Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: With growing availability of autoantibody testing and autoantibodies gaining more weight in the 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), an increasing incidence rate (IR) of seropositive RA might be expected. We therefore aimed to explore the temporal trends of IRs for patients with seropositive and seronegative RA using various data sources for serostatus definition.
Methods: Danish nationwide population-based cohort study using healthcare and clinical quality registries from 2000 to 2018. RA patients were identified with first-time M05/M06 ICD-10 code (except M06.1) in the Danish National Patient Registry (DNPR) and a redeemed prescription of a csDMARD in the following year in the Danish National Prescription Registry.
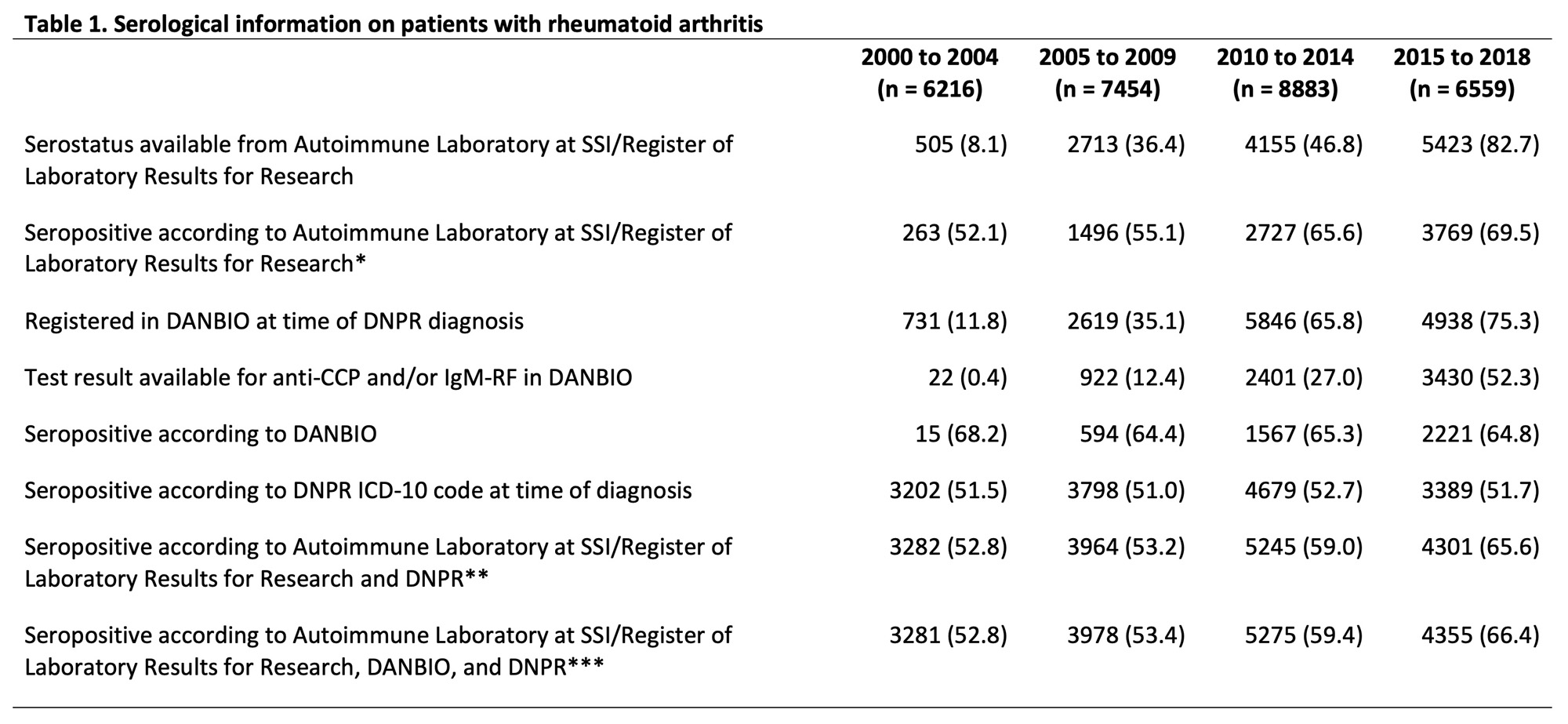
Autoantibodies and ICD-10 codes from laboratory and register-based data sources were combined to define the outcome: serological status of each RA case. The definitions used laboratory-reported IgM-RF and anti-CCP registered in the Autoimmune Laboratory at Statens Serum Institut and/or the Register of Laboratory Results for Research. Physician-reported IgM-RF and anti-CCP available in DANBIO were added for those with no laboratory-reported autoantibodies. Imputation of serostatus according to ICD-10 codes in the DNPR, was for those with missing autoantibodies from any of the previous data sources. An outcome definition without DANBIO data was also pre-specified. The robustness of the register-estimated incidences of seropositive and seronegative RA were assessed using solely laboratory-reported autoantibodies. Registration of a positive autoantibody or an M05 diagnosis classified as seropositive RA, whereas negative autoantibody or M06 outlined seronegative RA.
Annual age- and sex-standardised IRs were calculated as the number of incident seropositive and seronegative cases, respectively, divided by number of person-years in the general population in that given year.
Results: In total, 29 112 incident patients with RA were identified from 2000 to 2018 (Table 1). An increasing temporal trend in IR of seropositive RA and decreasing trend of seronegative RA was observed. The IRs were higher for seropositive RA than for seronegative RA from 2009 and onwards with a widening of the IR gap between 2009 and 2016, leading to approximately twofold higher IR of seropositive RA than of seronegative RA, regardless of the definition of seropositivity (Figure 1). The widening of the IR gap was driven by an initial increase in IRs with a rapid increase to year 2010 followed by a more fluctuating pattern for seropositive RA in combination with a decrease in the IR of seronegative RA. As testing for autoantibodies became more frequent, the rate of RA cases with missing values for autoantibodies decreased significantly over time.
Conclusion: The IR of patients with seropositive RA increased and decreased for seronegative RA during a period where autoantibody testing grew and the presence of autoantibodies received a greater weight in the classification criteria for RA. Temporal IR changes may be caused by a true change in RA serology subtypes, increase in autoantibodies testing or change in registration practice over time, or a combination of these factors.
* Outcome definition for seropositive rheumatoid arthritis using laboratory-reported autoantibodies from the Autoimmune Laboratory at Statens Serum Institut (SSI) and the Register of Laboratory Results for Research within 15 years before and 14 days after the case definition of RA was fulfilled.
** Outcome definition for seropositive rheumatoid arthritis with weighting of data by laboratory-reported autoantibodies from Autoimmune Laboratory at SSI/Register of Laboratory Results for Research > ICD_10 codes from the Danish National Patient Registry (DNPR).
*** Outcome definition for seropositive rheumatoid arthritis with weighting of data by laboratory-reported autoantibodies from Autoimmune Laboratory at SSI/Register of Laboratory Results for Research > physician-reported autoantibodies from DANBIO > ICD_10 codes from DNPR.
IgM-RF, immunoglobulin M rheumatoid factor; Anti-CCP, anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide.
Laboratory-reported autoantibodies originated from laboratory test results of IgM-RF and/or anti-CCP in the Autoimmune Laboratory Statens Serum Institut and/or the Register of Laboratory Results for Research, physician-reported autoantibodies from physician-reported IgM-RF and/or anti-CCP in DANBIO, and ICD_10 codes from the Danish National Patient Registry.
Missing values illustrated the identified patients with rheumatoid arthritis who had no available autoantibodies result in the Autoimmune Laboratory at Statens Serum Institut or the Register of Laboratory Results for Research within 15 years before to 14 days after they fulfilled the case definition of rheumatoid arthritis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Soussi B, Cordtz R, Duch K, Kristensen S, Linauskas A, Bork C, Schmidt E, Dreyer L. Temporal Trends in Incidence Rates of Seropositive and Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Danish Nationwide Population-based Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/temporal-trends-in-incidence-rates-of-seropositive-and-seronegative-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-danish-nationwide-population-based-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/temporal-trends-in-incidence-rates-of-seropositive-and-seronegative-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-danish-nationwide-population-based-study/