Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1100–1123) Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Whether the presence of subclinical monosodium urate (MSU) crystal deposition leads to a pro-inflammatory state in asymptomatic hyperuricemia (AH) is unknown. We aimed to compare the inflammatory state in peripheral blood between AH patients with and without sonographic deposits.
Methods: Observational, cross-sectional study. Patients with current serum urate ≥7 mg/dl and no history of acute arthritis were consecutively recruited from internal medicine, cardiology, nephrology, endocrinology, rheumatology, and primary care. We excluded those on urate-lowering treatment or colchicine, another inflammatory rheumatic disease, or being under immunosuppressive therapy (including transplants).
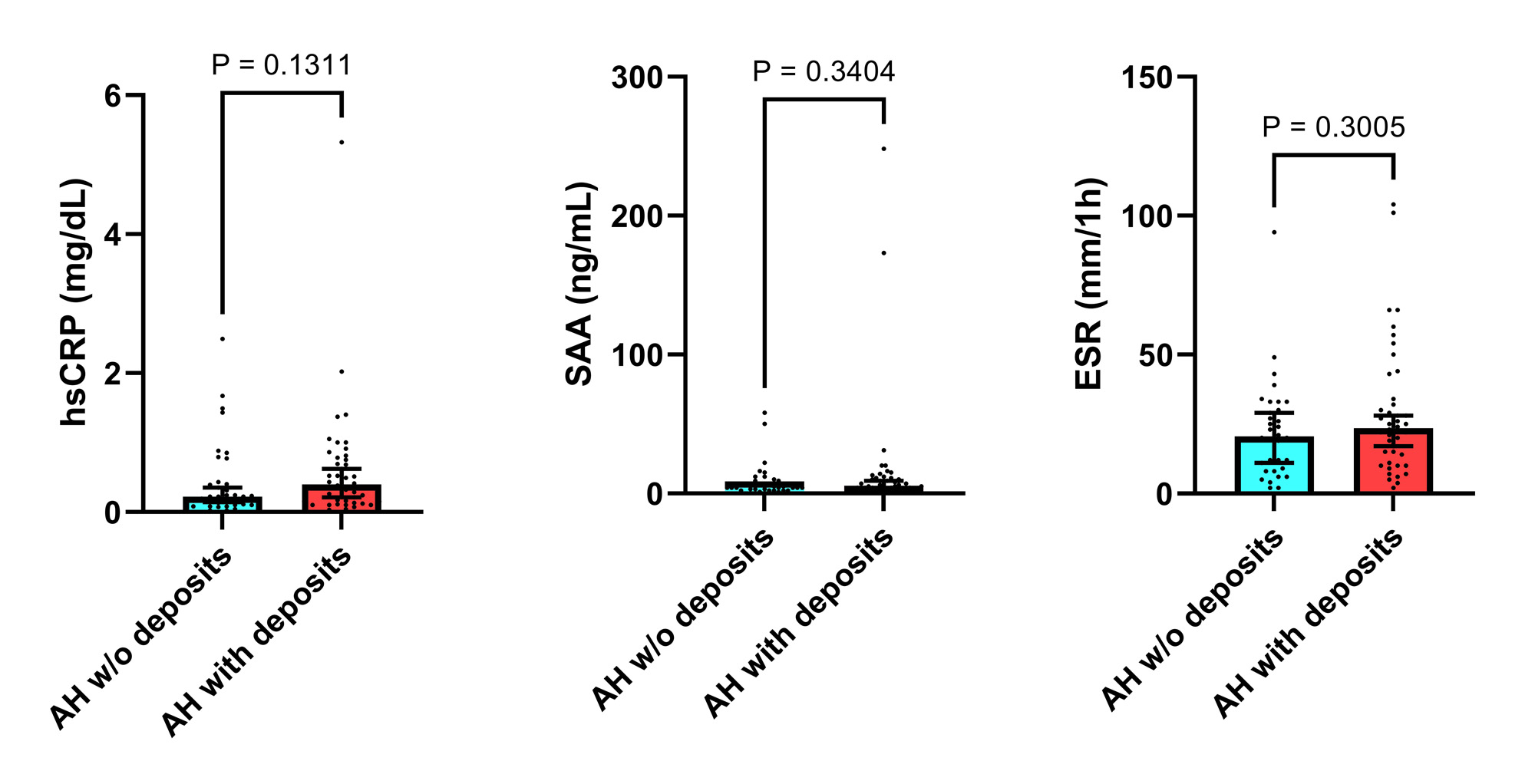
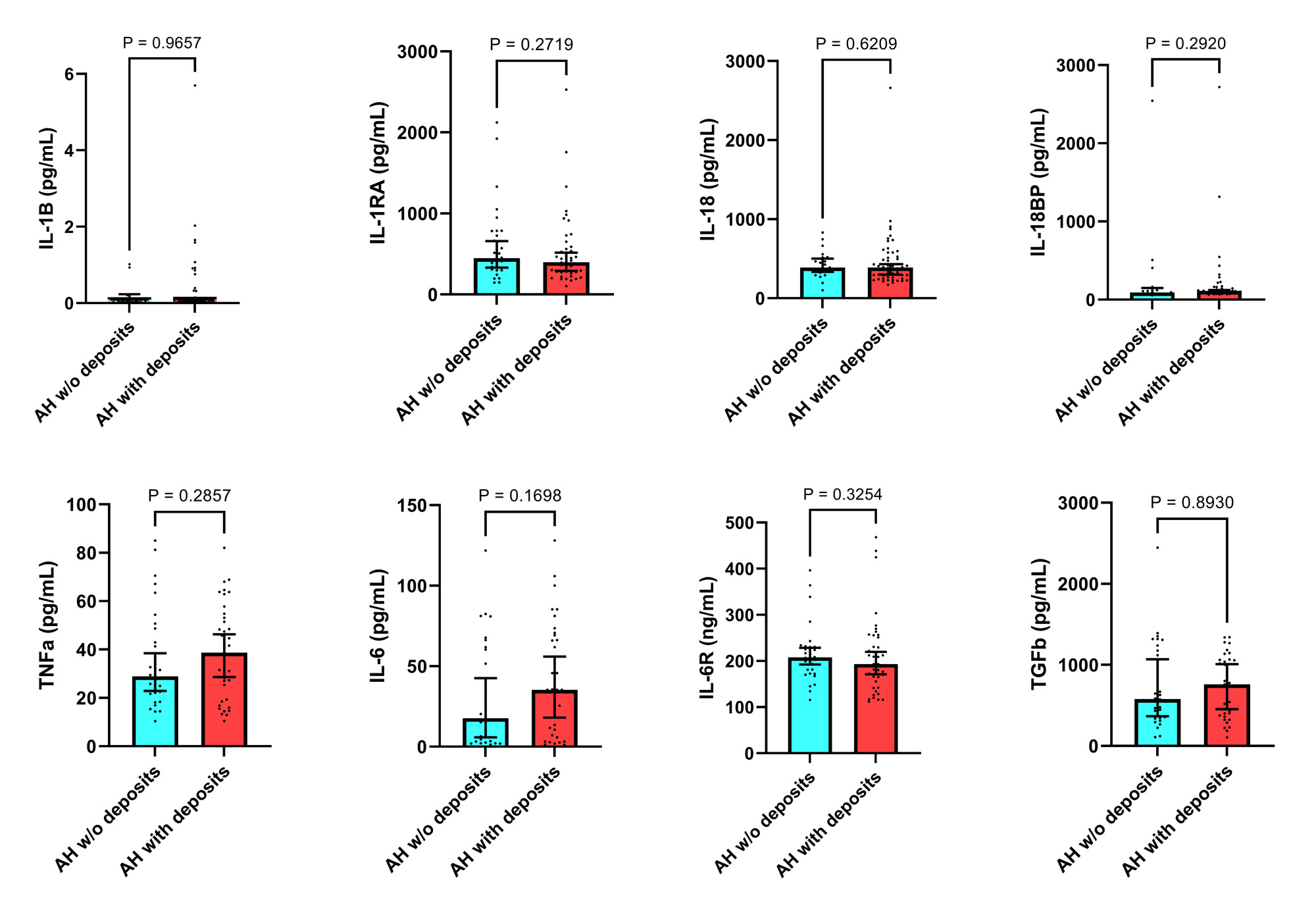
Two comparative groups were predefined. Group 1: AH without deposits; and Group 2: AH with deposits. As sonographic deposits, we considered grade 2-3 double-contour sign and/or tophus according to 2021 OMERACT definitions1, after a 10-location scanning (knees, tibiotalar joints, 1st and 2nd metatarsophalangeal joints, patellar and Achilles tendons) by a trained sonographer blinded to clinical and laboratory data. We measured serum levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) in mg/dl (by immunoturbidimetry), serum amyloid-A in ng/ml (by nephelometry), and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) in mm/1h, as acute phase reactants. Later, using commercial ELISA kits, we analyzed: i) inflammasome NLRP3-related cytokines: interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA), IL-18, IL-18 binding protein (IL-18BP); and ii) general pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines: tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, IL-6, soluble IL-6 receptor (sIL-6R), and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β.
GraphPad Prism (version 9.5.1) was used to compare AH groups, through Mann-Whitney U’s and Chi2 tests.
Results: 77 subjects with AH were recruited, 71.4% men, with a mean age of 59.8 years (SD 17.3) and body mass index (BMI) of 31.2 kg/m2 (SD 5.2). 37.7% and 29.9% had cardiovascular (CVD) and renal disease, respectively. Their mean uric acid was 7.6 mg/dl (SD 1.6).
Patients were classified into group 1 (n=35, 45.5%) or group 2 (n=42, 54.5%). There were no differences (group 2 vs. group 1) in age (67 vs. 56 years), men (69% vs.74.3%), BMI (31.7 vs. 29.9 kg/m2), CVD (38.1% vs. 37.1%), estimated glomerular filtration rate (73.42 vs. 75.03 ml/min/1.73m2), or current serum urate levels (7.35 vs. 7.40 mg/dl). The results of inflammatory markers and cytokines are presented in Figures 1 and 2. There were no differences between groups, but we observed numerical differences for hsCRP, IL-6, and TNF-α.
Conclusion: The inflammatory state was comparable in AH between those with and without sonographic deposits. Some hints were noted for hsCRP, IL-6, and TNF-α that further studies with larger sizes must confirm to establish the relevance of subclinical crystal deposition in AH.
Reference: [1] Christiansen SN. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2021;51:644.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Peral-Garrido M, Boix-Navarro P, Gómez-Sabater S, Caño-Alameda R, Bermúdez-García A, Lozano T, Sanchez-Ortiga R, Perdiguero M, Caro-Martínez E, Ruiz-García C, Pascual E, Francés R, Andrés M. Systemic Inflammation Associated with Silent Deposition of Monosodium Urate Crystals in Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/systemic-inflammation-associated-with-silent-deposition-of-monosodium-urate-crystals-in-asymptomatic-hyperuricemia/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/systemic-inflammation-associated-with-silent-deposition-of-monosodium-urate-crystals-in-asymptomatic-hyperuricemia/