Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2022
Title: RA – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The impact of autoantibodies on the efficacy of bDMARDs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is not yet clear. Despite the fact that this information has been collected by several randomized controlled trials (RCTs), efficacy data for seropositive and seronegative patients separately have generally not been published. Our aim was to comprehensively investigate the efficacy of bDMARDs in patients with RA with RF and/or ACPA compared to patients without these autoantibodies.
Methods: Previous systematic literature reviews performed by EULAR RA management task forces were searched for relevant RCTs published before February 2016 1-3. RCTs including both autoantibody-positive (≤80% of total population) and -negative RA patients were eligible. We contacted authors and/or sponsors of RCTs to report aggregate results from analyses of individual patient data on clinical efficacy outcomes stratified for the presence of autoantibodies (RF+ vs RF- and ACPA+ vs ACPA-). Per trial, relative risks (RR) or mean differences comparing two groups (RF+ vs RF- and ACPA+ vs ACPA-) were calculated for various outcomes (ACR 20/50/70, DAS28 remission, delta DAS28, delta HAQ and radiographic progression) at the timing of the primary endpoint for the bDMARD-arm and the non-bDMARD-arm separately. Subsequently, relative risk ratios (RRRs) were computed, as the ratio of RR of the bDMARD-arm and the RR from the non-bDMARD-treated arm, reflecting whether seropositivity preferentially affected treatment response to bDMARD therapy. A meta-analysis was conducted using a mixed-effect meta-regression in subgroups of patients according to baseline autoantibody status.
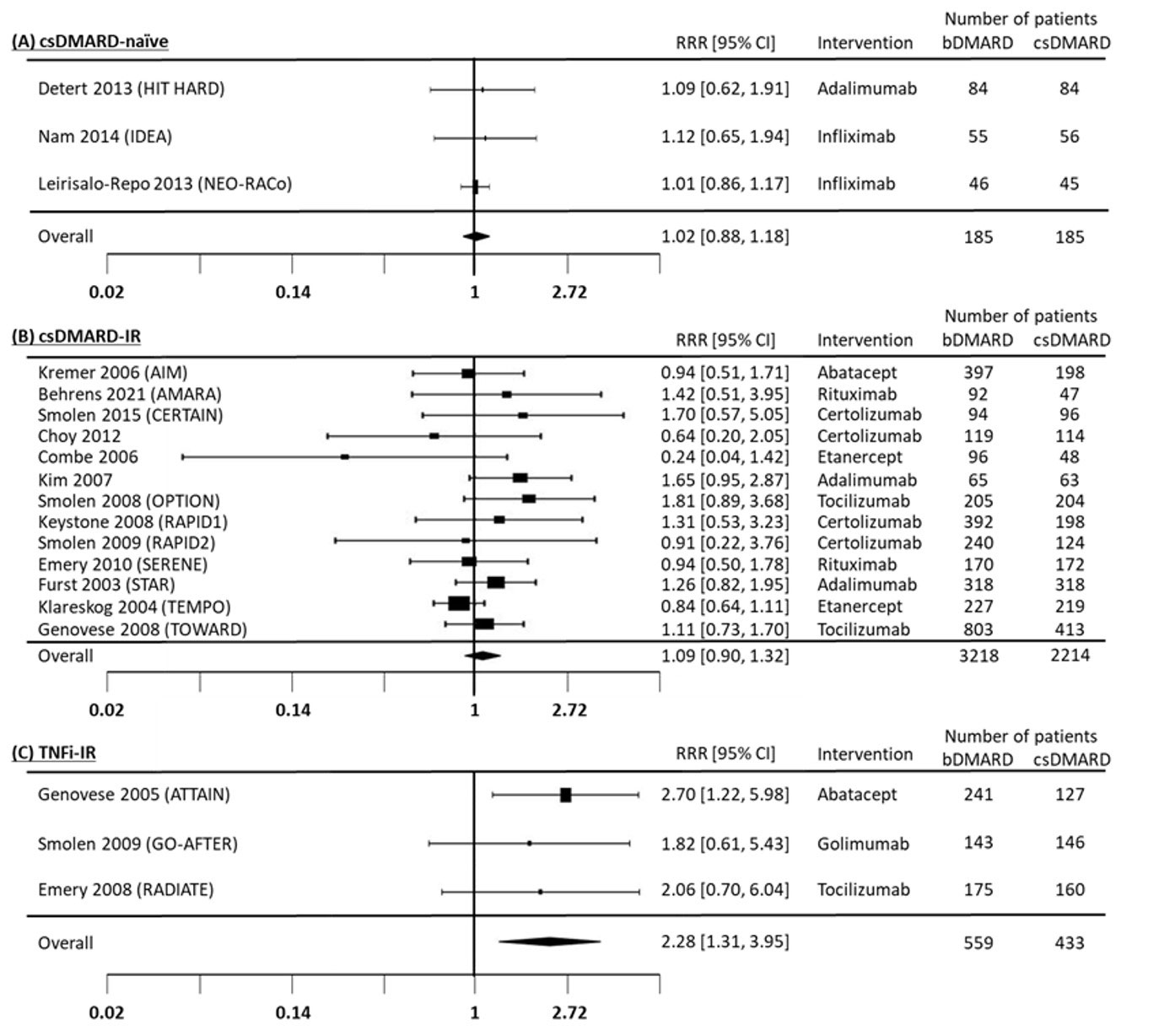
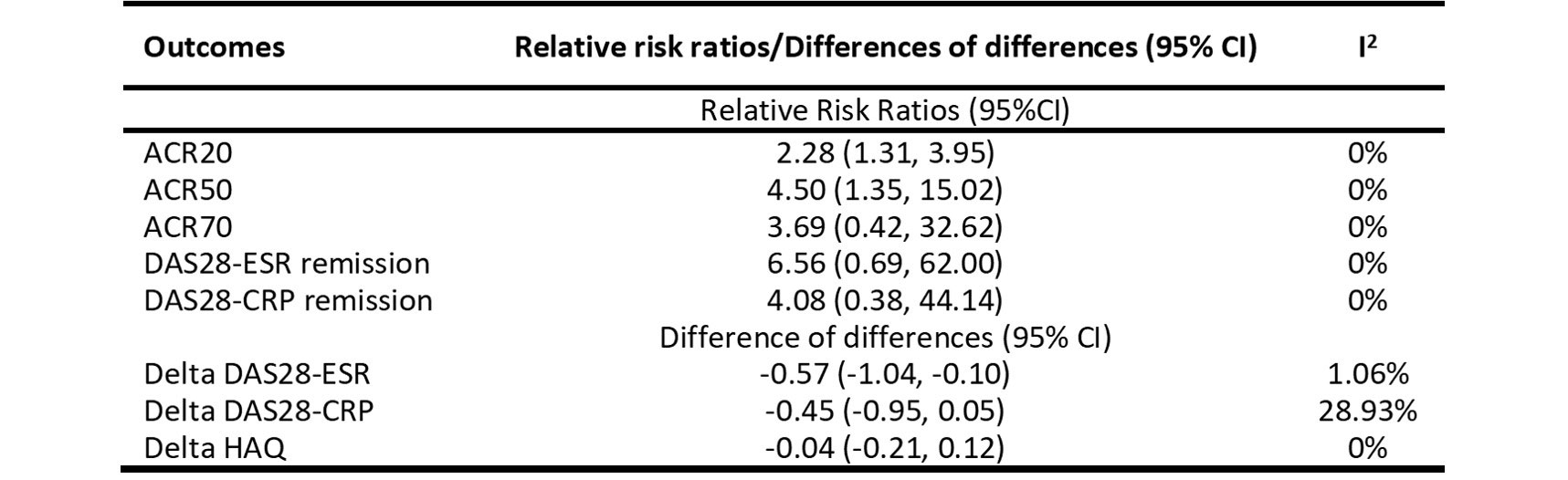
Results: Data from 28 eligible RCTs were analyzed: 6 including csDMARD-naïve patients, 14 including csDMARD-inadequate responders (csDMARD-IR), 3 including tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi)-IR patients and 5 with miscellaneous trial design (e.g. head-to-head trial). In csDMARD-naïve and csDMARD-IR, seropositivity was not associated with a better response to bDMARDs compared to non-bDMARDs. Pooled RRRs of 6-month ACR20 response were 1.02 (0.88-1.18) and 1.09 (0.90-1.32), respectively (Figure 1A and B). Other outcomes followed the same pattern, with no difference between the groups. In TNFi-IR patients, based on 3 trials, the RRR of ACR20 at 6 months was 2.28 (1.31-3.95) (Figure 1C), favouring efficacy in seropositive patients. Other outcomes showed a similar effect, though with large confidence intervals and several reflecting a non-significant difference between the groups (Table 1).
Conclusion: In csDMARD-naïve and csDMARD-IR patients, autoantibodies did not have an impact on the efficacy of bDMARDs in RA. In TNFi-IR patients, there is a possible higher efficacy of bDMARDs in the seropositive group, but the low number of trials, large confidence intervals and inconsistent results across outcomes ask for caution in the interpretation. Seronegative TNF-IR patients may have very heterogenous underlying pathophysiological mechanisms, with a lower probability of good treatment response. Overall, in less treatment-resistant patients, the presence of autoantibodies was not associated with the treatment effect of bDMARDs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Takase-Minegishi K, Böhringer S, Nam J, Kaneko Y, Behrens F, Saevarsdottir S, Detert J, Leirisalo-Repo M, van der Heijde D, Landewé R, Ramiro S, van der Woude D. The Impact of Autoantibodies (RF and ACPA) on the Efficacy of Biological Disease-modifying Antirheumatic Drugs in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-autoantibodies-rf-and-acpa-on-the-efficacy-of-biological-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-meta-analysis-of-randomized-controlled-trials/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-autoantibodies-rf-and-acpa-on-the-efficacy-of-biological-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-meta-analysis-of-randomized-controlled-trials/