Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2022
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
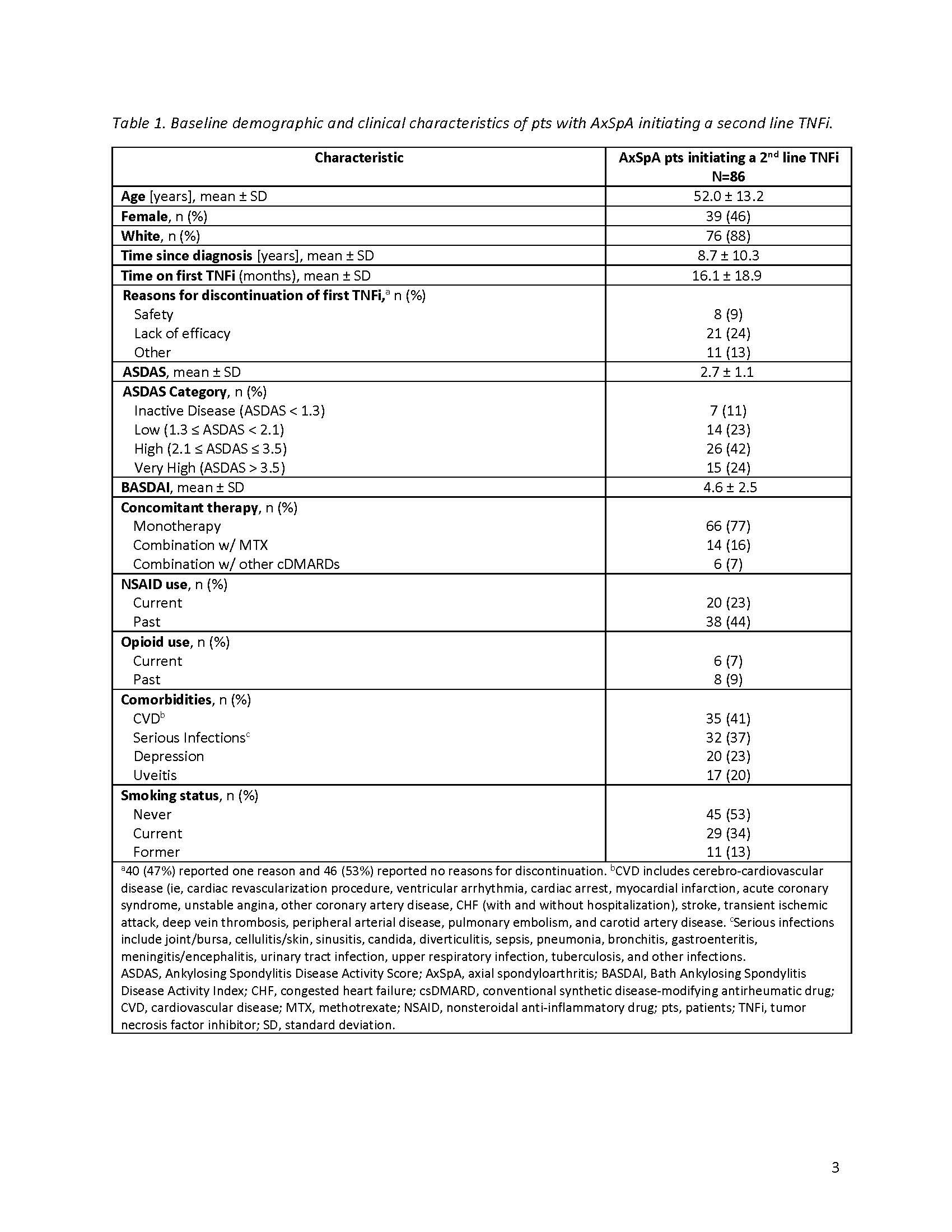
Background/Purpose: Axial spondyloarthritis (AxSpA) is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by inflammatory back pain, morning stiffness, and reduced functional capacity. Approved therapies for AxSpA include IL-17, Janus kinase, and TNF (TNFi) inhibitors. An inadequate response to a first line TNFi may result in switching to a second TNFi; the efficacy of this remains unclear. This study assessed disease activity and persistency of therapy (up to 2 years) among patients (pts) with AxSpA who cycle to a second TNFi after discontinuing a first line TNFi.
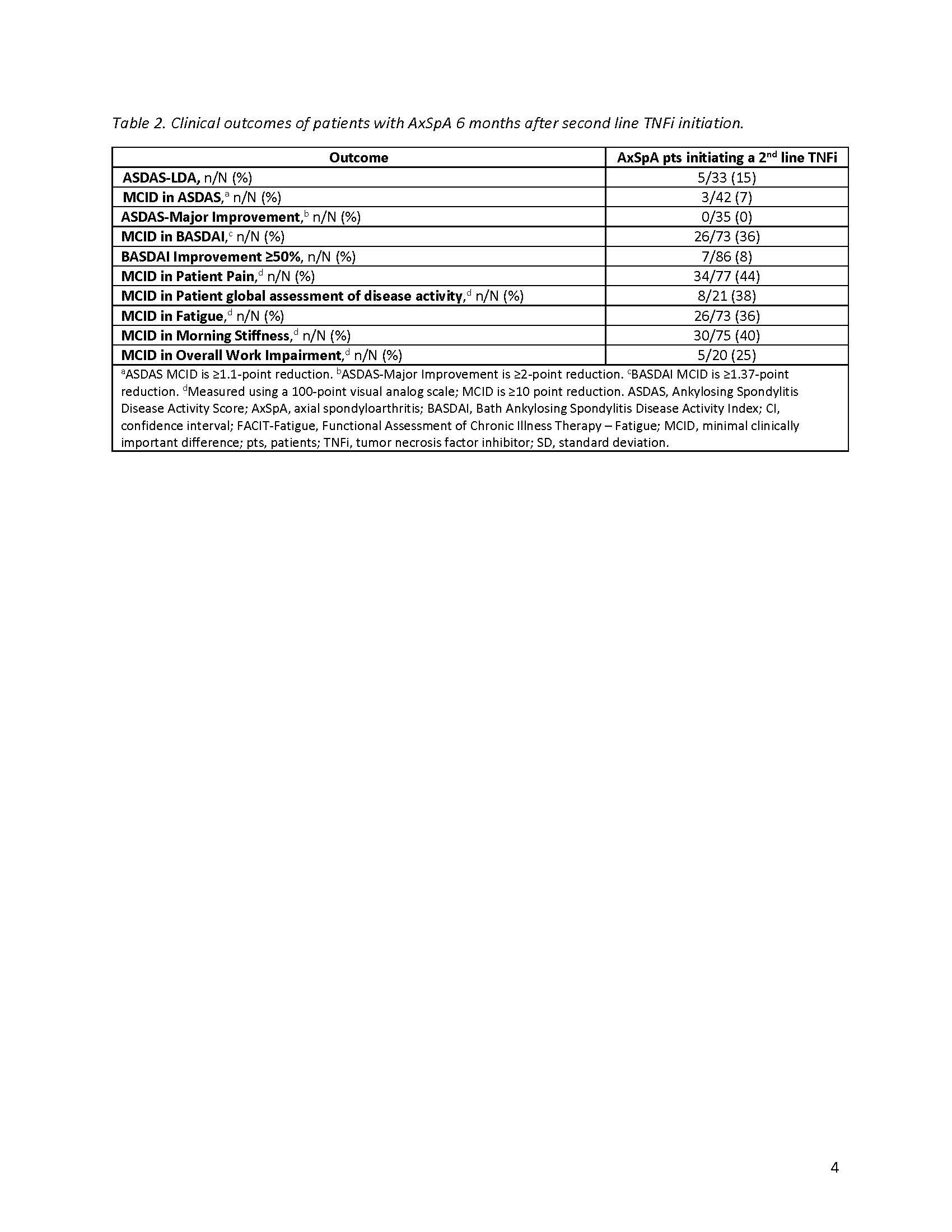
Methods: This study included pts with AxSpA, as determined by a treating rheumatologist, enrolled in the CorEvitas Psoriatic Arthritis/Spondyloarthritis Registry between May 2013–January 2022 who had discontinued a 1st line TNFi and initiated a 2nd line TNFi. Pts included in disease activity analyses had a 6-month follow-up visit; those included in persistency analyses had any follow-up up to 24-months after 2nd line TNFi initiation. Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) and BASDAI were collected at baseline and 6-months. Baseline pt characteristics were summarized descriptively. At 6-months, proportions of pts achieving ASDAS low disease activity (LDA; ASDAS < 2.1), minimal clinically important difference (MCID; ≥1.1-point decrease), and major improvement (MI; ≥2-point decrease); BASDAI MCID (≥1.4-point reduction) and improvement ≥50%; and MCID in patient-reported outcomes were calculated. For persistency analysis, Kaplan-Meier survival estimates were used to calculate the proportion of pts with persistent (ie, continued) 2nd line TNFi use over 24 months.
Results: The disease activity analyses included 86 pts with an average age (± standard deviation) of 52.0 ± 13.2 years and a mean of 8.7 ± 10.3 years since AxSpA diagnosis (Table 1). On average, pts spent 16.1 ± 18.9 months on a first line TNFi before discontinuation, with lack of efficacy cited as the most common reason for discontinuation. At baseline, 42% of pts had high (≥2.1) and 24% very high ( >3.5 ) disease activity as measured by ASDAS. The mean BASDAI score was 4.6 ± 2.5, indicating poorly controlled disease. Seventy-seven percent were receiving TNFi monotherapy, with 23% currently receiving NSAIDs. After 6 months of therapy with a 2nd line TNFi, 15% achieved ASDAS-LDA and 7% achieved MCID in ASDAS (Table 2); no pts achieved MI. Thirty-six percent of pts achieved MCID in BASDAI, yet only 8% had a ≥50% improvement. Less than half of patients achieved MCID in patient-reported pain (44%), fatigue (36%), morning stiffness (40%), and overall work improvement (25%). Of the 120 pts in the persistency analysis, 21% remained on the 2nd line TNFi through 24-months (Figure).
Conclusion: These data demonstrate that cycling to a second line TNFi provides limited benefits to pts with AxSpA who discontinued a first line TNFi. Few pts showed clinically meaningful improvement in disease severity after 6 months and less than a quarter of pts remained on therapy after 2 years. While these data were limited by small sample size, they do highlight the high burden and unmet needs for pts with AxSpA that do not respond to a first line TNFi.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease P, McLean R, Blachley T, Middaugh N, Mittal M, Clewell J, Jones H, Ogdie A. The Impact of Cycling Among Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors on Disease Control in Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis: A Study from the CorEvitas PsA/SpA Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-cycling-among-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitors-on-disease-control-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-study-from-the-corevitas-psa-spa-registry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-cycling-among-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitors-on-disease-control-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-study-from-the-corevitas-psa-spa-registry/