Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1191–1220) Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
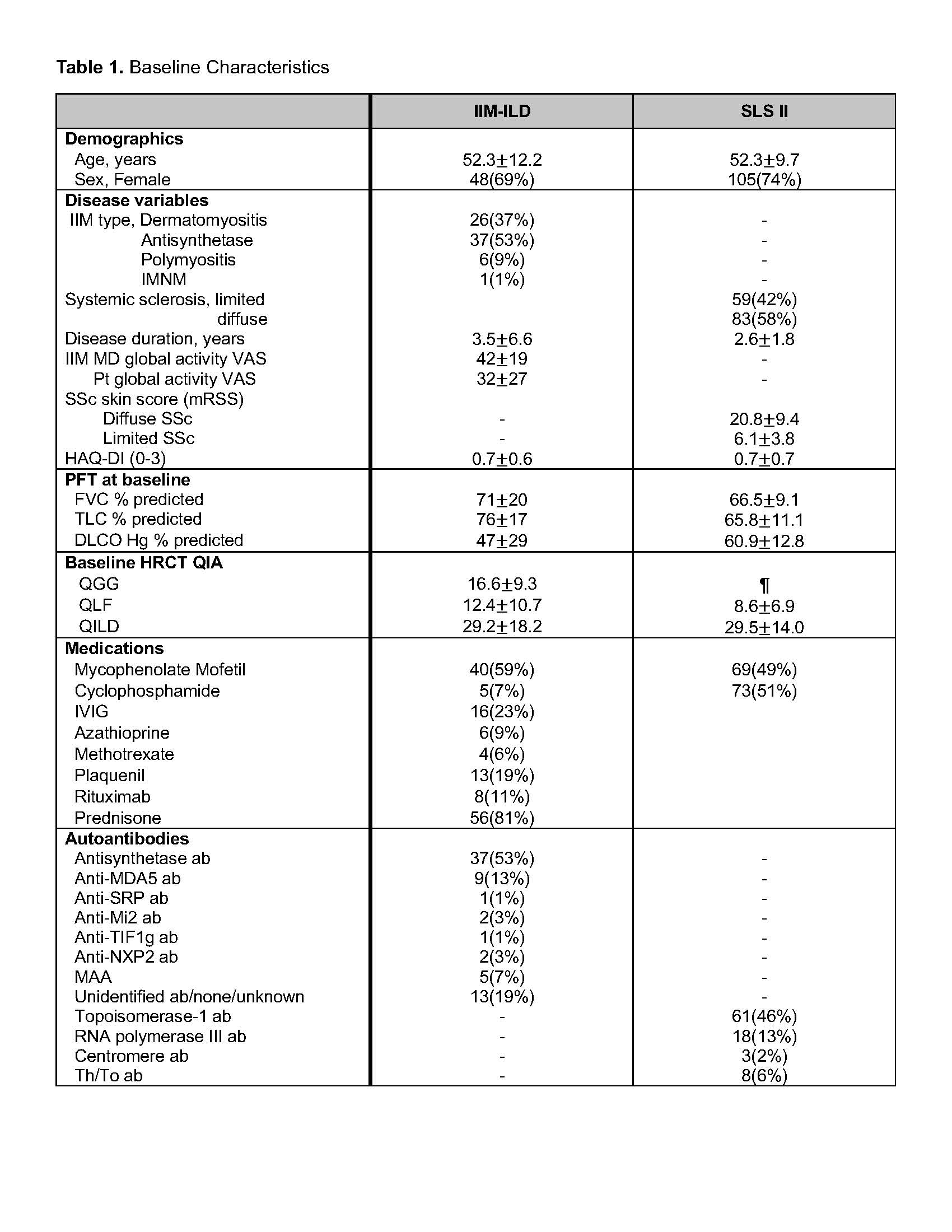
Background/Purpose: HRCT is used as a surrogate for important histopathological findings when evaluating patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD). Quantitative imaging analysis (QIA) using CT texture-based scores were shown to associate with lung physiology and patient reported outcomes in IIM-ILD. The current work aims to examine changes in HRCT patterns of IIM-ILD as they transition from one pattern to another during follow-up, and compare transition patterns of IIM-ILD to that of ILD related to systemic sclerosis (SSc-ILD).
Methods: We evaluated changes in the quantitative extent of ground glass, fibrotic pattern and normal lung obtained at baseline and follow-up in HRCT scans. Patients with ILD confirmed by HRCT and on immunosuppressive treatment were included from 2 longitudinal IIM-ILD cohorts. In each within-patient baseline to follow-up HRCT pair, we calculated the transitional probability expressed as a proportion of voxels representing a particular pattern of ILD that changes from the initial pattern to another pattern at follow-up, the denominator being the total number of voxels within the initial pattern at baseline. Net improvements in ground glass and fibrotic patterns were determined by subtracting unfavorable transitional probabilities from favorable ones and statistically analyzed with the null hypothesis of net improvement being 0. In order to compare transitional probability with SSc-ILD, we selected IIM-ILD patients with comparable follow up time between HRCTs to the Scleroderma Lung Study II (SLS II) for which transitional probability had previously been reported using similar methodology (PMID:31430058).
Results: Transitional probability was calculated in 70 IIM-ILD patients that had baseline and follow-up HRCT scans adequate for voxelwise registration. The cohort included 53% antisynthetase and 37% dermatomyositis associated ILD patients with a mean disease duration of 3.5 years (Table 1). Mean transitional probability for each transition pattern is shown in Figure 1. Fifty-five percent of baseline ground glass and 46% of baseline fibrosis transitioned to a normal pattern. Net probabilities of improvement for both ground glass to normal transition (PGG→NORML- PNORML→GG) and fibrosis to normal transition (PFibro→NORML – PNORML→Fibro) were significant (mean 0.44 and 0.39 respectively, p< 0.0001 for both). We compared transitional probabilities of 36 IIM-ILD patients with those in SLS II (Table 2). Favorable transitional probabilities (PGG→NORML, PFibro→NORML, PFibro→GG) were significantly greater in IIM-ILD compared to SSc-ILD patients whereas the majority of SSc-ILD remained stable. Unfavorable transitional probabilities (PNORML→GG, PGG→Fibro and PNORML→Fibro) were overall low in both groups, showing a slight trend to be greater in the IIM-ILD compared to the SSc-ILD group (2/3 comparisons not statistically significant).
Conclusion: Transitional scoring assessment of ILD demonstrated that significant portions of ground glass and fibrotic patterns at baseline transitioned to a normal pattern with treatment in both IIM and SSc patients with ILD. However, IIM-ILD had significantly greater proportions of favorable transition patterns than SSc-ILD.
 Values are presented as mean±SD
Values are presented as mean±SD
IIM-ILD group(n=70) is comprised of 2 separate cohorts: one single-center observational cohort (n=59) and one multicenter clinical trial cohort of antisynthetase ILD (Attack My-ILD ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03215927, n=11)
¶ Data unavailable at time of abstract submission
Abbreviations: IIM, idiopathic inflammatory myopathy; IMNM, immune mediated necrotizing myopathy; VAS, visual analog scale; PFT, pulmonary function test; QIA, quantitative imaging analysis; QGG, quantitative ground glass score; QLF, quantitative lung fibrosis score; QILD, quantitative total ILD score; MAA, myositis associated antibody (Ro, Ku, Pm-scl)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bae S, Kim G, Lee J, Markovic D, Tashkin D, Goldin J, Aggarwal R, Charles-Schoeman C. Transitional Changes on High Resolution Computed Tomography (HRCT) in idiopathic inflammatory Myopathy- Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (IIM-ILD) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/transitional-changes-on-high-resolution-computed-tomography-hrct-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathy-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-iim-ild/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/transitional-changes-on-high-resolution-computed-tomography-hrct-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathy-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-iim-ild/

.jpg)
.jpg)