Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Depression is a prevalent comorbidity in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), affecting up to 38.8% of individuals. Depression can profoundly affect physical well-being, including increased pain perception and fatigue. Moreover, untreated depression may hinder treatment adherence and overall disease management in RA. Psychological distress can influence the perception of joint tenderness and swelling, potentially leading to fluctuations in these clinical measures. In this study, our aim was to investigate the subjective and objective measures of disease activity according to the severity of depression, with a focus on disease activity on musculoskeletal ultrasound (US).
Methods: At the ORCHESTRA (Ottawa Rheumatology CompreHEnSive TReatment and Assessment) Clinic, RA patients starting a new bDMARD/tsDMARD therapy are assessed using a comprehensive screening process which includes a protocoled US scan at baseline and three months after new therapy initiation. Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ) scores were used to measure depression. The B-mode and Doppler findings were scored according to the OMERACT definitions on a scale between 0-3 per joint. Analyses was performed to compare disease features, clinical and US detected disease activity, according to the severity of depression.
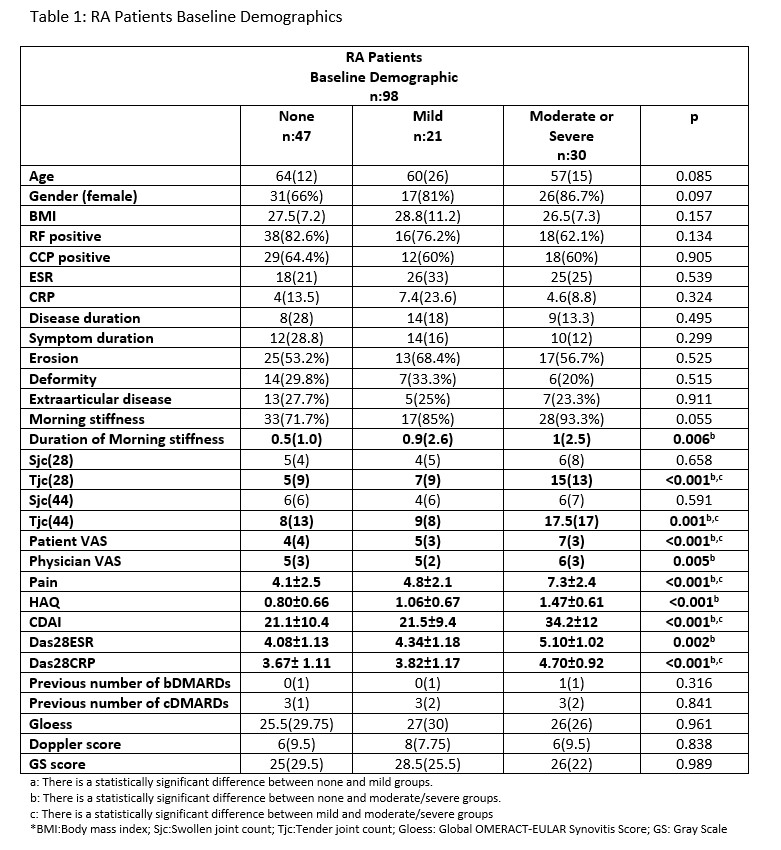
Results: Within 98 RA patients, 47, 21 and 30 patients had none, mild or moderate-to-severe depression, respectively (Table-1). Demographic features were comparable across depression states. Subjective disease measures, including duration of morning stiffness, tender joint counts, VAS scores reported by both patients and physicians, HAQ scores as well and composite indices (CDAI scores, DAS28-ESR and DAS28-CRP scores) were higher in patients with moderate-severe depression, compared to mild or no depression (table-1). In contrast, the depression severity did not have any impact on objective measures, including the swollen joint counts and ultrasound scores (both GLOESS and Doppler scores).
Conclusion: Depression is a frequent comorbidity in RA, and affects how much the patient is impacted with the disease. RA patients with moderate-to-severe depression report higher subjective patient-reported outcomes, despite similar ultrasound scores for inflammation. This observation suggests that the presence of moderate-severe depression reduces the reliability of PROs in assessing disease activity in RA and objective measures are needed to choose the right therapeutic approach. When the target of RA is set as remission, a comprehensive approach is required, which includes addressing depression as an integral part of the management.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bayindir Tsechelidis O, Sabido-Sauri R, Gazel U, Acikgoz S, Sangwa S, Ivory C, Hepworth E, Aydin S. Treat (Depression to Reach)-to-Target in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treat-depression-to-reach-to-target-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treat-depression-to-reach-to-target-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/