Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) pathogenesis involves a range of immune cells, for instance T-cells, neutrophils and macrophages. They produce proinflammatory factors, such as proteolytic enzymes, which interact with tissue components such as collagens, leading to a release of unique tissue fragments into the circulation. Type IV collagen is a basement membrane supporting endothelium and epithelium. From previous studies, we know that T-cell activity may be quantified by measuring C4G, a metabolite of Granzyme B (a cytotoxic granule enzyme) mediated degradation of type IV collagen, while C4M is a marker of MMP activity 1. Quantifying these unique metabolites reflecting the interaction between immune cell and type IV collagen may provide a deeper understanding of the tissues affected by RA and be more relevant to disease activity and progression than simply quantifying the immune cell number or cytokines 2. The objective was to investigate the association between the unique immune cell activity metabolites C4G and C4M, and clinical outcomes in RA before and after intervention with tocilizumab, methotrexate (MTX) and placebo.
Methods: This is an explorative post-hoc analysis of left-over samples from the AMBITION trial (NCT00109408). The two biomarkers were measured pre- and post-treatment serum samples (8 weeks) in 169 biological naïve RA patients treated with either tocilizumab (TCZ, 8 mg/kg), placebo or methotrexate (MTX) monotherapy (7.5-20 mg/kg). Biomarker levels were correlated to clinical outcomes by Spearman’s correlation. Comparison between treatment and treatment groups were done by ANCOVA, adjusted for baseline biomarker levels, age, sex, BMI, and disease duration.
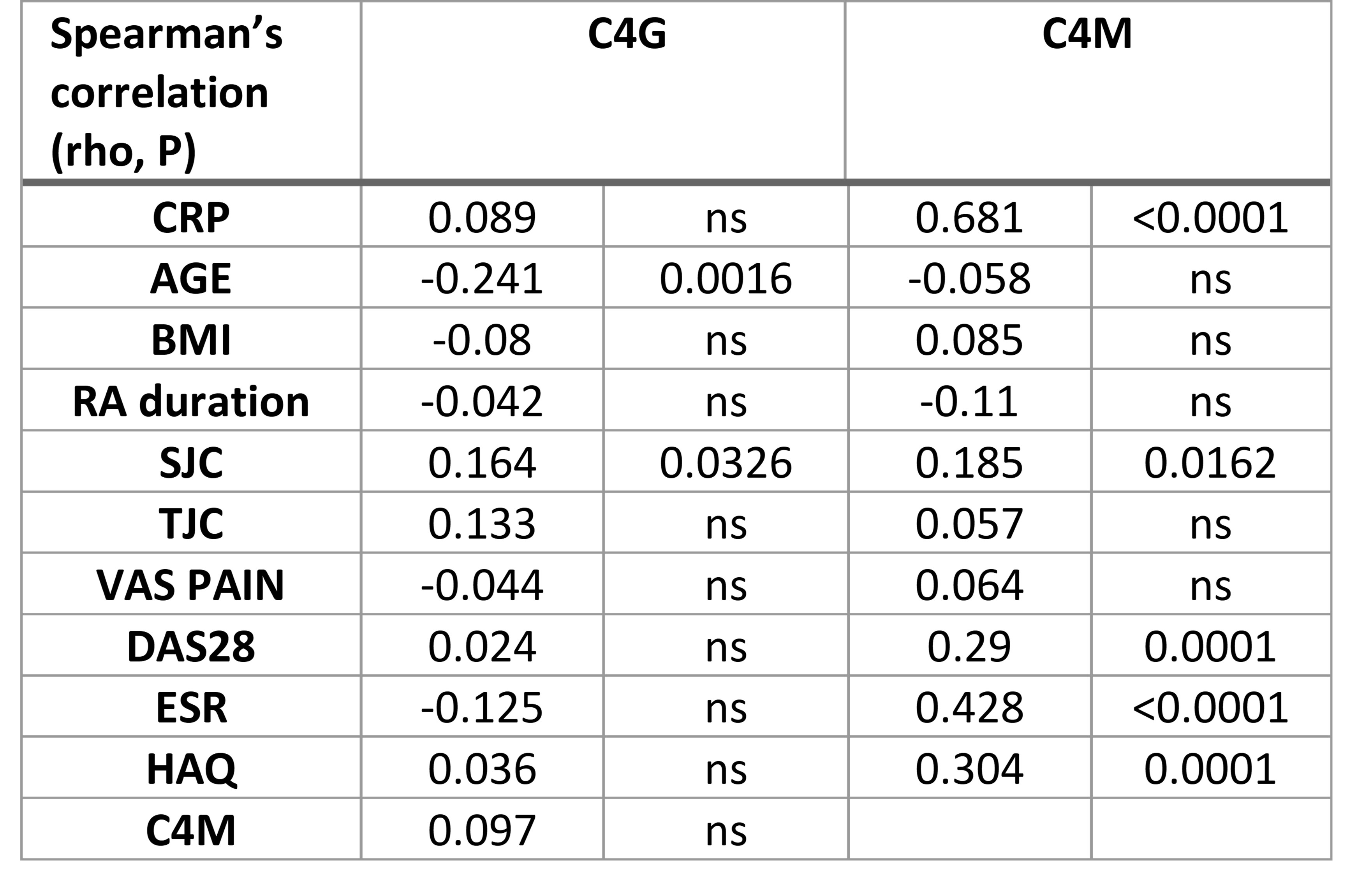
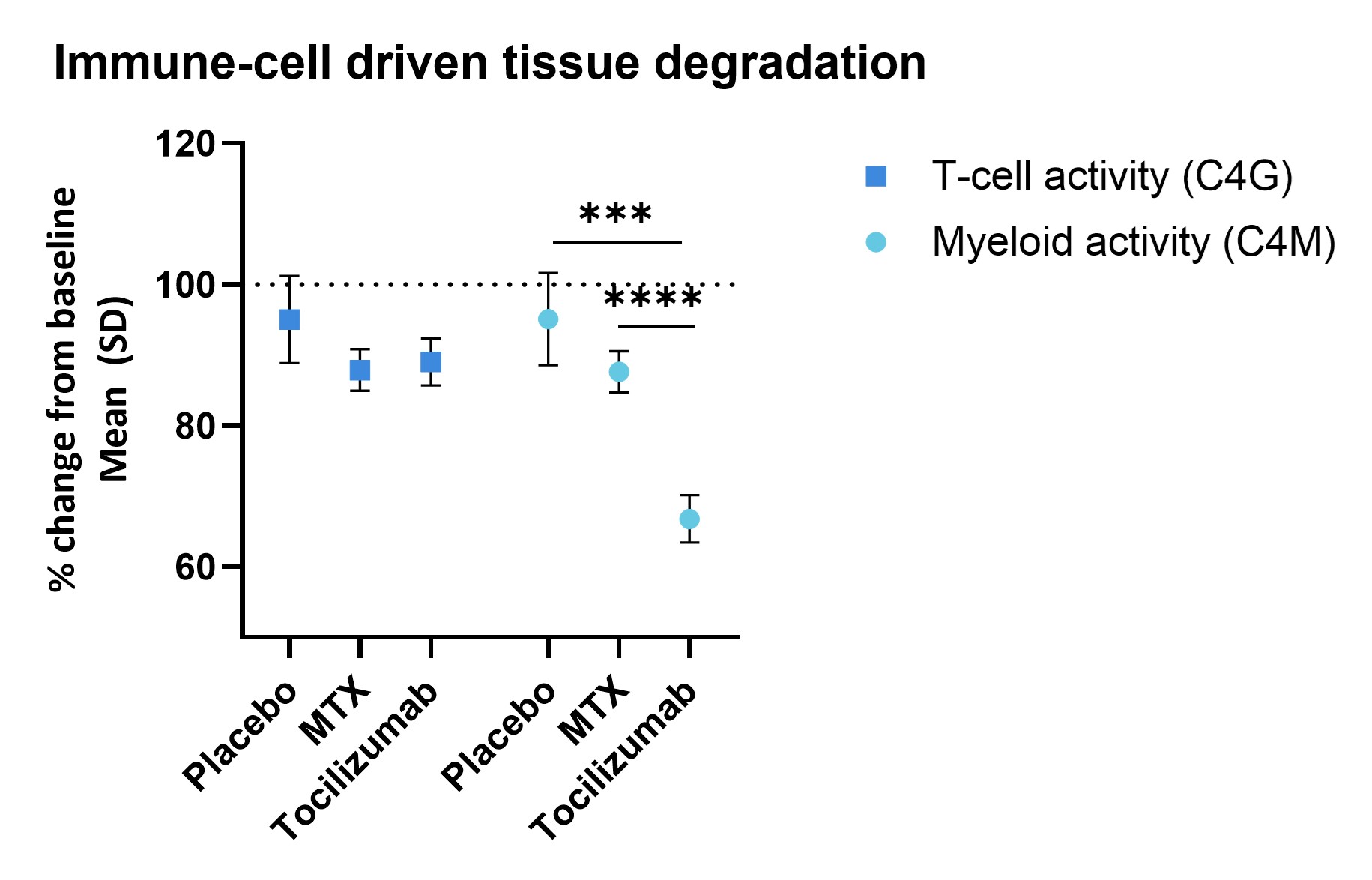
Results: Patients had a median (IQR) age of 50 (42-59) and were primarily female (79%) and white (88%). Baseline serum C4G was correlated significantly correlated to age and swollen joint count (SJC) (table 1), while C4M was correlated to CRP, SJC, DAS28, ESR, health assessment questionnaire (HAQ). Additionally, patients treated with TCZ had significantly decreased levels of C4M, but not C4G, compared to the MTX and placebo group (figure 1).
Conclusion: Type IV collagen is a basement membrane protein important for tissue integrity. It is degraded during RA leading to a destabilized tissue. The two biomarkers C4G and C4M were differentially associated with clinical outcome measures. Importantly, only C4M, MMP derived tissue destruction, could be inhibited by tocilizumab. None of the markers were modulated by MTX.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sinkeviciute D, Madsen S, Willumsen N, Drobinski P, Karsdal M, Bay-Jensen A. Tocilizumab Demonstrates Superior Inhibition of MMP-Mediated Basement Membrane Collagen Degradation Compared to Methotrexate or Placebo [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tocilizumab-demonstrates-superior-inhibition-of-mmp-mediated-basement-membrane-collagen-degradation-compared-to-methotrexate-or-placebo/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tocilizumab-demonstrates-superior-inhibition-of-mmp-mediated-basement-membrane-collagen-degradation-compared-to-methotrexate-or-placebo/