Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Bone marrow lesions (BML) and synovitis on MRI are independently associated with the severity and progression of osteoarthritis (OA) and randomized controlled trials have targeted reducing the size of BML and degree of synovitis for the treatment of OA. We have developed the OMERACT Knee Inflammation MRI Scoring System (KIMRISS) and have recently refined it to maximize reliability and sensitivity to change. Innovations include custom-designed electronic overlays suitable for a touch-screen interface for assessment of BML in 500 subregions on consecutive sagittal slices, a web-based interface with direct online scoring, and real-time iterative calibration (RETIC) prior to formal reading exercises. We aimed to test the feasibility, reliability, and responsiveness of KIMRISS versus an established method, MOAKS, in a multi-reader exercise.
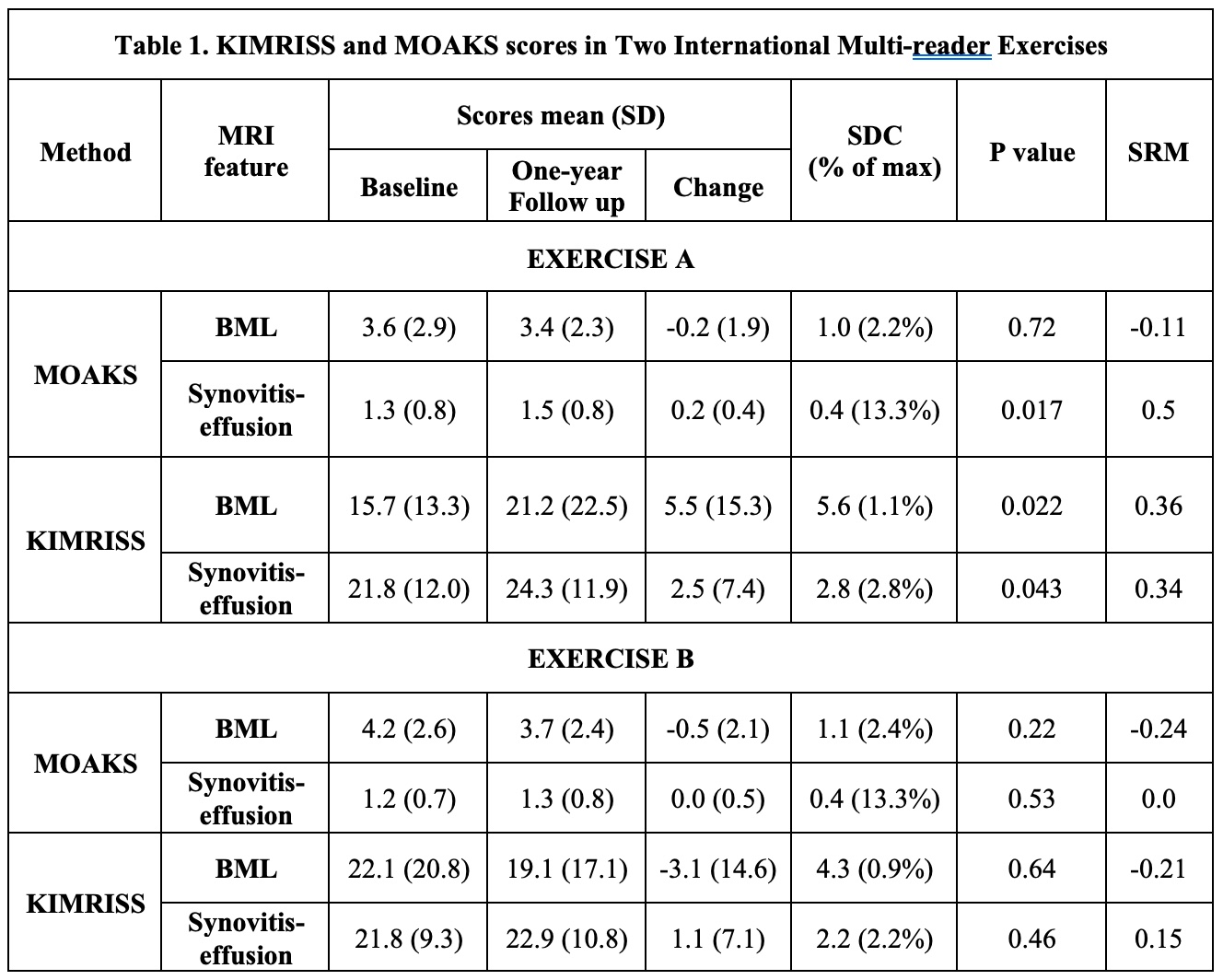
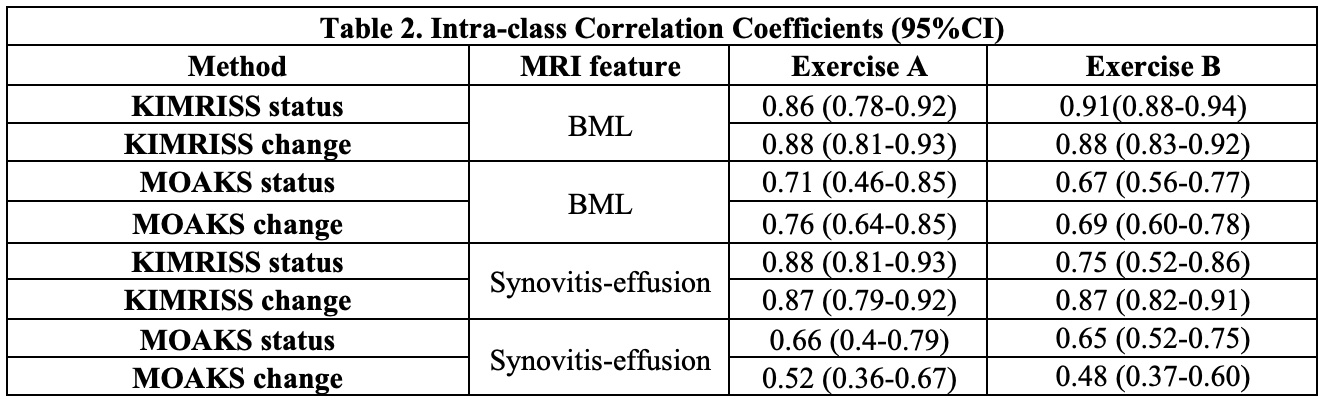
Methods: KIMRISS incorporates web-based graphic overlays for each of femur, tibia, and patella to score BML in 500 subregions on consecutive sagittal slices. S-E is recorded as the largest diameter of the fluid signal on all consecutive sagittal slices (scoring range 0-100). All scores are pro-rated for a standardized number of MRI slices. In a pre-reading exercise for KIMRISS, readers scored a RETIC module to attain scoring proficiency, pre-specified as an ICC of ≥0.80 and ≥0.70 for status and change scores of BML and S-E when compared to developer reads. A new web-based scoring platform with overlays designating subregions for scoring BML was developed for MOAKS. We compared reliability for status and change scores of BML and S-E in 2 international multi-reader exercises of baseline and 1-year MRI scans from the Osteoarthritis Initiative: A. 4 expert readers and an OMERACT fellow scored 38 cases selected for MOAKS BML score ≥1. B. 8 expert readers and an OMERACT fellow scored 60 cases selected for MOAKS BML ≥3 and Kellgren-Lawrence (K-L) grade < 3. Reliability was assessed by intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC) and Smallest Detectable Change (SDC), responsiveness by the standardized response mean (SRM), and feasibility using the System Usability Scale (SUS scoring range 0-100).
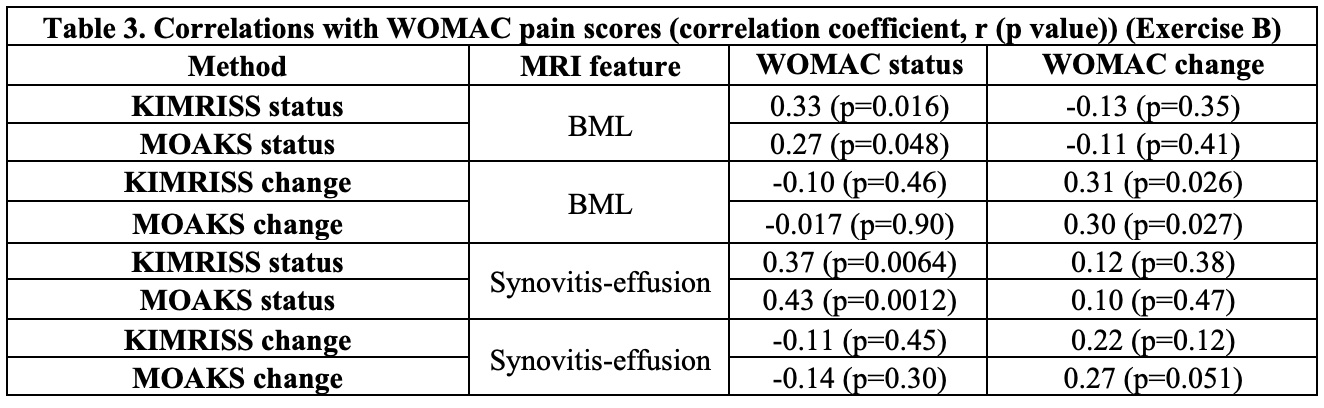
Results: For exercises A/B, subjects were 55.3%/ 26.7% male, mean(±SD) age 61.7(±9.1)/61.9(8.8) years, and radiographic K-L grade ≤2 in 39.4%/100%. Change was small in both exercises (< 5% of scoring range for KIMRISS and MOAKS BML and S-E) with comparable responsiveness (Table 1). Despite this, ICC for change was consistently good to very good for both BML and S-E and consistently better for KIMRISS with lower SDC as % of scoring range (Table 2). Significant correlations between WOMAC baseline pain scores and KIMRISS and MOAKS baseline BML and S-E scores were observed; significant correlations between WOMAC change and KIMRISS and MOAKS BML change were also noted (Table 3). Mean SUS scores were 88.2 for KIMRISS and 54.3 for MOAKS.
Conclusion: The KIMRISS method for scoring BML and Synovitis-Effusion scores highly for feasibility and demonstrates consistently high reliability when compared to MOAKS. Correlations with WOMAC pain are demonstrable with both methods for both BML and S-E. Further validation for responsiveness is necessary in cases with greater change in MRI features than in the OAI dataset.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Maksymowych W, Jaremko J, Pedersen S, Eshed I, Weber U, Bird P, McReynolds A, Wichuk S, Paschke J, Lambert R. The OMERACT Knee Inflammation MRI Scoring System: Validation of Quantitative Methodologies and Tri-compartmental Overlays by Comparison with the MRI Osteoarthritis Knee Score [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-omeract-knee-inflammation-mri-scoring-system-validation-of-quantitative-methodologies-and-tri-compartmental-overlays-by-comparison-with-the-mri-osteoarthritis-knee-score/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-omeract-knee-inflammation-mri-scoring-system-validation-of-quantitative-methodologies-and-tri-compartmental-overlays-by-comparison-with-the-mri-osteoarthritis-knee-score/