Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: In the contemporary era, the continuous update of international rheumatoid arthritis (RA) guidelines has significantly impacted the diagnosis and management of RA patients in China. The enhanced availability of novel therapeutic agents, including biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (tsDMARDs), has expanded the range of treatment options for RA. Despite these advancements, a systematic investigation of the current treatment strategies and outcomes among early rheumatoid arthritis (ERA) patients in China remains lacking.
Methods: Data was collected from CREDIT, a comprehensive, multicenter Chinese registry of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), focusing on the temporal trends of patient conditions, therapeutic strategies, and treatment outcomes among ERA patients from 2016 to 2023. The study cohort comprised DMARD-naive RA patients with a disease duration of less than one year and moderate to high disease activity at baseline. We characterized the temporal trends in clinical profiles, therapeutic regimens, and treatment outcomes. Logistic regression analysis was employed to determine the factors that influence the decision of prescriptions and the achievement of treatment targets.
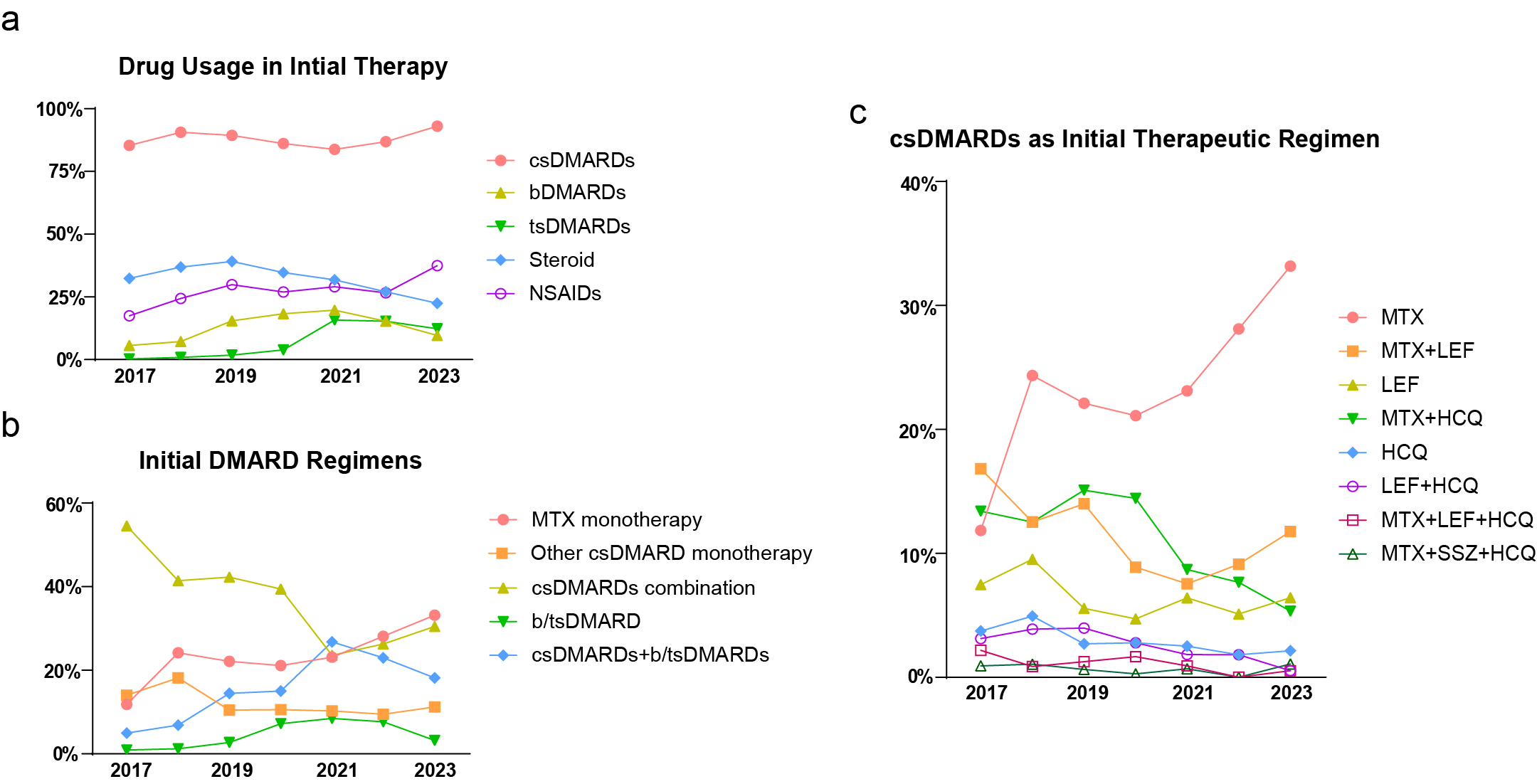
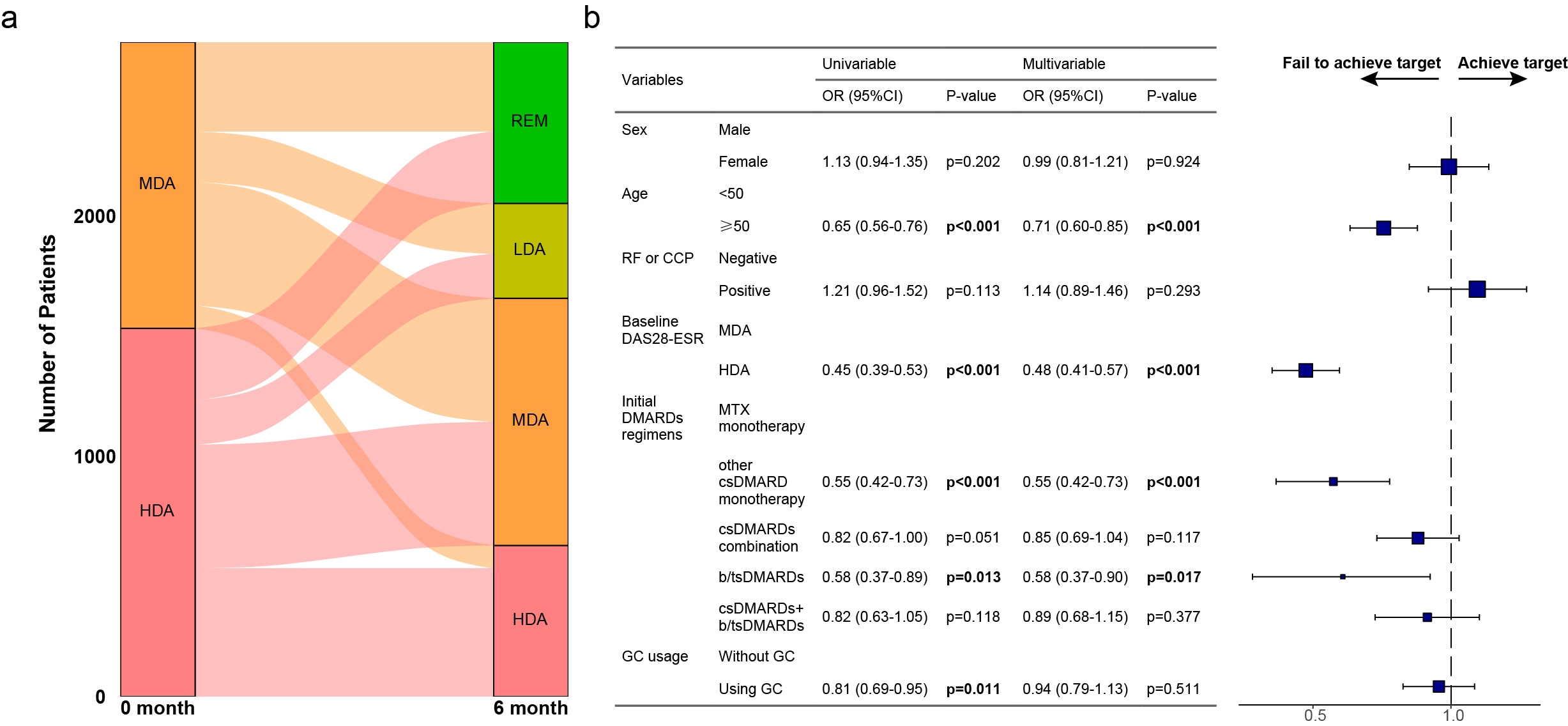
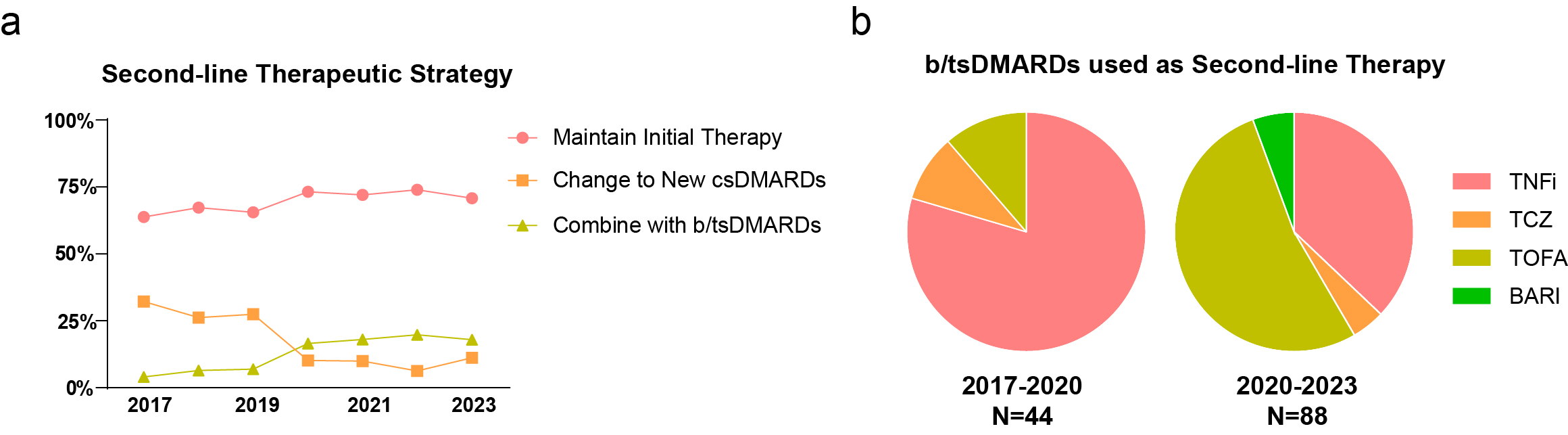
Results: A total of 2,775 patients were enrolled in the study. The prevalence of conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs) usage among ERA patients was 87.9%. 33.8% and 27.0% of the patients were prescribed with glucocorticoids (GCs) and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). 13.3% and 5.9% patients received bDMARDs and tsDMARDs as their initial treatment (Fig 1a). Within the initial DMARD regimens, the utilization of Methotrexate (MTX) demonstrated a progressive annual increase, emerging as the predominant DMARD of choice after 2022 (Fig 1b and 1c). After initial therapy, 39.1% of the patients have achieved the therapeutic target to remission or low disease activity (LDA) (Fig 2a), and older age, higher baseline disease activity, using csDMARD monotherapy other than MTX and using b/tsDMARDs without csDMARDs combination were identified as factors negatively impacting the attainment of treatment targets (Fig 2b). Among patients who did not meet the target after the initial csDMARD therapy, up to 20% of them were subsequently prescribed with b/tsDMARDs as escalated regimens (Fig 3a). Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi), especially Tofacitinib (TOFA) have risen in prominence, becoming the most frequently utilized class of b/tsDMARDs after 2019 (Fig 3b).
Conclusion: Under the guidance of the international recommendations, the treatment of ERA patients in China have become more standardized. In addition to clinical characteristics of patients, adherence to guideline-directed therapeutic regimens emerges as a significant determinant in achieving treatment targets. Increased prevalence of b/tsDMARDs has benefited more patients in ameliorating the disease.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Deng Y, Yu C, Qiao L, Jiang N, Wang Y, Tian X, Wang Q, Li M, Zeng X. Temporal Trends in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis (ERA) Patients with Moderate to Severe Disease Activity: A Multicenter Cohort Study of Treatment Strategies and Outcomes in Chinese Patients in the Modern Era [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/temporal-trends-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-era-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-disease-activity-a-multicenter-cohort-study-of-treatment-strategies-and-outcomes-in-chinese-patients-in-the-modern/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/temporal-trends-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-era-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-disease-activity-a-multicenter-cohort-study-of-treatment-strategies-and-outcomes-in-chinese-patients-in-the-modern/