Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1264–1307) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The risk of aortic stenosis is increased in people with RA and valvular heart disease (VHD) is among the most over-represented causes of cardiovascular death in RA. Thus, VHD is an under-appreciated extra-articular manifestation in RA, whose risk factors in RA are largely unknown. Because aortic and mitral valve disease comprise the majority of the VHD burden in the U.S., we examined the associations of RA-related clinical variables with the risk of incident aortic and mitral valve disease in a large cohort of U.S. Veterans with RA.
Methods: We studied participants in the Veterans Affairs RA (VARA) registry, a multicenter, prospective cohort of U.S. Veterans with RA. Using diagnostic and procedural codes in linked VA, Medicare, and National Death Index data, a composite VHD outcome was defined as the development of aortic stenosis or insufficiency, non-rheumatic mitral stenosis, mitral insufficiency, aortic or mitral valve procedural intervention, or death related to aortic or mitral valve disease. Participants who experienced the VHD outcome prior to enrollment were excluded. Included participants were followed from registry enrollment to the first of the composite outcome, death, or end of study period (12/2020). RA disease activity was assessed using DAS28-CRP (DAS28-ESR if missing) and CDAI. From banked serum at enrollment, rheumatoid factor, anti-CCP, and hsCRP concentrations were measured using nephelometry or ELISA. We examined the association of these RA-related clinical variables with VHD risk in multivariable Cox regression models, adjusting for demographics, BMI, smoking status, hypertension, diabetes, coronary artery disease, and medication (methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, TNFi, prednisone, statin) use at baseline.
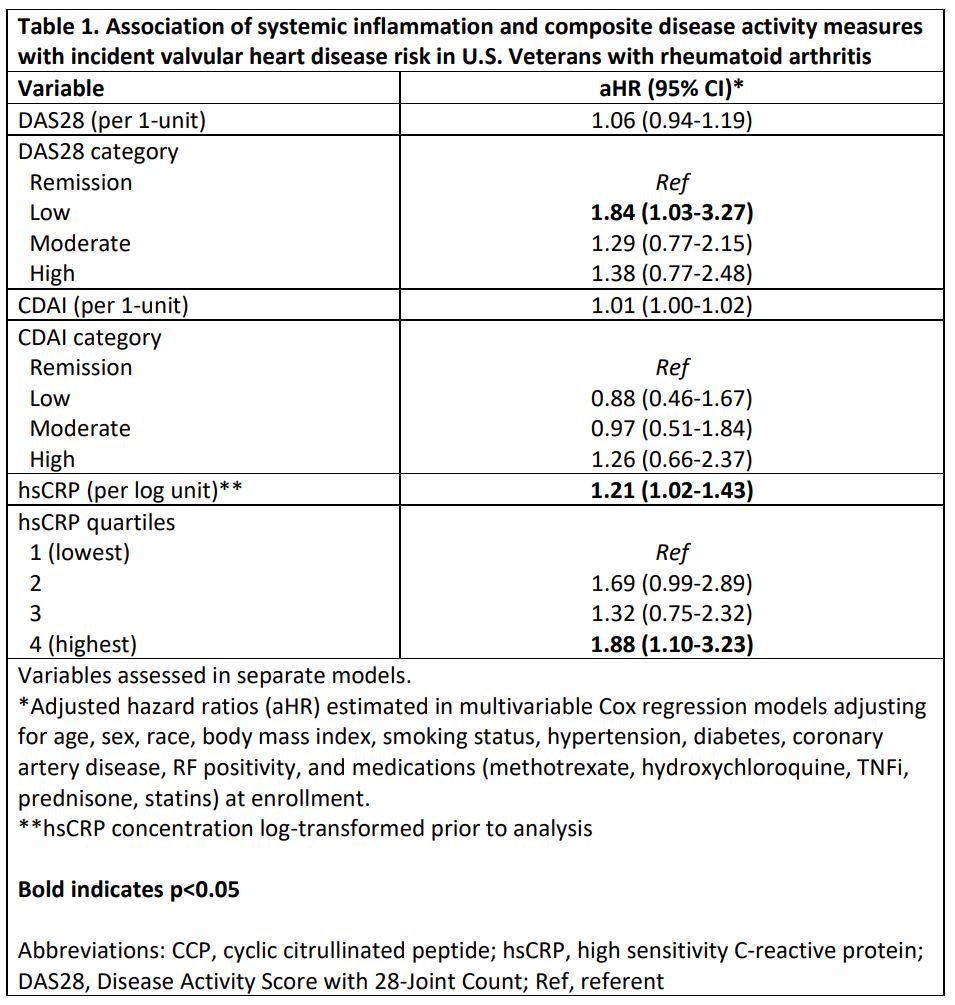
Results: Among 2,848 eligible participants (mean age 71.6 years, 88% male, mean DAS28 3.8), we observed 128 composite VHD events over a mean follow up of 6.7 years (IR 6.67 [5.61-7.93] per 1000 person years). The incidence of aortic (IR 3.72 [2.95-4.68]) and mitral disease (IR 3.25 [2.54-4.16]) were similar. After multivariable adjustment, hsCRP concentration was significantly associated with incident VHD (Table 1; aHR 1.21 [1.02-1.43] per log unit increase; aHR 1.88 [1.10-3.23] for highest hsCRP quartile). Non-significant trends toward elevated VHD risk were observed in those who were RF (aHR 1.26 [0.78-2.03]) or anti-CCP positive (aHR 1.27 [0.80-2.03]), whereas higher autoantibody concentrations were not associated with VHD (Table 2). Referent to participants in DAS28 remission, those with higher DAS28 categories demonstrated trends toward higher VHD risk. DAS28 and CDAI scores, as well as high CDAI disease activity, similarly demonstrated non-significant trends with VHD risk.
Conclusion: In this prospective RA cohort, baseline systemic inflammation as assessed by hsCRP was associated with a higher risk of incident VHD. Composite clinical RA disease activity measures were not significantly associated with incident VHD, though estimates were imprecise and only baseline disease activity measures were evaluated. Continued study is warranted to identify mediators that drive VHD risk in RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Johnson T, Yang Y, Roul P, Baker J, Sauer B, Cannon G, Kunkel G, Binstadt B, Joseph A, Wysham K, Lenert A, Kerr G, Reimold A, Duryee M, Thiele G, Mikuls T, England B. Systemic Inflammation Is Associated with Incident Valvular Heart Disease in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Multicenter, Prospective Cohort Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/systemic-inflammation-is-associated-with-incident-valvular-heart-disease-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-multicenter-prospective-cohort-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/systemic-inflammation-is-associated-with-incident-valvular-heart-disease-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-multicenter-prospective-cohort-study/