Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0671–0710) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) possesses the highest case-related mortality of all rheumatic diseases. B cell-targeting, including CD19-targeting CAR-T cells, has shown efficacy but failed to eliminate the SSc-specific anti-topoisomerase-I autoantibodies. 1-4
Methods: We treated three high-risk cases of severe treatment-refractory diffuse cutaneous SSc (dcSSc) with the plasma cell-depleting antibody teclistamab (Table 1). After six cycles of teclistamab, one cycle of rituximab was administered to block recovery of autoantibody-producing cells. All patients were anti-topoisomerase-I antibody positive and have not responded sufficiently to multiple immunosuppressive therapies. Immunosuppressive and antifibrotic therapies were discontinued prior to baseline (BL). Patients were followed for more than six months.
Results: Treatment with teclistamab depleted all plasma cells in the skin. Anti-topoisomerase-I-autoantibody titers seroconverted in two patients and dropped by 83% in the third patient. This immunological response was associated with a decrease of the modified Rodnan skin score, stabilization of SSc-ILD, resolution of tendon friction rubs and decreases in the EUSTAR-AI. The effect on SSc-associated primary myocardial involvement was heterogeneous. Treatment with teclistamab was associated with several adverse events including cytokine release syndrome, hypogammaglobulinemia and mild infections (despite regular immunoglobulin replacement).
Conclusion: Teclistamab may offer potential as a rescue therapy for selected patients suffering from severe, treatment-refractory dcSSc, even with advanced disease.
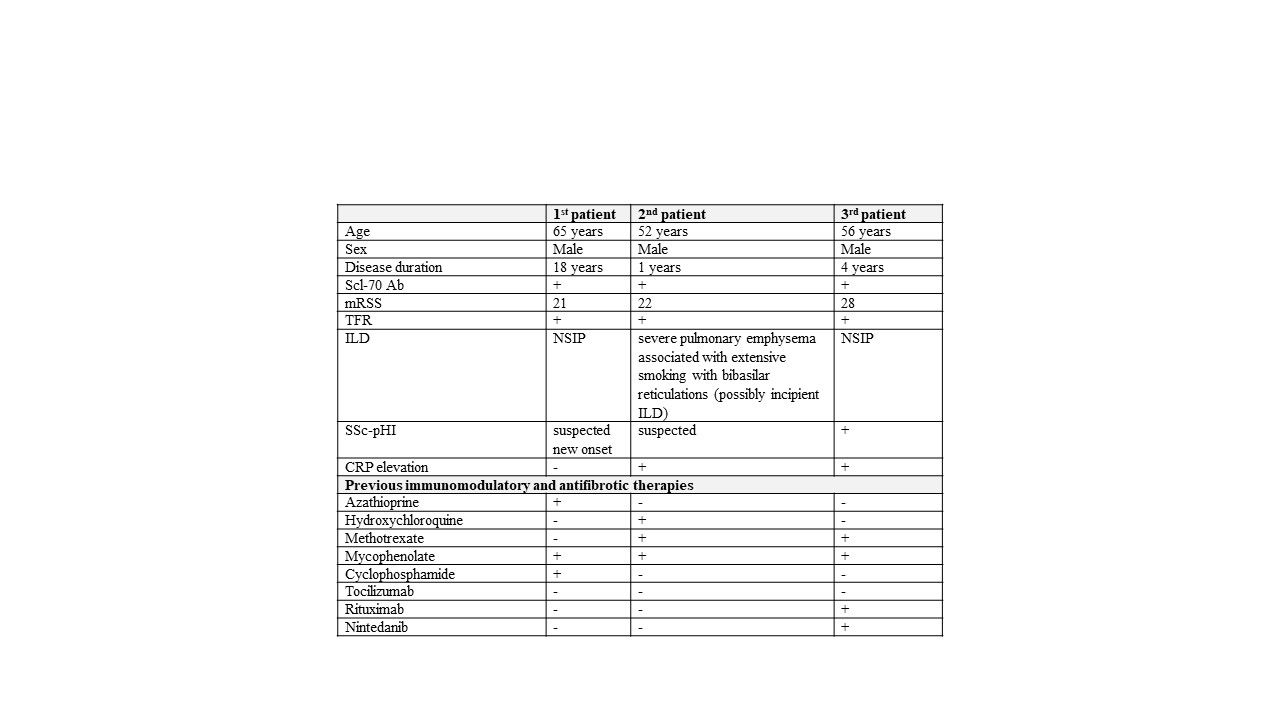 Table 1. Patient characteristics at baseline.
Table 1. Patient characteristics at baseline.
Abbreviations: Scl-70 Ab, anti-topoisomerase-I (Scl70) autoantibodies; mRSS, modified Rodnan Skin Score; TFR, tendon friction rubs; ILD, interstitial lung disease; SSc-pHI, systemic sclerosis primary heart involvement
.jpg) Image 1. Selected clinical outcomes
Image 1. Selected clinical outcomes
(modified Rodnan skin score, mRSS; EUSTAR activity index, AI).
.jpg) Image 2. Immunological outcomes
Image 2. Immunological outcomes
(serological anti-topoisomerase-I titres and multi-color immunofluorescence stainings of skin biopsies from patient 3 using CODEX; DAPI stains nuclei, CD3 stains T cells and CD20, PAX5 and CD138 stain B cells and plasma cells, respectively)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Györfi A, Stuetz A, Duesing C, Lahu L, Deicher F, Li Y, van Saan C, Matei A, Hoelscher A, Bruch P, Koziel S, Roehrich M, Cramer M, Homey B, Buehring B, Kreuter A, Radujkovic A, Heußel C, Lorenz H, Grieshaber-Bouyer R, Schett G, Distler J, Merkt W. Targeting the plasma cell niche in systemic sclerosis: A case series about the bispecific anti-BCMAxCD3 antibody teclistamab in severe, treatment-refractory patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/targeting-the-plasma-cell-niche-in-systemic-sclerosis-a-case-series-about-the-bispecific-anti-bcmaxcd3-antibody-teclistamab-in-severe-treatment-refractory-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/targeting-the-plasma-cell-niche-in-systemic-sclerosis-a-case-series-about-the-bispecific-anti-bcmaxcd3-antibody-teclistamab-in-severe-treatment-refractory-patients/
