Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0380–0422) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis(RA)is a chronic autoimmune disease that is characterized by inflammation and destrction of synovial jionts which result in high disabilty. Treat-to-Target is critical to preveting disability and improving outcomes. Accurate evaluation of disease activity is crucial to guide clinical decision-making and develop effective management plan. Synovial biopsy is an emerging tool that can prvide valuable information about the molecular and cellular processes undrlying RA. There is several diffferent types of needles for synovial biopsy. But they maynot be widely available or feasible for use because of unsuitalbe for small joints or compliated procedure We improved a spring-loaded biopsy needle which can make the procedure easier and safer. This needle now is commonly used in clinical practice in our center. We reports the findings from our study of RA patients treated with adalimumab who underwent synovial biopsy.
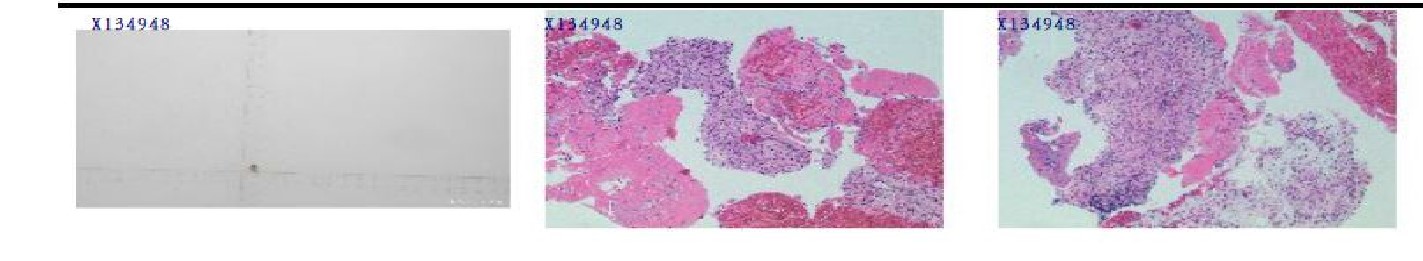
Methods: Thrty RA patients who had inadequate response to MTX were treated with adalimumab and assessed using various indicators of disease activity, including DAS28, ESR,CRP, and radiography imaging. Synovial biopsy was also performed to assess the level of synovial inflmmation before and after 3-months administration of adalimumab. The Synovial biopsy scores were compared to the other indicators of disease activity to evaluate their correlation. We improved a novel spring-loaded synovial biopsy needle which can provide more accurate samples. it consists of a small cylindrical outer sheath and an inner stylet that contains a spring-loaded sampling needle. Once the needle is in place, the negative pressure suction mechinism enables the sample to enter the core of the sampling needle and than release the spring which draw back the inner needle and cut sample quickly. The improved synovial biopsy needles provide an easier and safter procedure.
Results: Of the 30 patients, 22 patients responded well to adalimumab, with significant improvement in DAS28, ESR, and CRP levels. But 8 patinets failed to achieve ACR 20. In 22 patients, 6 patients accheive clinical remission with less than 2.6 of DAS 28. Synovial membrane inflammation scores(GSS) were calculated by inflammatory infiltration, stromal activation and synovila lining hyperplasia(0-9). A significant positive correlation between the GSS and DAS28 score was found in RA patients. in 8 patients who failed the treatment of adalimumab, inflltratrion of lymphoplasmcytic cell in the synovial membrane were predominant. But in 4 patiens who accheived clinical remission, GSS sitll remains high level(more than 6).
Conclusion: Our study suggest that a large infiltration of lymphoplasmacytic cells in the synovial mebbrane is a negative predictor for response of adalimumab in RA. Synovial membrane inflammatory scores(GSS) may be a useful tool for assessing disease activity in RA patients and may help indentify patients who need more aggressive treatment even they acchieved clinical remission with DAS 28. The improved spring-loaded synovial biopsy needles can help faciliated more accurate and effective synovial biopsy for assessing disease activity in RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wu R, Peng Y. The Role of Synovial Biopsy in Evaluating Rheumatoid Arthritis Acitivity in Patients: Findings from a Study of 30 Patients Treated with Adalimumab [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-role-of-synovial-biopsy-in-evaluating-rheumatoid-arthritis-acitivity-in-patients-findings-from-a-study-of-30-patients-treated-with-adalimumab/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-role-of-synovial-biopsy-in-evaluating-rheumatoid-arthritis-acitivity-in-patients-findings-from-a-study-of-30-patients-treated-with-adalimumab/