Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Lorecivivint (LOR), an intra-articular (IA) CLK/DYRK inhibitor thought to modulate inflammatory and Wnt pathways has previously appeared safe, improved patient-reported outcomes (PROs) compared with placebo (PBO) over several clinical trials. Over its development program as a disease-modifying OA drug, inclusion / exclusion criteria have changed as knowledge of disease state enrichment factors was gained and need to be accounted for in order to ascertain an integrated assessment of treatment benefit. A meta-analysis to integrate assessment of LOR efficacy by comparing 6 and 12 month efficacy across several LOR trials was conducted.
Methods: To be included in the meta-analysis, trials were blinded, placebo-controlled, and have observed PROs at least twelve months after single study medication administration. Shorter duration trials with extension follow-up trials were allowed. Two key enrichment criteria, symptomatic unilateral disease and negative widespread diffuse pain, were retrospectively applied to older trial populations to account for differences in inclusion / exclusion criteria. Least square estimates and their 95% confidence intervals as well as total sample size were abstracted from baseline-adjusted ANCOVA for each study.
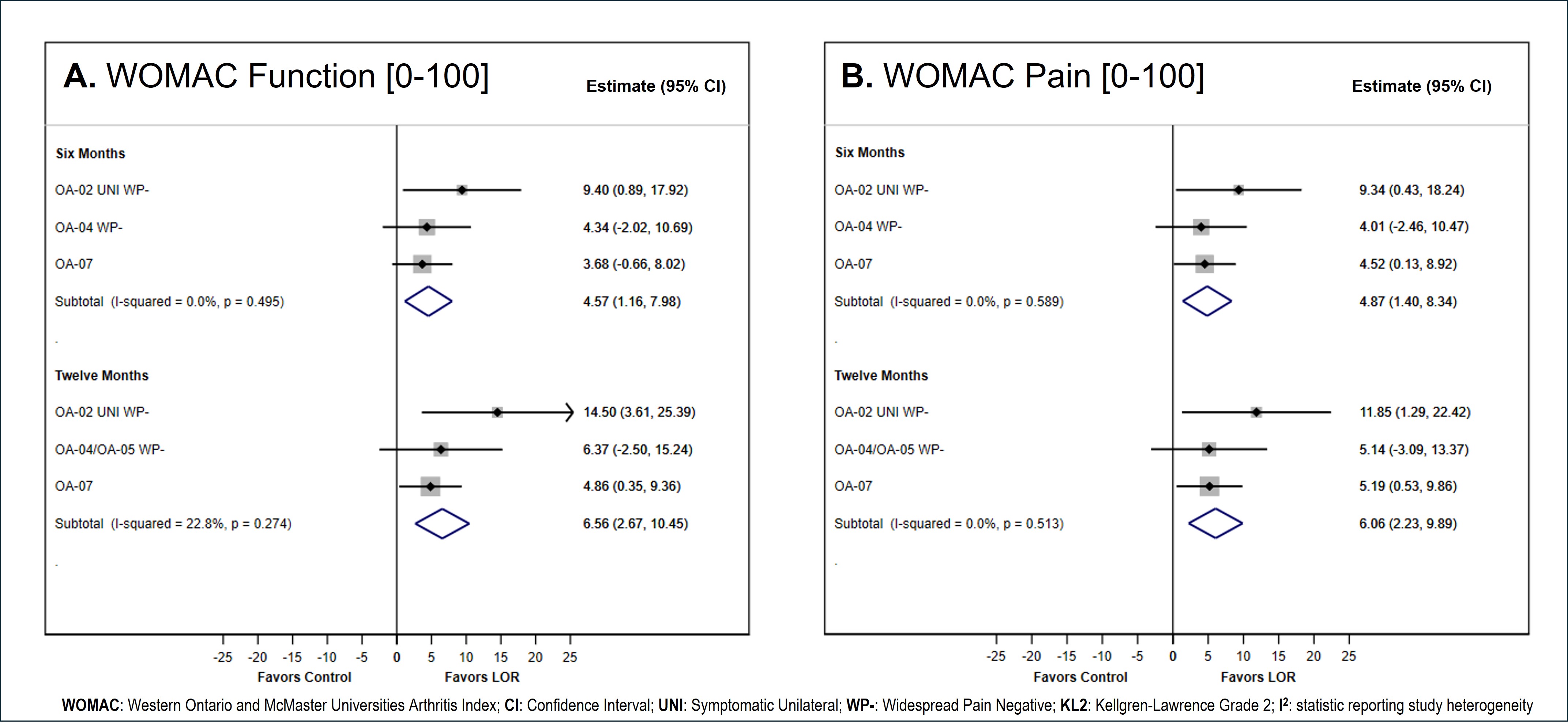
Results: Four trials evaluating LOR efficacy for at least 12 months were identified: 1) OA-02 (NCT02536833), 2) OA-04 (NCT03122860) and its extension OA-05 (NCT02951026), 3) OA-11 (NCT03928184) and 4) OA-07 (NCT04520607). While OA-07 was an extension of OA-11, it met criteria for inclusion as patients were treated at the start of OA-07 with the same randomized treatment received in OA-11.
Initial meta-analysis models had significant heterogeneity, as estimated by the statistics I2, for WOMAC Pain (6 months I2 = 63.6%, P=0.041, 12 months I2 = 68.2%, P=0.024) and WOMAC Function (6 months I2 = 50.4%, P=0.109, 12 months I2 = 66.4%, P=0.030). Exploratory models examined the impact of each trial on heterogeneity, leading to the identification of OA-11 as the key contributor to meta-analysis variability and subsequent exclusion from the final meta-analysis. The final meta-analysis models estimated significant treatment effect of LOR over PBO for both WOMAC Pain (6 months ∆=4.87, 95% CI [1.40, 8.34]; 12 months ∆=6.06, 95% CI [2.23, 9.89]) and WOMAC Function (6 months ∆=4.57, 95% CI [1.16, 7.98]; 12 months ∆=6.56, 95% CI [2.67, 10.45]) (Figure 1).
Conclusion: In this meta-analysis of knee OA trials, LOR showed significant improvement in both pain and functional outcomes over 6 and 12 months after a single injection compared to placebo. LOR continues to show promise as a safe and effective treatment for knee OA with benefits across pain, function and structure.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Swearingen C, Tambiah J, Yazici Y. Treatment Effect of Lorecivivint Across Multiple Trials in Patients with Knee OA: A Meta-analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-effect-of-lorecivivint-across-multiple-trials-in-patients-with-knee-oa-a-meta-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-effect-of-lorecivivint-across-multiple-trials-in-patients-with-knee-oa-a-meta-analysis/