Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Craniofacial localized scleroderma’s (LoS) indolent and subtle course poses challenges in quantifying disease progression. Traditional serial photography and the Localized Scleroderma Cutaneous Assessment Tool (LoSCAT) are validated measures used to assess changes in craniofacial LoS but are limited by their subjective nature and lack of sensitivity to change. Three-dimensional (3D) stereophotogrammetry is a non-invasive imaging strategy with preliminary evidence for utility as an outcome measure in craniofacial LoS, though previous findings have been limited by retrospective design and insufficient comparison to validated measures. As a result, we performed a prospective cohort study assessing changes in craniofacial LoS over time using 3D stereophotogrammetry, serial photography and the LoSCAT. We hypothesized that 3D stereophotogrammetry has greater sensitivity than serial photography and the LoSCAT at detecting changes in craniofacial LoS.
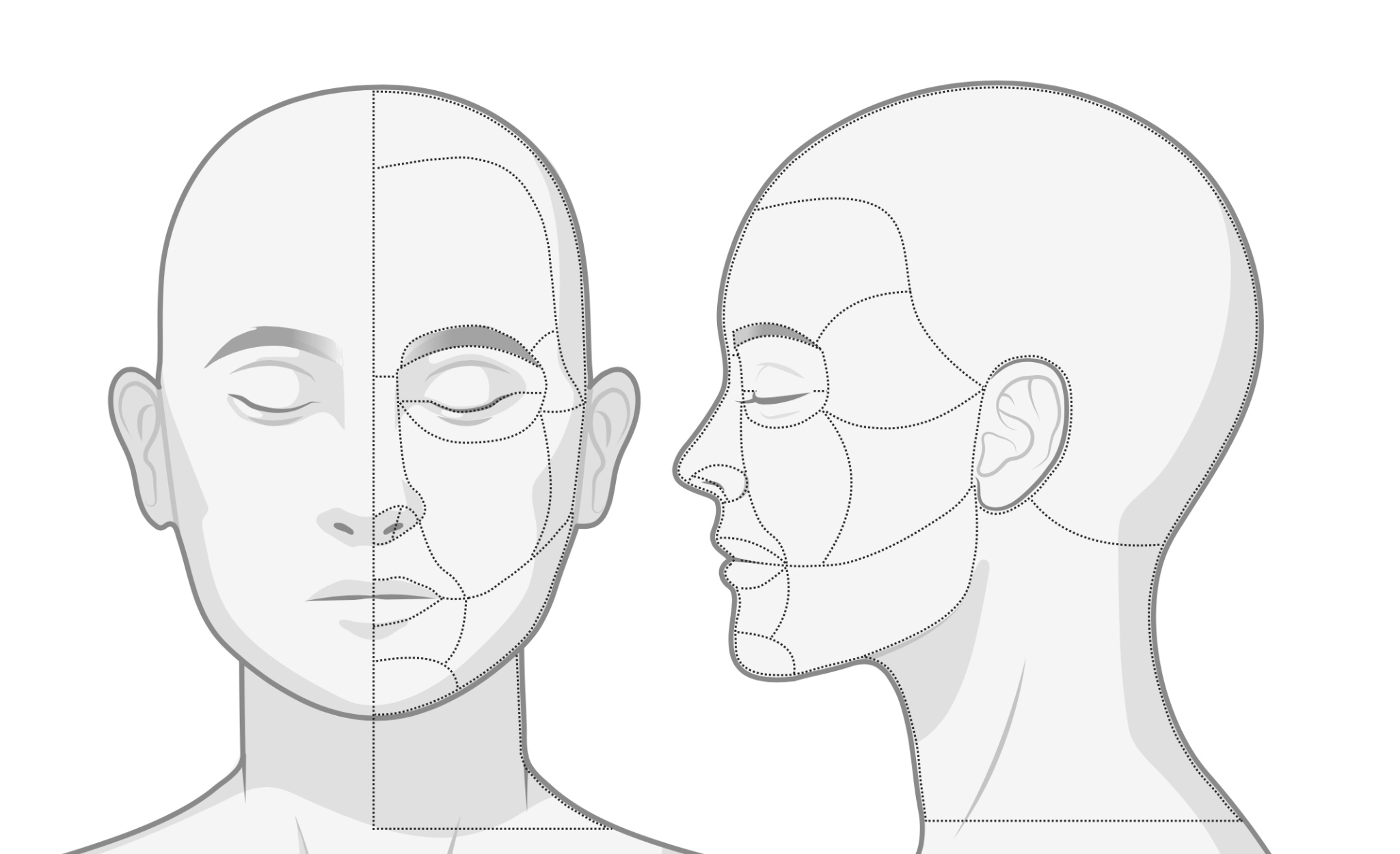
Methods: 11 patients with craniofacial LoS were recruited from an outpatient dermatology clinic and completed two study visits from February 2017 to May 2023. Patients were imaged using standardized protocol in a center dedicated to advanced imaging with 3D and serial photography and had LoSCAT scores assessed by a single expert physician. 3D images were analyzed for asymmetry using in-house mathematical models in MATLAB and converted to 3D heatmaps. Lesion involvement was assessed using 16 distinct craniofacial regions (Figure 1). Worsening and improvement were defined as an increase or decrease in at least one craniofacial region involved or at least one point on the LoSCAT by visit 2. Fisher’s exact and Wilcoxon signed rank tests were performed to compare craniofacial region involvement and patient outcomes for 3D stereophotogrammetry, serial photography, and the LoSCAT.
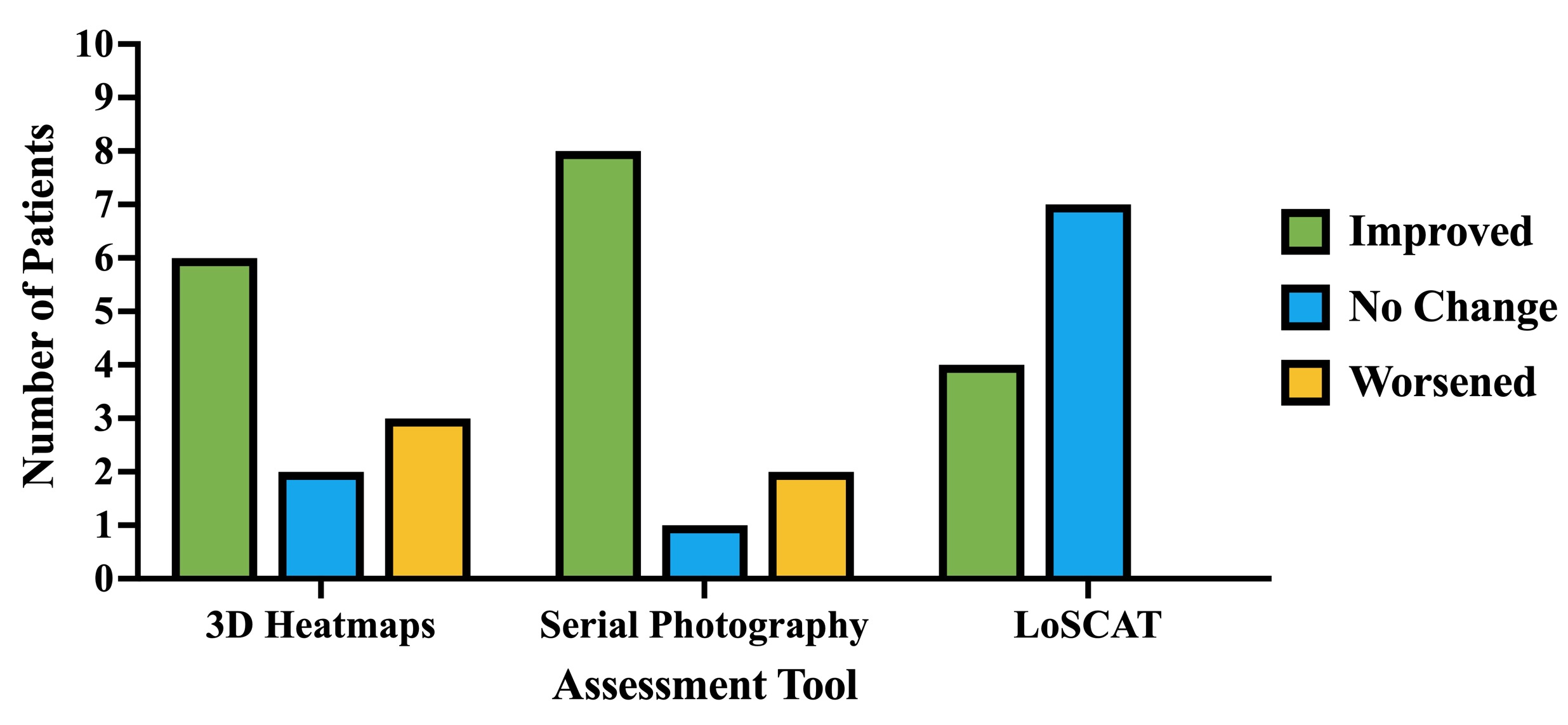
Results: The average number of craniofacial regions involved was 7.8±2.3 for 3D heatmaps and 7.9±3.7 for serial photography (Table 1). Regions most frequently involvement included the lower eyelid and temple (n=17, 77.3%) for 3D heatmaps and the forehead and chin (n=17, 77.3%) for serial photography. 3D heatmaps were more sensitive at detecting involvement of the upper eyelid (p=0.001) while serial photography was more sensitive at detecting involvement of the scalp (p=0.002) and lateral nasal sidewall (p=0.012). Of all measures, the LoSCAT had the highest proportion of patients with no change (n=7, 63.6%), 3D heatmaps had the highest proportion of patients with worsening (n=3, 27.3%), and serial photography had the highest proportion of patients with improvement (n=8, 72.7%) (p=0.040) (Figure 2).
Conclusion: 3D stereophotogrammetry is more sensitive than serial photography at assessing upper eyelid involvement in craniofacial LoS but did not perform as well in assessing involvement of the scalp and lateral nasal sidewall. Importantly, in corroborating previous findings, 3D stereophotogrammetry has greater sensitivity in detecting worsening than either serial photography or the LoSCAT. Furthermore, the existing LoSCAT has poor sensitivity to assess changes in craniofacial LoS, underscoring the need for validation of a craniofacial LoSCAT measure.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cepica T, Foster J, Sarlashkar P, Hallac R, Jacobe H. Three-dimensional Stereophotogrammetry Has Utility in Tracking Upper Eyelid Involvement and Overall Disease Worsening in Patients with Craniofacial Localized Scleroderma [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/three-dimensional-stereophotogrammetry-has-utility-in-tracking-upper-eyelid-involvement-and-overall-disease-worsening-in-patients-with-craniofacial-localized-scleroderma/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/three-dimensional-stereophotogrammetry-has-utility-in-tracking-upper-eyelid-involvement-and-overall-disease-worsening-in-patients-with-craniofacial-localized-scleroderma/