Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 5:00PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: The ESSDAI and ESSPRI, used alone, are not able to capture all features of primary Sjögren’s syndrome (pSS). The NECESSITY consortium developed the Sjögren’s Tool for Assessing Response (STAR), a composite index comprising 5 domains to assess response to treatments on all disease aspects in clinical trials.
The objective is to assess STAR response according to baseline systemic activity, and in each of its 5 domains; and to evaluate the added value of ocular staining score (OSS), salivary gland ultra-sound (SGUS) and rheumatoid factor (RF) in STAR scoring.
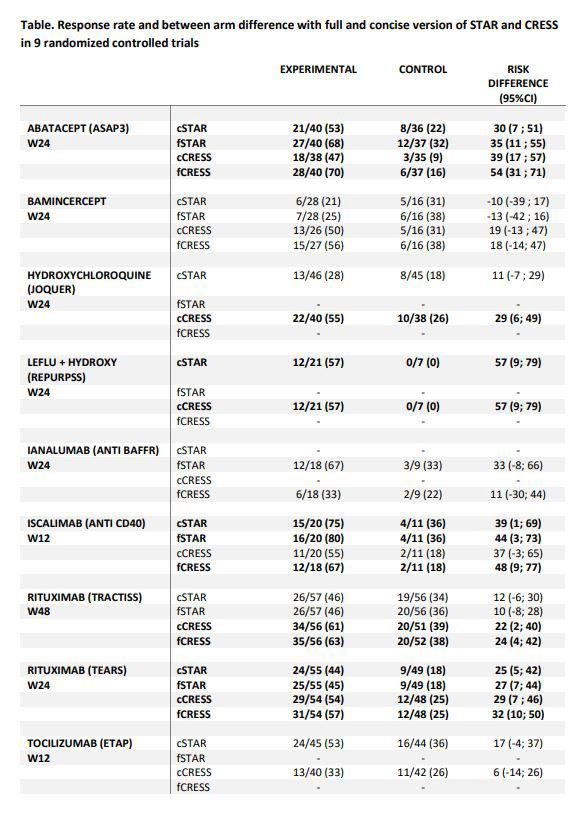
Methods: This study relies on the 9 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) used for STAR development. OSS, SGUS and RF were not available for most trials. Thus, concise STAR (cSTAR) was calculated without these items at all available visits in each trial. A trial was categorized as positive if showing a significant between-arm difference in at least one visit. Stratified analyses according to baseline clinESSDAI (< 5 vs ≥5) were performed whenever possible. The response rate in each STAR domain was calculated, along with a full STAR (fSTAR) including OSS, SGUS and RF when available to determine whether they affected the scoring. SGUS response was defined as a 25% improvement of the available scoring, since only 1 trial used Hocevar score. The same analyses were run for the concise Composite of Relevant Endpoints for Sjögren’s Syndrome (cCRESS) and full CRESS (fCRESS).
Results: cSTAR and cCRESS, classified identically 6/9 trials. Abatacept (ASAP-III), leflunomide+hydroxychloroquine and rituximab (TEARS) trials were categorized as positive trials with both scores. By contrast, the hydroxychloroquine (JOQUER) and rituximab (TRACTISS) trials were positive with cCRESS only and the iscalimab trial with cSTAR only. Stratified analyses according to baseline activity showed similar between group difference in both subgroups (clinESSDAI < or ≥5) with cSTAR. For the systemic domain, CRESS definition (final clinESSDAI< 5) classified patients with low activity as responders (even if no decrease in clinESSDAI) compared to STAR definition (decrease of clinESSDAI ≥3 points), leading to increased overall responder rates, particularly for treatment with biologic activity (rituximab, hydroxychloroquine). In patients with moderate to high activity, a larger rate of response was observed in both arms with STAR definition, both definitions displaying similar between arm difference. For other domains, adding RF to IgG response improved between arm differences in 3/5 trials. Adding OSS to Schirmer’s test made no obvious difference in between-arm differences, in the 2 trials available. Adding SGUS scoring to whole saliva slightly increased between arm differences in the 3 available trials.
Conclusion: cSTAR and cCRESS responses were consistent across most of the trials. Some differences were observed mainly driven by the definition of systemic response ; CRESS classified patients with low activity as responders even in the absence of improvement of ESSDAI or ESSPRI. Adding RF and SGUS seemed to increase the overall responsiveness of the STAR and CRESS.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Seror R, Baron G, CORNEC D, Perrodeau E, Camus M, Bowman P, Bombardieri M, Bootsma H, Arends S, gottenberg j, Fisher B, Hueber W, Van Roon J, Devauchelle V, de Wolff L, Gergely P, Mariette X, Porcher R. The Sjogren Tool for Assessing Response (STAR): Assessment of Response Rates Overall, According to Baseline Activity and by Domain: Reanalysis of 9 Clinical Trials in Primary Sjogren Syndrome [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-sjogren-tool-for-assessing-response-star-assessment-of-response-rates-overall-according-to-baseline-activity-and-by-domain-reanalysis-of-9-clinical-trials-in-primary-sjogren-syndrome/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-sjogren-tool-for-assessing-response-star-assessment-of-response-rates-overall-according-to-baseline-activity-and-by-domain-reanalysis-of-9-clinical-trials-in-primary-sjogren-syndrome/