Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Epidemiology & Public Health Poster I: COVID-19 & Rheumatic Disease
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: To evaluate the impact of the Coronavirus Disease 2019 pandemic (COVID-19) on the access to rheumatology care for patients with chronic rheumatic diseases in the Arab countries.
Methods: A web-based cross-sectional survey was designed by the Arab Adult Arthritis Awareness group (AAAA) consisting of 16 rheumatologists representing countries from the Arab League of Associations for Rheumatology (ArLAR) and was validated by the ArLAR scientific committee. The survey was disseminated through social media and patients’ associations’ channels between May 8 and May 22, 2020. The steering committee developed recommendations to improve the care of patients with chronic rheumatic diseases during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Results: A total of 2163 patients were included in the analysis; 72% were females; their mean age was 40 years (SD 11.9). The Levant, the Gulf, and North Africa contributed almost equally to the sample (Table 1). The COVID-19 pandemic had a significant negative impact on rheumatology visits in 82% of cases, including 27% where it had been impossible to contact the rheumatologist. The negative impact was also significant on the access to hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) (47% of cases), and on chronic medication persistency (partial or complete discontinuation in 28%) (Table 2). The negative impact on rheumatology visits was associated with the female gender, the country of residence, the medication non-persistency, the isolation due to COVID-19, and the impact on mental health (Table 3). The pandemic had an impact on mental health in 73% of the participants (minor in 48%, major in 25%). The impact on mental health was associated with the country of residence, the rheumatology visits, the medication non-persistency, the decreased access to HCQ, the personal infection with SARS-CoV-2, the isolation due to COVID-19 and the negative impact on income. Sixty-one patients (2.8%) stated that they had COVID-19, 5% said that a close contact was infected, and 47% were in isolation because of COVID-19. When asked about their attitude towards telemedicine, 98.8% said that they would accept a teleconsultation (50% through the internet and 48.8% through a telephone contact).
Conclusion: The current study highlights the deleterious consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic on the continuity of rheumatology care, the persistence on chronic medication, and the patients’ mental health, all key predictors of disease prognosis. Therefore, an action plan, including establishing a telemedicine platform, securing drug availability, and promoting medication persistence through the appropriate communication channels, is strongly recommended.
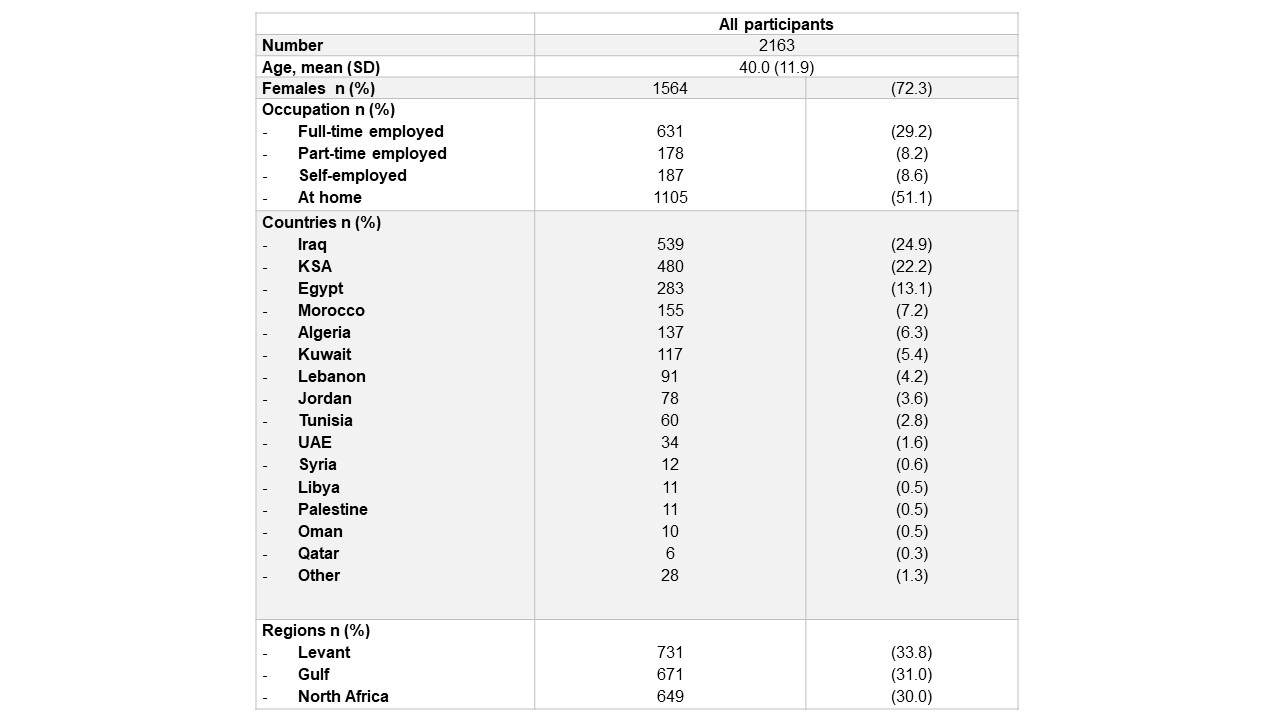 Table 1. Characteristics of the 2163 participants in the survey
Table 1. Characteristics of the 2163 participants in the survey
 Table 2. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on patients with chronic rheumatic diseases
Table 2. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on patients with chronic rheumatic diseases
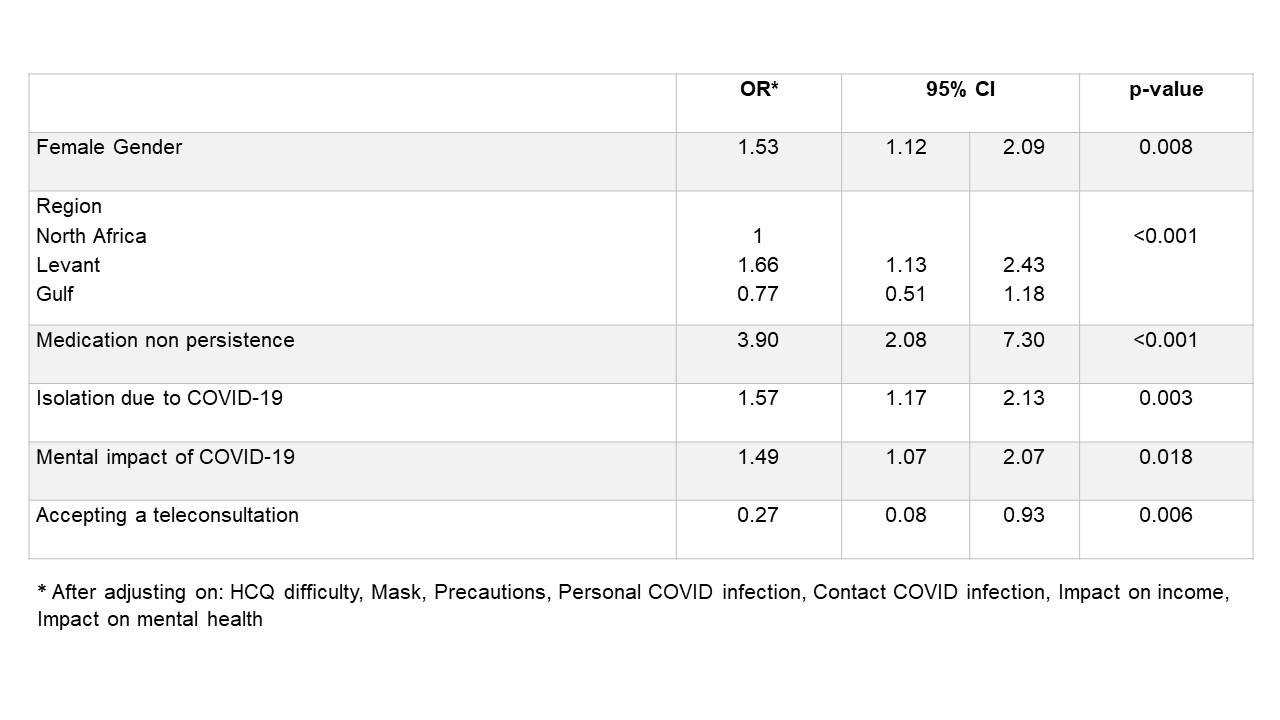 Table 3. Factors associated with a negative impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the patient’s visit to the rheumatologist
Table 3. Factors associated with a negative impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the patient’s visit to the rheumatologist
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ziade N, El Kibbi L, Hmamouchi I, Abdulateef N, Halabi H, Hamdi W, Abutiban F, el Rakawi M, Eissa M, Masri B. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Patients with Chronic Rheumatic Diseases: A Study in 15 Arab Countries [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-the-covid-19-pandemic-on-patients-with-chronic-rheumatic-diseases-a-study-in-15-arab-countries/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-the-covid-19-pandemic-on-patients-with-chronic-rheumatic-diseases-a-study-in-15-arab-countries/
