Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster IV: Lifespan of a Disease
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Although more effective therapeutics and treatment strategies for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) have improved many patient-reported outcomes (PROs), still a sizeable number of patients in clinical remission report reduced wellbeing.Therefore, we explored PROs contributing to wellbeing of patients with early RA.
Methods: Patients from the 2-year pragmatic treat-to-target Care in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis (CareRA) trial were included. Patients were treated intensively, with combinations of csDMARDs and glucocorticoids, except 1 group starting MTX only in a tight-step-up approach.
Eight different validated questionnaires were taken, including the Arthritis Self-Efficacy Scale (ASES), the multidimensional Fatigue Inventory (MFI), the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) the Revised Illness Perception Questionnaire (IPQ-R), the Utrecht Coping List (UCL), the Short Form 36 (SF-36), RA Quality of Life questionnaire (RA-QOL) and the Social Support List (SSL). Questionnaires were obtained at baseline, week (W)16, 52 and 104 except for the IPQ and UCL, which were only taken at baseline and W16.
Regression models were constructed to define wellbeing at W16, 52 and 104. Three proxies for patient wellbeing were chosen, on a scale of 0-100: (P1) Patient Global Assessment (PGA) on a Visual Analogue Scale (VAS); (P2) a patient factor derived from a previous principal component analysis combining PGA, pain and fatigue on VAS and the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ)1; and (P3) based on the time-weighted average of reconstructed EuroQoL-5 Dimension (EQ-5D) scores based on HAQ, age, pain on VAS and gender2. Three patients` groups per time point were created including all patients, patients in remission (DAS28crp< 2.6) and not in remission. As predictors, all subscales of the 8 validated questionnaires, summing to 83 variables, with and without VAS-Pain were used per time point in 54 models in total. Data reduction used forward, backward and stepwise selection based on the Aikake information criteria. Missing data was handled by multiple imputation (n= 15).
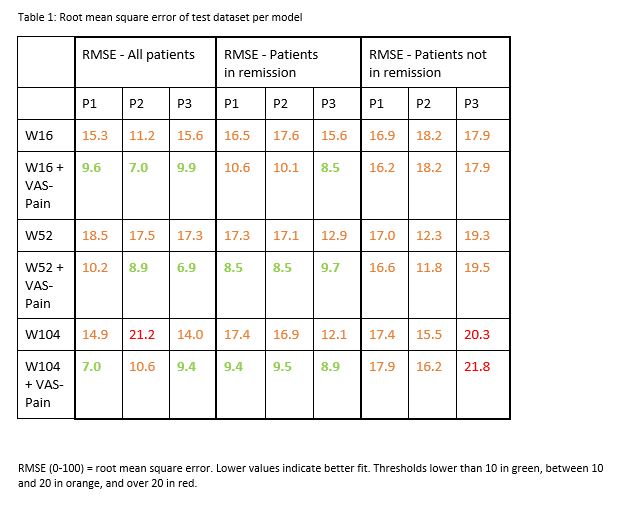
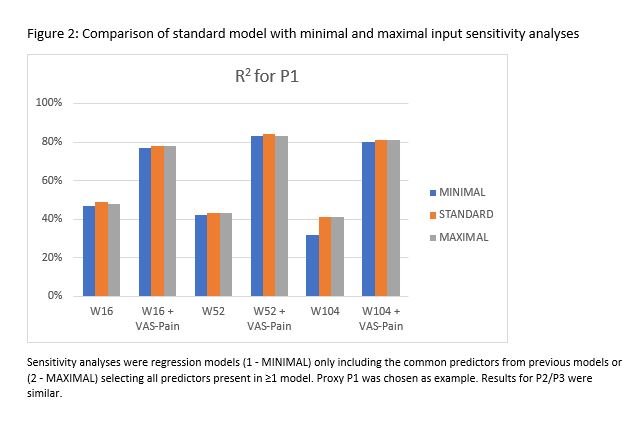
Models were validated by randomly splitting the data in a training (75%) and test (25%) set. The root mean square error (RMSE) compared these 2 datasets to test model robustness. We performed sensitivity analyses with regression models (1 – MINIMAL) only including the common predictors from previous models or (2 – MAXIMAL) selecting all predictors present in ≥1 model.
1Pazmino et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79 (S1):578
2Pazmino et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(5):556-565
Results: In total, 379 patients were included. Overall, 63 of the 83 predictors were used in the regression analyses. Figure 1 shows the complexity versus the predictive capacity per model. Table 2 gives the RMSE per model. R2 for the original models was between 3-92%, for minimal models 6%-86%, and for maximal models 1%-87%. Figure 2 compares the standard to the sensitivity analyses for PGA.
Conclusion: VAS-pain remains essential in determining patient wellbeing, even in patients in remission where pain levels should be theoretically lower. Determining uniformly patient wellbeing is challenging as different definitions lead to ambiguous results.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
De Cock D, Poffe T, Verbeke G, Pazmino S, Stouten V, Bertrand D, Westhovens R, Verschueren P. The Challenge of Assessing Wellbeing from the Patients` Perspective in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-challenge-of-assessing-wellbeing-from-the-patients-perspective-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-challenge-of-assessing-wellbeing-from-the-patients-perspective-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis/