Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: In inflammatory arthritis swelling is regarded as a sign of synovitis and is associated with radiographic progression. However, the association of tenderness with radiographic progression is not clear. The aim of this study was to assess the predictive value of tenderness alone and with consideration of sonographic signs for synovitis, disease duration and baseline radiographic damage for subsequent radiographic progression in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Methods: Clinical and sonographic (grey scale (GS) and power Doppler (PD)) examination of 22 joints of the hand were performed cross-sectionally in consecutive patients with RA and PsA with at least one tender joint. Radiographs were scored for erosions and joint space narrowing (JSN) at inclusion and radiographic progression of each joint was assessed after 2 years. The impact of tenderness on progression was analyzed in non-swollen joints for RA and PsA separately with logistic regression analyses. As a second step, the association of PD, GS, disease duration, C-reactive protein, baseline erosions and JSN and global joint counts with subsequent structural damage was assessed using univariate logistic regression in tender non-swollen joints again on the joint level.
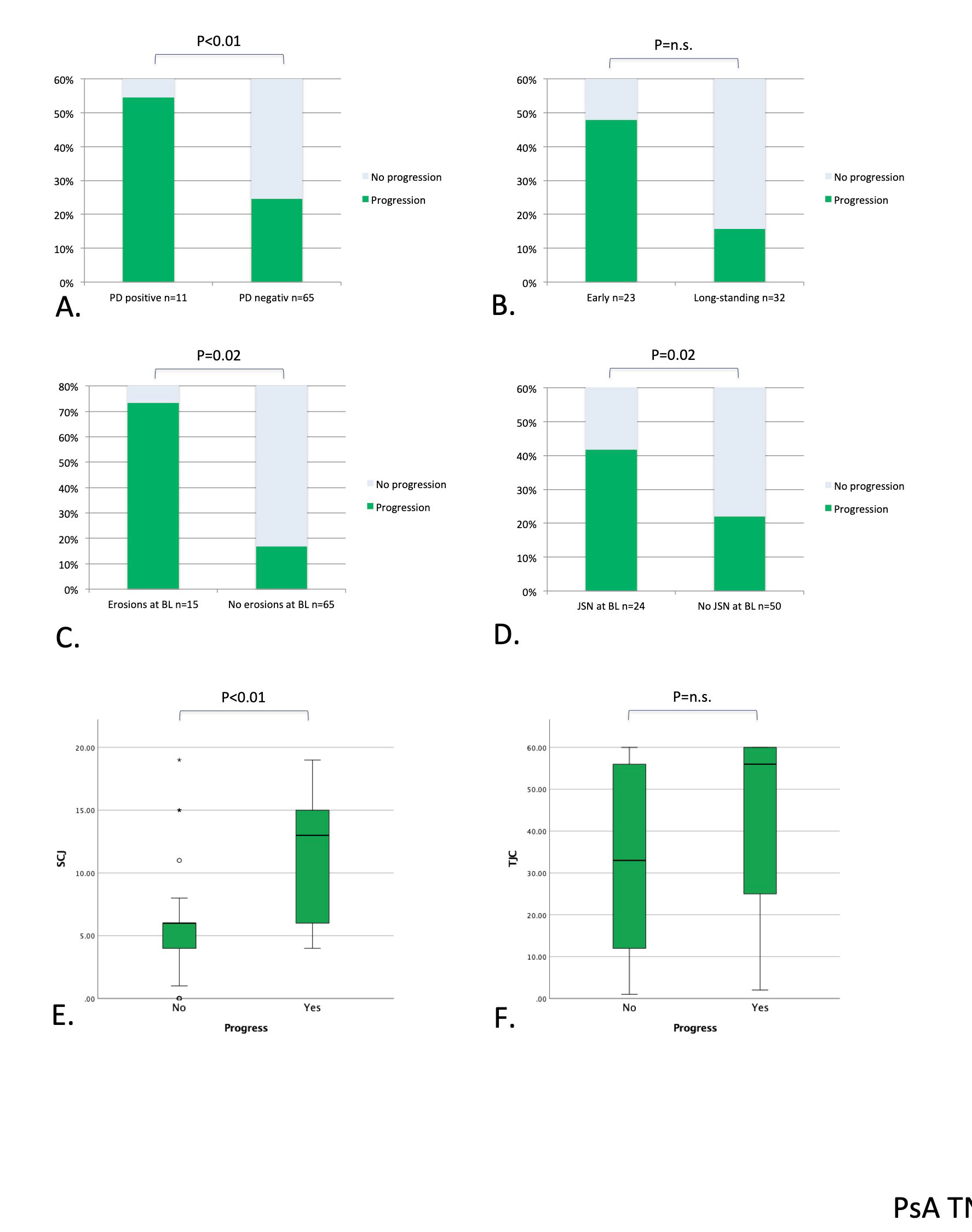
Results: We included 1207 joints in 54 RA patients and 396 joints in 18 PsA patients. Tenderness was associated with subsequent radiographic progression in non-swollen joints in PsA (OR 3.44, 95%CI 1.78-6.62, p< 0.01) but not in RA (OR 1.60, 95% CI 0.99-2.48, p=0.55) (Figure 1). In tender non-swollen joints in RA patients, PD (OR 3.74, 95% CI 1.10-13.30, p=0.04) and baseline erosions (OR 4.42, 95% CI 1.22-15.95, p=0.02) had a significant impact on radiographic progression. In PsA patients, PD (OR 8.46, 95% CI 1.72-41.72, p< 0.01), baseline erosions (OR 6.71, 95% CI 1.43-31.39, p=0.02), baseline JSN (OR 7.27, 95% CI 1.47-35.89, p=0.02) and SJC (OR 1.26, 95%CI 1.07-1.48, p< 0.01) were associated with radiographic progression.
Conclusion: Our findings indicate that tenderness in non-swollen joints is associated with subsequent radiographic progression in PsA, while in RA it is a risk factor for radiographic progression only in the presence of additional factors, such as sonographic signs for synovitis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gessl I, Popescu M, supp G, Deimel T, Studenic P, Durechova M, zauner m, Smolen J, Mandl P. Tenderness and Radiographic Progression in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tenderness-and-radiographic-progression-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-2/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tenderness-and-radiographic-progression-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-2/