure 1). SSc patients (without myocardial involvement) were more often positive for troponin I than healthy controls (30.0% vs. 65.0%, p = 0.006) (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Elevated troponin T and I levels were identified in SSc patients without myocardial involvement possibly indicating subclinical myocardial involvement in the majority of patients. However, these elevated levels were not of additive value to identify SSc patients with clinical myocardial involvement.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hoekstra E, Liem S, Levarht N, Fehres C, Ahmed S, Ajmone Marsan N, Huizinga T, de Vries-Bouwstra J. Troponin I Levels in Systemic Sclerosis Patients with Myocardial Involvement [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/troponin-i-levels-in-systemic-sclerosis-patients-with-myocardial-involvement/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/troponin-i-levels-in-systemic-sclerosis-patients-with-myocardial-involvement/