Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Recently, a gain of-function mutation within TLR7 was identified to induce SLE in a murine model and increased the survival of activated B lymphocytes, age associated B cells (ABCs), extrafollicular B lymphocytes and production of autoantibodies, mediated by MyD88. The aim of this study is to analyze the role of TLR7, 9 and MyD88 expression in diverse B cell subsets as renal response predictors in patients with lupus nephritis.
Methods: We included patients with SLE who fulfilled the ACR/EULAR 2019 classification criteria and active proliferative LN (Class III or IV +/- V). A blood sample was taken at baseline and 6 months after induction treatment. Patients with a history of treatment with anti-CD20 drugs or IV Ig were excluded. The outcome variable was renal response, complete or partial. We measured the expression of TLR7, 9 and MyD88 in the following B cell subsets: ABCs [CD19posCD21neg/lo CD11chi Tbetpos], antibody-secreting cells (ASC) [CD19pos CD27hi CD38hi], classic memory cells (CMC) [CD19pos CD27pos IgD pos/neg], double negative cells (DNC) [CD27neg IgD neg], naive cells (NaC), non-classic memory cells (NCMC) [CD27 neg] and transitional cells (TrC) [CD21 neg/lo] from a peripheral blood sample, using multiparametric flow cytometry. Samples were acquired in a BD LSR Fortessa flow cytometer and data were analyzed by support of the Flow Jo software. We quantified the absolute cell numbers and the percentage of cells expressing TLR7, TLR9, and MyD88, alongside determining the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). Assessment of correlation between quantitative variables was performed using the Spearman correlation coefficient. The analysis of variables before and after induction treatment was executed using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test and the association between immunological variables and the development of renal response was evaluated using logistic regression.
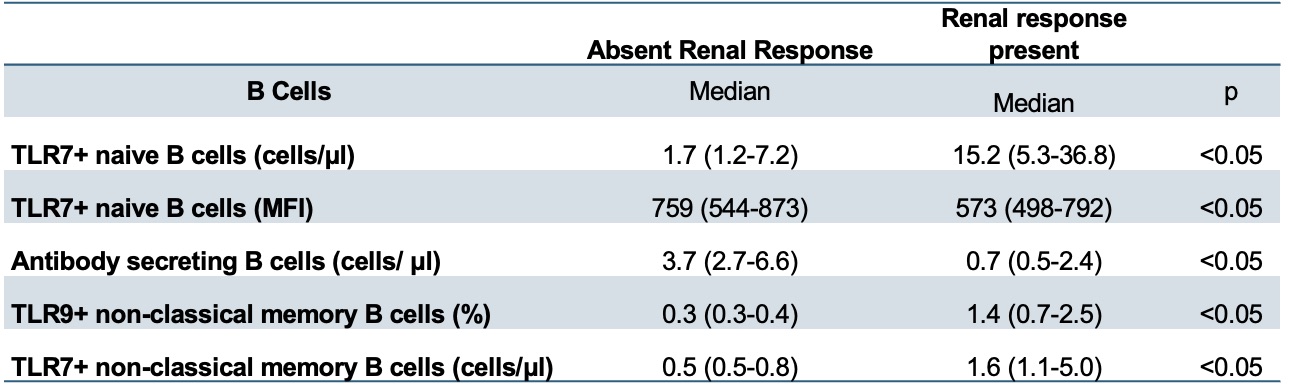
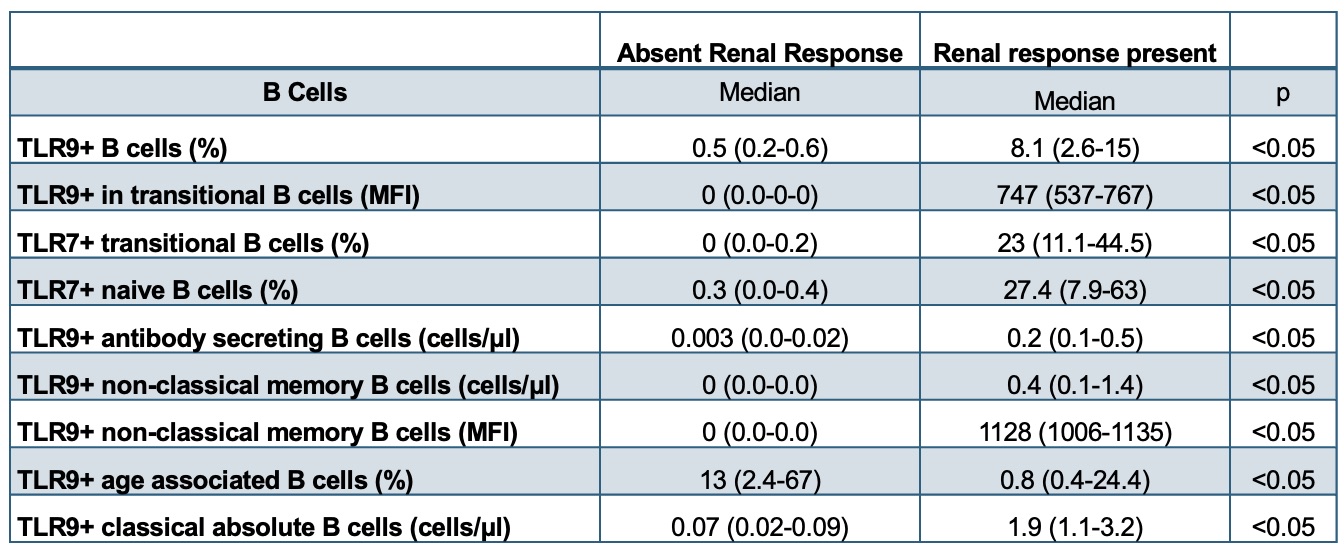
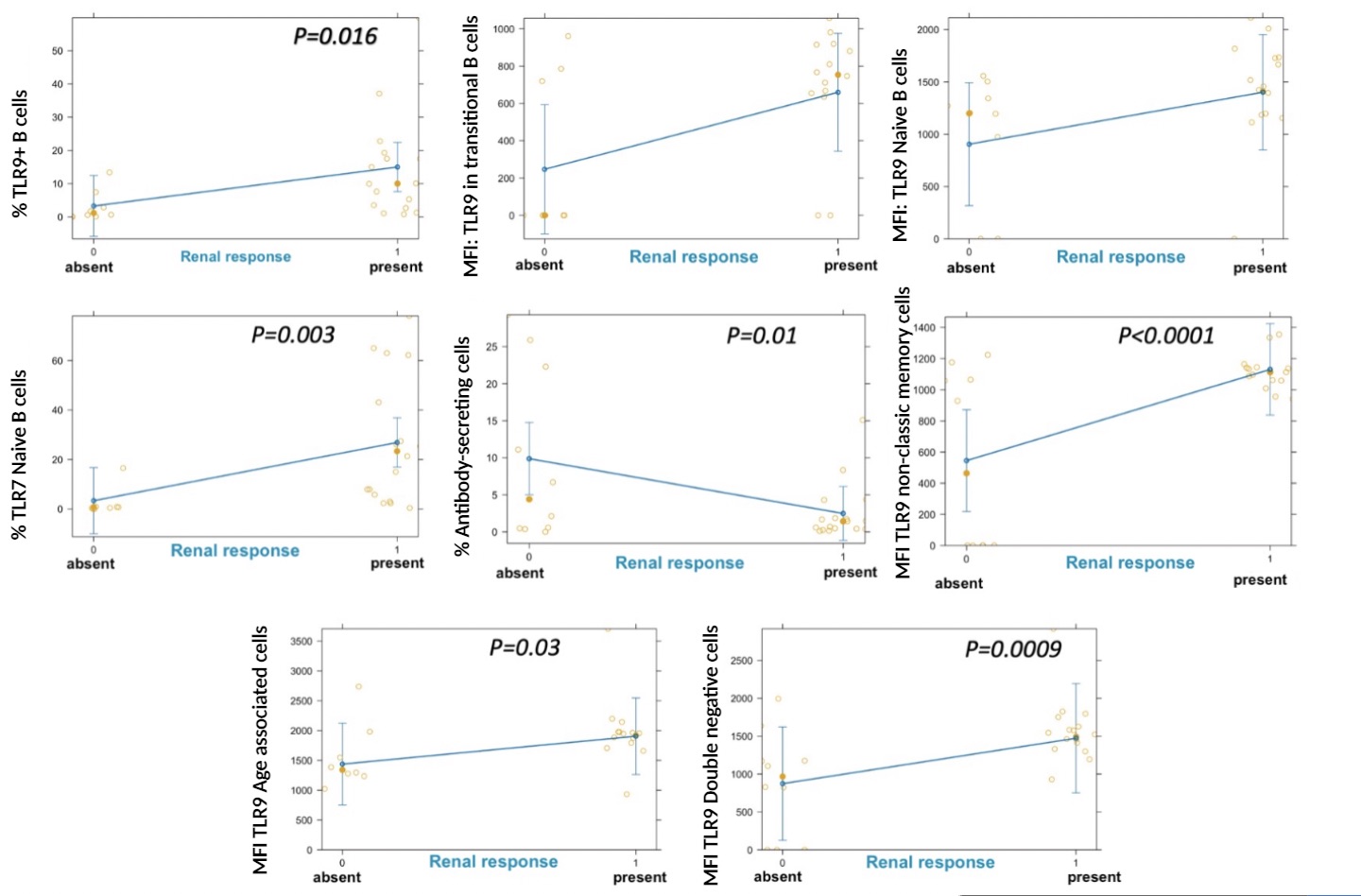
Results: 30 patients were included and 66% reached renal response. These patients presented a lower expression of TLR7 in NaC (MFI, 573 (498-792) vs 759 (544-873), p< 0.05) and expansion of TLR9+ NCMC (1.4% (0.7-2.5) vs 0.3% (0.3-0.4), p< 0.05) (Table 1). At follow up, we observed an expansion of TLR9+ B cells (8.1% (2.6-15) vs 0.5% (0.2-0.6), p< 0.05); enhanced expression of TLR9 in TrC (MFI, 747 (537-767) vs 0 ((0.0-0.0), p< 0.05); expansion of TLR7+ TrC (23% (11.1-44.5) vs 0 %(0.0-0.2), p< 0.05); higher percentage of TLR7+ NaC (27.4 %(7.9-63) vs 0.3 %(0.0-0.4); higher expression of TLR9 in NCMC (MFI, 1128 (1006-1135) vs 0 (0.0-0.0), p< 0.05); expansion of classical TLR9+ B cells (1.9 (1.1-3.2) vs 0.07 (0.02-0.09), p< 0.05), and a decreased percentage of TLR9+ ABCs (0.8 % (0.4-24.4) vs 13% (2.4-67), p< 0.05) (Table 2). Patients with renal response presented an increase in the percentage of TLR9+ B cells (15 vs 5, p=0.016). Interestingly, enhanced TLR9 expression was observed in NCMC (MFI 1128 vs 0, p< 0.05), as well as in ABC (MFI 2000 vs 1500, p=0.03) and DNC (MFI 1500 vs 900, p=0.009). (Figure 1). No differences were observed among treatments.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that renal response is associated with enhanced TLR9 expression in the effector humoral compartment, which might be implicated in the molecular mechanisms of renal damage in lupus nephritis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cassiano-Quezada F, Torres-Ruiz J, Balderas Miranda J, Maravillas-Montero J, Santana-de Anda K, Alcalá-Carmona B, Mejía-Domínguez N, Reyna-Juárez Y, Ostos-prado M, Juarez-Vega G, Gomez-martin D. The Role of Intracytoplasmic Toll- Like Receptors (TLR) and MyD88 in B Cell Subsets as Renal Response Predictors in Patients with Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-role-of-intracytoplasmic-toll-like-receptors-tlr-and-myd88-in-b-cell-subsets-as-renal-response-predictors-in-patients-with-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-role-of-intracytoplasmic-toll-like-receptors-tlr-and-myd88-in-b-cell-subsets-as-renal-response-predictors-in-patients-with-lupus-nephritis/