Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The Spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) inhibitor fostamatinib was not approved as treatment for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) due to insufficient effect on joint structure in the phase III OSKIRA-1 study. Here we use a translational model system to investigate the direct effect of Fostamatinib on the extracellular matrix (ECM) of the target tissues (cartilage, bone, and synovium) for a better understanding of the insufficient effect in joint structure found in OSIKRA-1.
Methods: Human mature osteoclasts (HOC) seeded on bone, bovine cartilage explants (BEX) and human synovial explants (SME) were treated with the active metabolite of Fostamatinib, R406, at 5µM-0.05µM. Osteoclasts were co-stimulated with 25 ng/ml M-CSF and RANKL, while BEX and SME were co-stimulated with TNFα 2 ng/mL and OSM 10 ng/mL (O+T) or TNFα 10 ng/mL, respectively. CTX-1 and Calcium (Ca2+) were measured in conditioned medium (CM) from HOC. Metabolic activity of HOC was assessed with Alamar Blue®. C2M and AGNx1 were measured in CM from BEX, while acMMP3, C1M, and C3M were measured in CM from SME. The biomarkers in BEX and SME CM were measured at 4 time points and the total release were quantified by area under the curve (AUC). CTX-1, C2M, AGNx1, acMMP3, C1M, C2M and C3M were measured with ELISA. Ca2+was measured with ADVIA Chemistry system. Statistical differences of metabolic activity was calculated with One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test. Statistical differences between biomarkers levels or AUC were calculated with Kruskall Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparision test.
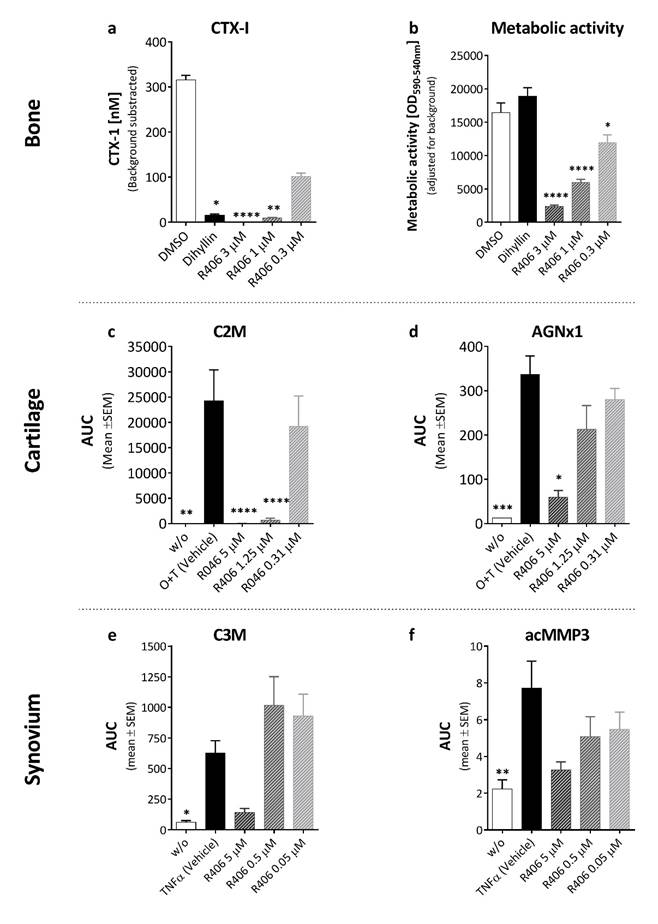
Results: R406 decreased the release of CTX-1 (Fig 1A) and Ca2+ in a dose-dependent manner, with a significant decrease at 1µM (P<0.01). This might be due to a toxic effect of R406 on HOC (Fig 1B) (P<0.05). In cartilage, R406 decreased the total release of C2M and AGNx1 in a dose-dependent manner. C2M was inhibited a concentrations down to 1.25µM (P=0.034), and AGNx1 down to 5µM (P=0.012). In synovial explants, R406 tended to decrease release of C3M (Fig 1e), C1M and acMMP3 (Fig 1f) at 5µM, but this was not significant.
Conclusion: Serum-based biomarkers of the joint ECM turnover were measured in CM from HOC, cartilage and synovial explant cultures. R406 decreased bone resorption and HOC metabolic activity in a dose-dependent manner, together with the MMP-mediated degradation of type II (C2M) collagen and aggrecanse degradation of aggrecan (AGNx1) in cartilage. However, R406 had limited effect on the inflammation driven MMP-mediated degradation of type I (C1M) and III (C3M) collagen and activation of MMP-3. From these data it is expected that Fostamatinib would have some effect on bone and cartilage, but not on inflammation driven degradation of the synovium.
Figure 1
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kjelgaard-Petersen CF, Bay-Jensen AC, Christiansen TG, Karsdal MA, Hägglund P, Thudium CS. Test of the Spleen Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Fostamatinib in a Translational Joint Tissue Model Show Significant Effect on Bone, but Not on Synovial Tissue [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/test-of-the-spleen-tyrosine-kinase-inhibitor-fostamatinib-in-a-translational-joint-tissue-model-show-significant-effect-on-bone-but-not-on-synovial-tissue/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/test-of-the-spleen-tyrosine-kinase-inhibitor-fostamatinib-in-a-translational-joint-tissue-model-show-significant-effect-on-bone-but-not-on-synovial-tissue/