Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA), a chronic progressive inflammatory arthritis, affects peripheral joints and causes patient disability. PsA patients also have skin plaques initiated by activation of epidermal dendritic cells, which stimulate the IL23-dependent activation and proliferation of Th17 cells. Indeed, the IL17/IL23 pathway is critical in PsA pathogenesis and represents an important target to control disease progression. Tofacitinib, a JAK1 and JAK3 inhibitor, impairs the production of IL6 and IL23, cytokines crucial for Th17 differentiation. Here, we study the efficacy of tofacitinib and the immune mechanisms implicated in the amelioration of psoriasis (PsO) and arthritis in an IL23-driven murine model.
Methods: Two groups of B10.RIII mice were intravenously injected with 3 μg of IL23 minicircle to induce PsO and arthritis. Mice were gavaged daily with tofacitinib at 50mg/kg or vehicle for two weeks, starting seven days after the injection of the IL23 minicircle. Plasma and infiltrating synovial cells were collected on day 20 after injection of IL23 minicircle. Cytokines and chemokines were quantitated by LEGENDPlex bead-based immunoassay and synovial cells were collected for bulk RNA sequencing.
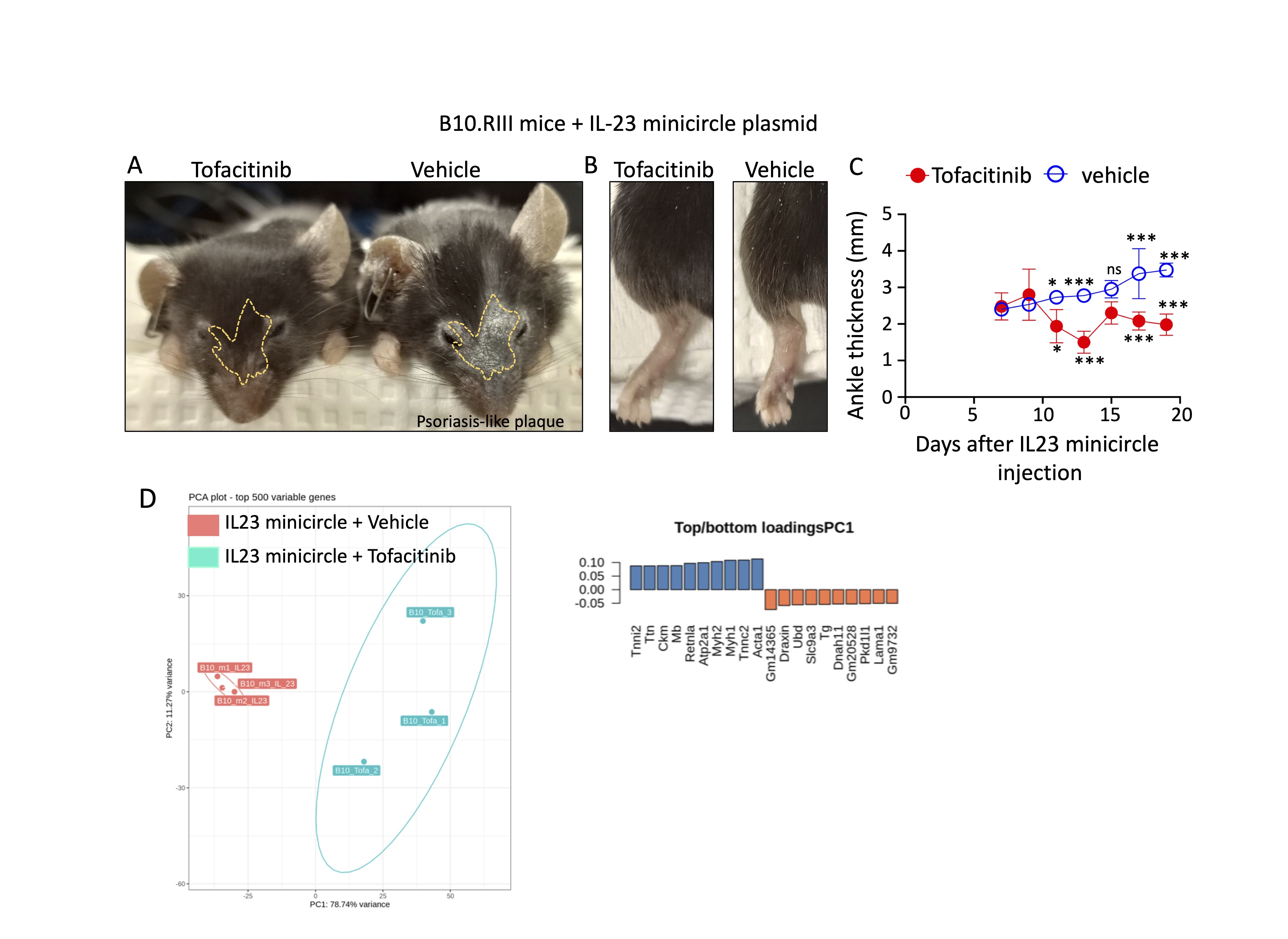
Results: B10.RIII injected with IL23 minicircle and treated with tofacitinib for 2 weeks did not lose body weight, supporting the safety of daily administration by gavage. Hydrodynamical injection of IL23 minicircle significantly increased IL17 and IL23, suggesting the generation of Th17 cells. In addition, Cxcl9 reduction likely prevented the recruitment of Th1 cells. We also found a significant increase in Cux1, Grk2 and Csf3r, genes implicated in the local generation and attraction of neutrophils. Importantly, there was a significant decrease in PsO plaques, joint swelling, and ankle thickness in tofacitinib-treated mice (vehicle: 3.9 vs tofacitinib: 1.9 mm, p = 0.001). Plasma samples from B10.RIII mice treated with tofacitinib showed a significant increase in Thymus and Activation Regulated Chemokine (TARC; 1.56-fold, p = 0.0027), Macrophage-Derived Chemokine (MDC; 2.1-fold, p = 0.002), and eotaxin, (6.2-fold, p = 0.0002); chemokines induced by IL4 and IL13. In addition, there was a decrease in CXCL13 and CCL20, which orchestrate the recruitment of CXCR5+ B cells, CCR6+ monocytes and memory T lymphocytes to inflamed sites. We also found a significant increase in the expression of Fizz1 (Retnla), which is expressed by alternatively activated macrophages, a population involved in bone regeneration. Finally, Ubiquitin D (UBD) likely prevented the downregulation of type 2 cytokines (IL4 and IL5).
Conclusion: Tofacitinib therapy ameliorated psoriasis and arthritis via modulation of Th1 and Th17 responses and by supporting type 2 polarization in the synovia of B10.RII mice injected with IL23 minicircle. This modulation inhibits the generation of classically activated macrophages, a proinflammatory population actively involved in the process of osteoclast formation and bone erosion.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Garcia-Hernandez M, Rangel-Moreno J, Paine A, Rangel-Garcia A, Krantz M, Martino D, Nuzzo M, Ritchlin C. Tofacitinib Therapy Ameliorates Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Psoriasis and Arthritis by Inducing Type 2 Immunity [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tofacitinib-therapy-ameliorates-inflammation-in-a-mouse-model-of-psoriasis-and-arthritis-by-inducing-type-2-immunity/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tofacitinib-therapy-ameliorates-inflammation-in-a-mouse-model-of-psoriasis-and-arthritis-by-inducing-type-2-immunity/