Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Non-articular pain (NAP) is often reported by early RA (eRA) patients, impacts RA remission (REM) but remains poorly defined and this hampers RA care. The contribution of regional musculoskeletal pain (MSP) conditions to NAP in RA is not well understood. We previously reported that areas of NAP reported by eRA patients on a body pain diagram (BPD) were frequently co-located with areas of joint inflammation documented by rheumatologists. The objectives of this study were to examine associations between 1) presence of NAP on patient-reported BPD with a MSP diagnosis charted by the rheumatologist and 2) NAP and RA disease activity (DA).
Methods: Data were obtained from patients with eRA (symptoms< 1 year) enrolled in the Consortium of Early Arthritis Cohorts (CATCH) and who completed the Stanford CHOIR BPD during the first year of follow up (baseline (BL), 6 or 12 months (mo)). NAP was grouped into 3 categories: 1) none (no sections on BPD) 2) regional (1-3 sections) or 3) widespread (3+sections). We performed a chart review to identify rheumatologist-documented prespecified MSP diagnoses that could correspond to patient-reported NAP. Descriptive statistics were calculated, and comparisons used Fisher exact tests.
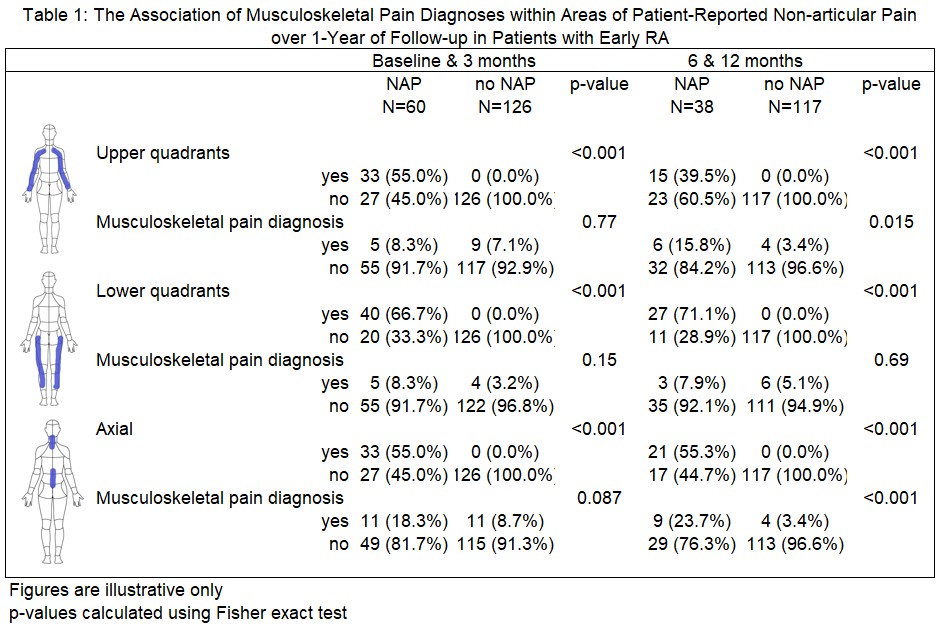
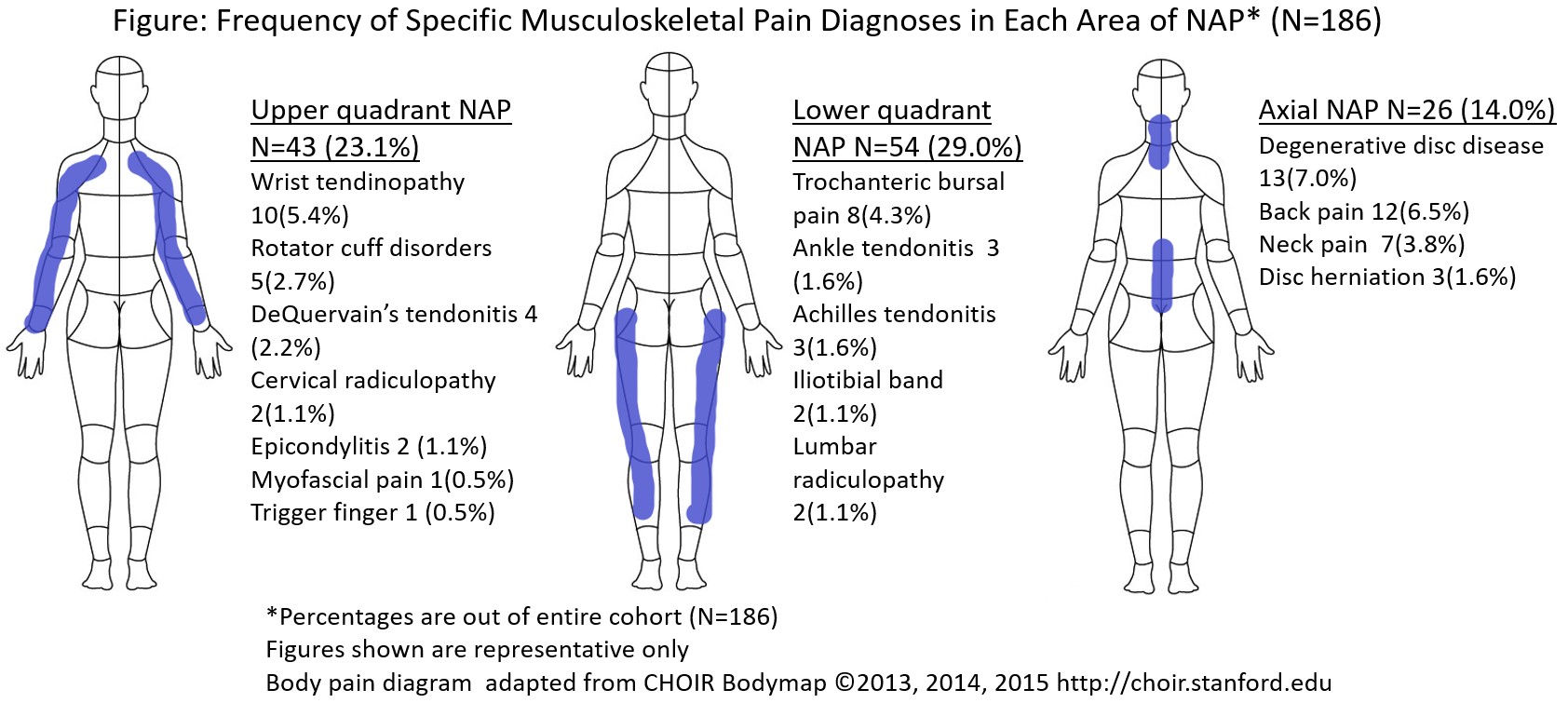
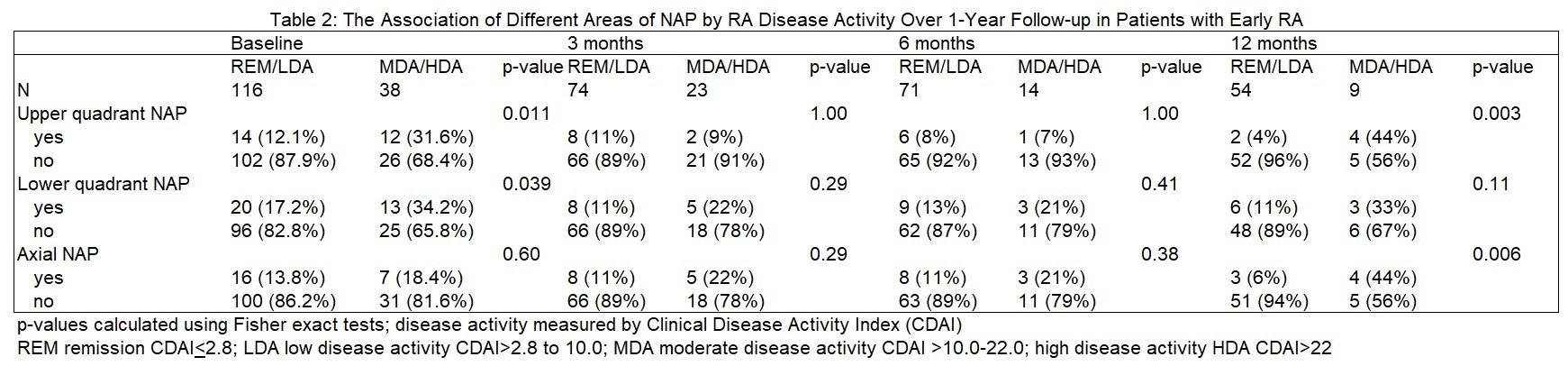
Results: The sample included 187 early RA patients; 81% female, mean (Sd) age 49(16); 76% seropositive, median symptoms duration (IQR) 8 mo (5, 11). 66% were treated with MTX-inclusive regimens. Among NAP patients early in disease course (BL or 3 mo visits, N=60), 55% reported upper quadrant pain (UQP), 67% reported lower quadrant pain (LQP) and 55% reported axial pain. Later in follow-up (6 or 12-mo, N=38) 40% of NAP patients report UQP, 71% report LQP and 55% report axial pain. The overall frequency of a documented MSP diagnosis in NAP patients was low especially at Bl or 3 mo (8.3% for UQP, 8.3% of LQP and 18.3% in axial NAP). At 6 or 12 mo, the frequency of MSP diagnoses increased in all sections of NAP (in UQP 8.3% to 15.8%, axial 18.3% to 23.7%) but not in LQP (8.3% to 7.9%). MSP diagnoses were more frequently found in those who reported NAP compared to those who did not (Table 1). This reached significance at 6 or 12 mo for UQP (15.8% versus 3.4% without NAP, p=0.02) and axial NAP (23.7% versus 3.4%, p< 0.001) but not for LQP (Table 1). The most reported diagnoses included degenerative disc disease, back pain, wrist tendinopathy and trochanteric bursal pain (Figure). At BL, 32% of those in moderate or high DA reported UPQ versus 12.1% of those who were in REM/LDA (p=0.011). Similar patterns were found for LQP but did not reach significance for axial NAP (Table 2). At 12 mo, 44% of those who were in moderate/high DA versus 4% of those in REM/LDA reported UQP (p=0.003). Significant differences were seen for those who reported axial NAP but did not reach significance for LQP (Table 2).
Conclusion: NAP was commonly reported by about a third of eRA patients early in their disease course, but a MSP diagnosis that could explain NAP was infrequently documented. Patient-reported NAP was associated with specific MSP conditions. Patients with increased RA DA more often reported NAP, adding further evidence to suggest a role for RA inflammation in NAP. Timely diagnoses of specific causes of NAP may help direct more personalized RA care.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Meng C, Butler M, Jannat-Khah D, Lee Y, Bingham C, Bykerk V. The Association of Patient-Reported Non-Articular Pain with Musculoskeletal Pain Diagnoses and RA Disease Activity in a Prospective Real-World Cohort of Patients with Early RA [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-association-of-patient-reported-non-articular-pain-with-musculoskeletal-pain-diagnoses-and-ra-disease-activity-in-a-prospective-real-world-cohort-of-patients-with-early-ra/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-association-of-patient-reported-non-articular-pain-with-musculoskeletal-pain-diagnoses-and-ra-disease-activity-in-a-prospective-real-world-cohort-of-patients-with-early-ra/