Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is a challenging disease to treat and lack effective therapies. Rituximab (RTX) can deplete CD20+ peripheral B cells. Telitacicept (TA) is a dual inhibitor targeting BAFF and APRIL. This study was to investigate the efficacy and safety of TA following RTX for refractory/severe APS.
Methods: This prospective observational study enrolled Primary APS (PAPS, n=12) & Seconary APS (SAPS, secondary to systemic lupus erythematosus, n=29) patients treated with RTX monotherapy or 200-500mg RTX followed by TA 160mg qw for 24 weeks. Stable standard-of-care included glucocorticoids (GC), hydroxychloroquine , and anticoagulants/antiplatelet. The complete remission rate (CR) was the proportion of increased antiphospholipid antibodies (a PL) or lupus anticoagulant (LA) value decreased to normal range, and overall remission rate (OR) was the aPL titers decreased into two times above the normal value or LA decreased to normal range. The incidence of new APS-related clinical events, overall remission ratio of thrombocytopenia (TP), and adverse events (AE) were analyzed.
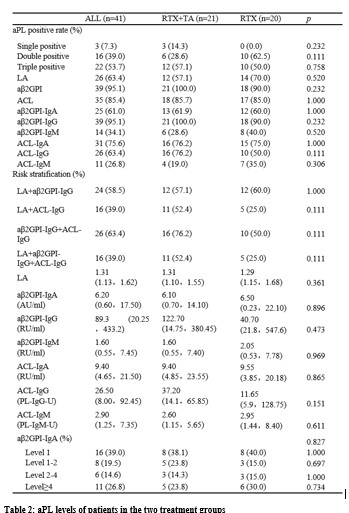
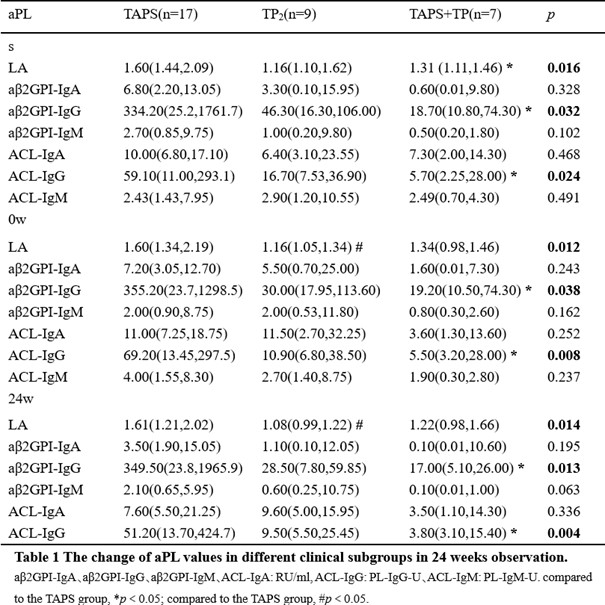
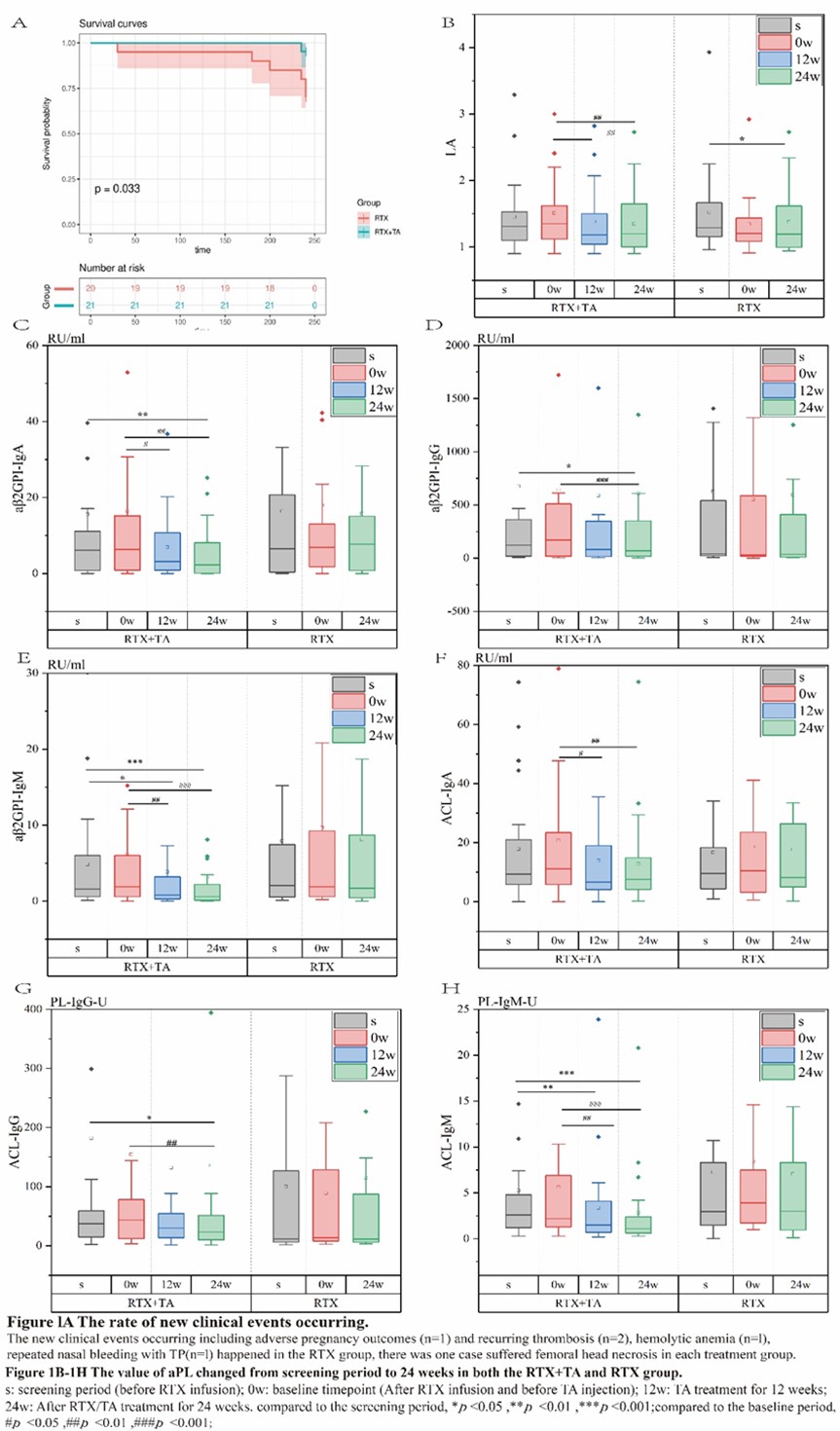
Results: There were 21 patients in the RTA+TA group and 20 in the RTX group who completed this study . During the screening period (before the use of RTX), the triple positivity of aPL was 53.7%, among which aβ2GPI-IgG showed highest positivity rate (95.1%). It was observed that aβ2GP1-IgG and aCL-IgG were higher in the RTX+TA group than in the RTX (Table 2). Among the four different clinical subgroups, the patients with only thrombotic APS (TAPS) showed the highest positive rate of LA, and much higher values of LA, aβ2GPI-IgG, and ACLIgG at screening and 24w. The median values of aCL-IgG and aCL-IgM decreased sharply from 0w to 24w in the TAPS group with additional TA treatment (Table 2). The new clinical events occurring ratio was significant lower in the RTX+TA group than in the RTX group (1/21 vs. 6/20) (Figure 1A). There were eight patients with TP in each treatment group. The PLT count in the RTX+TA group was significantly lower than that in the RTX group during the screening, but higher at baseline and 24w. The OR rates of aβ2GPI-IgA, aβ2GPI-IgM, ACL-IgM, ACL-IgA, and ACL-IgG in the RTX+TA group were >50%, especially the OR of aβ2GPI-IgA and aβ2GPI-IgM were significantly higher than RTX group. All aPL values in the RTX+TA group were significantly lower vs. both screening and baseline. However, in the RTX group, only the LA value at 24w significantly decreased from that of the screening (Figure 1B-1H). Both groups received a GC dose of 10 mg/day during screening, and the RTX+TA group had 5.0mg/day vs. 7.5mg/day in the RTX group at 24 weeks (p=0.011). AE was mild in both groups, including 14 RTX infusion-related reactions and two RTX-associated secondary infections. TA injection had five slight and one moderate local reactions. No additional infections were reported after TA administration.
Conclusion: In this 24w prospective observational study, RTX followed by TA therapy was a promising strategy for refractory/severe APS. This immunotherapy strategy effectively reduced the incidence of new-onset APS-related events and lowered aPL values without increasing new infections using TA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Shu Q, Zuraw Q, Zhang X, Pons-Estel G, Sun S, Che Q, Li X, Li J, Liu Q. The Efficacy and Safety of Telitacicept Following Rituximab Immunotherapy on Antiphospholipid Syndrome, a Prospective 24- Week Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-efficacy-and-safety-of-telitacicept-following-rituximab-immunotherapy-on-antiphospholipid-syndrome-a-prospective-24-week-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-efficacy-and-safety-of-telitacicept-following-rituximab-immunotherapy-on-antiphospholipid-syndrome-a-prospective-24-week-study/