Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III: Bench to Bedside
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Complement activation is known to play a major role in lupus nephritis (LN). Urinary membrane attack complex (C5b-9) has been shown to correlate with proteinuria and renal injury in other diseases such as diabetic nephropathy, IgA nephropathy and ANCA vasculitis, but its role is unclear in LN. This study aims to determine whether urine C5b-9 is associated with proteinuria and markers of glomerular or tubular disease activity in LN.
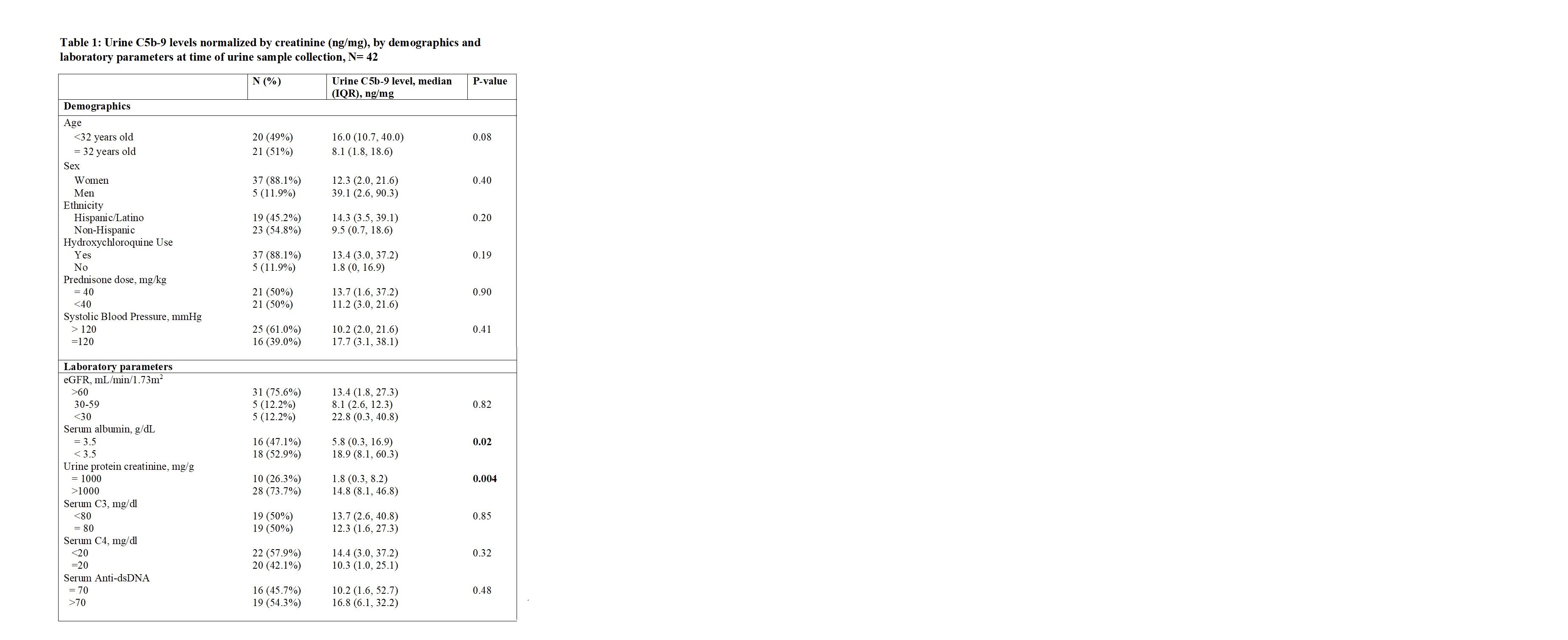
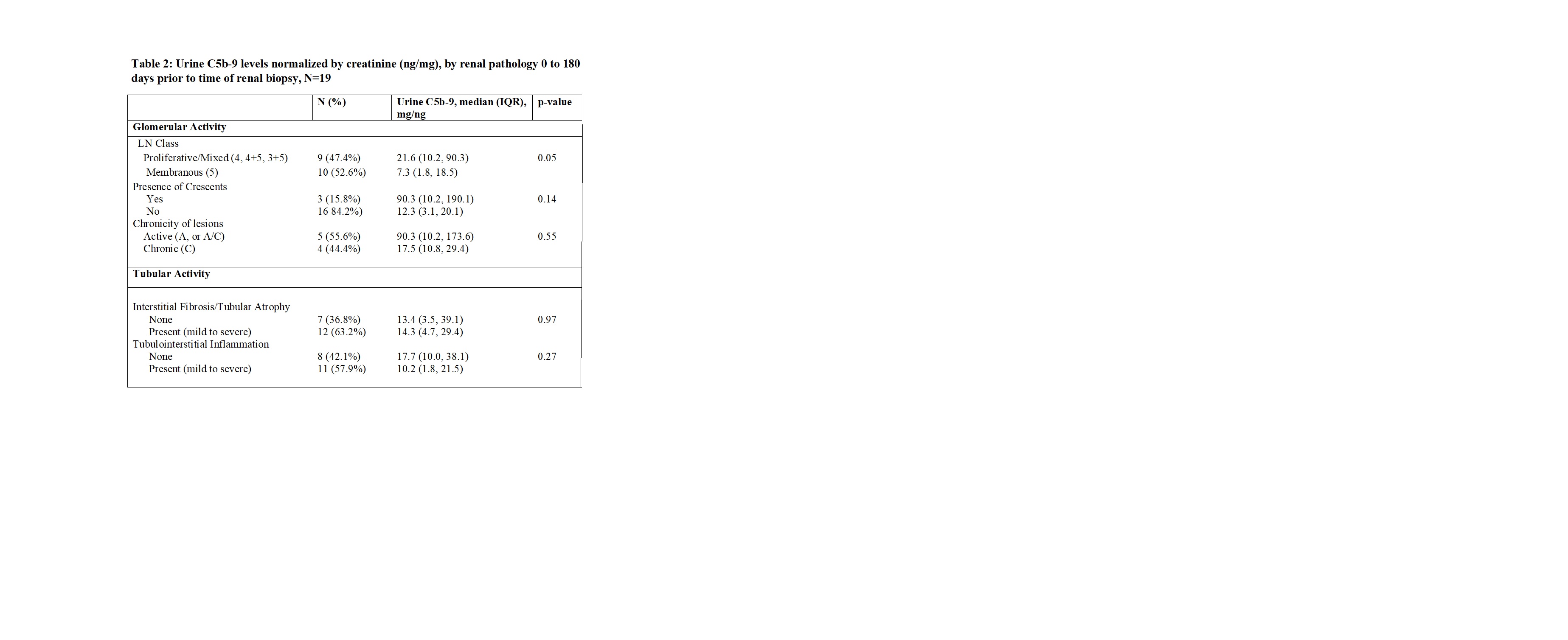
Methods: Urine samples from 42 adult and pediatric lupus patients with clinically indicated renal biopsies performed between 2010 and 2019, and 3 normal controls were collected. The urine C5b-9 levels were measured using specific enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kit (Quidel Corporation) and normalized by urine creatinine excretion. The urine samples were ran immediately after thawing in duplicate and analyzed on a standard curve. Urine C5b-9 levels were correlated with demographic and laboratory parameters at time of urine collection (Table 1) and with renal pathology 0 to180 days prior to time of renal biopsy (Table 2).
Results: Patient with LN (n=42) had higher median (IQR) urine C5b-9 of 12.8 ng/mg (2.0, 27.3) as compared to 0 ng/mg (0, 2.4) among normal controls (n=3), p=0.03. Of the 42 LN patients, the median age (IQR) is 32 years (19, 41), 37 (88.1%) females and 19 (45.2%) Hispanic. Patients with low serum albumin (< 3.5 g/dL) had higher median (IQR) urine C5b-9 as compared to those with normal albumin: 18.9 ng/mg (8.1, 60.3) vs. 5.8 ng/mg (0.3, 16.9), p=0.02. Similarly, patients with elevated urine protein creatinine ( >1000mg/g) had significantly higher median (IQR) urine C5b-9: 14.8ng/mg (8.1, 46.8) vs. 1.8ng/mg (0.3, 8.2), p=0.004. There was no significant association in eGFR, serum C3, C4, dsDNA and urine C5b-9 levels. 19 of the 42 LN patients had urine sample collected 0 to180 days prior to time of renal biopsy, of which 10 had urine sample collected on the day of renal biopsy. Of the 19 LN patients, 9 (47.4%) had proliferative/mixed class. LN patients with proliferative/mixed class had higher median (IQR) urine C5b-9 compared with membranous class: 21.6 ng/mg (10.2, 90.3) vs. 7.3 ng/mg (1.8, 18.5). However, tubular interstitial fibrosis and inflammation was found not to be associated with urine C5b-9 levels.
Conclusion: Although limited by sample size, this pilot study suggested that urine C5b-9 is associated with low serum albumin and proteinuria in LN. In addition, urine C5b-9 levels checked before or at time of biopsy may be a potential marker of glomerular activity in LN. More studies are needed to investigate urine C5b-9 as a biomarker of glomerular or tubular activity.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wang S, Moore E, Lally B, Goilav B, Putterman C, Broder A. The Association of Urinary Membrane Attack Complex (C5b-9) with Proteinuria and Glomerular Activity in Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-association-of-urinary-membrane-attack-complex-c5b-9-with-proteinuria-and-glomerular-activity-in-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-association-of-urinary-membrane-attack-complex-c5b-9-with-proteinuria-and-glomerular-activity-in-lupus-nephritis/