Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2022
Title: Abstracts: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes II: Cardiovascular and Other Comorbidities
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The systemic immune inflammation index (SII) is an inflammation-based biomarker that is an influential prognostic factor in diseases with an inflammation-related etiology. This index is the product of the counts of neutrophils X platelets divided by lymphocytes (nxp/l). Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is characterized by systemic inflammation affecting joints and other tissues and organs. This severe inflammation has been associated with premature all-cause and cardiovascular (CV) mortality. Therefore, we aimed to study the ability of SII to predict mortality in a cohort of Rheumatoid arthritis.
Methods: We studied 1211 RA patients. First, we examined demographic characteristics stratified by all-cause or cardiovascular mortality. Then, we included the following covariables in the analysis: age, sex, lipid profile, smoking status, glucose level, CBC, and SII. We next divided the SII into two quantiles after establishing a cut-point between positive and negative SII predictors in the logistic regression. Finally, we analyze the data through logistic regression to establish an association between SII and mortality.
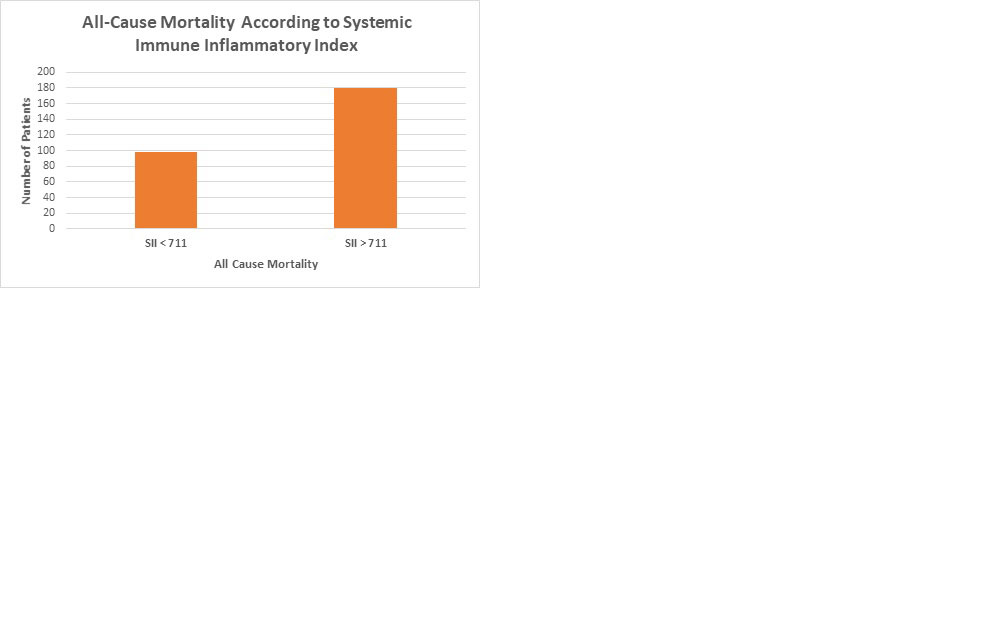
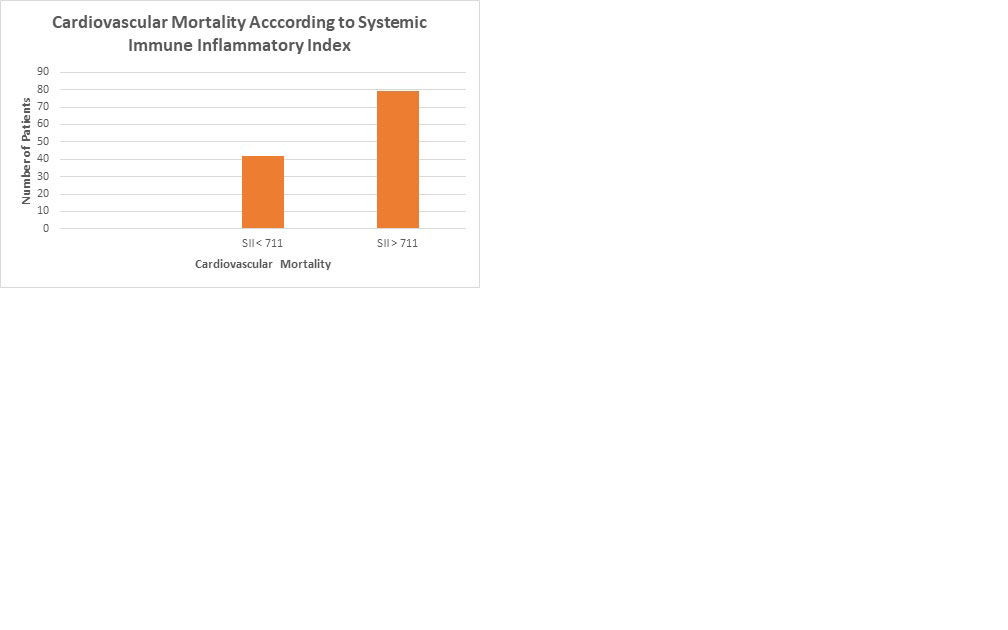
Results: We studied 1211 patients [906 (75%) women]. The mean follow-up time was 9.9 person-years with 278 deaths (2.7 per 100 person-years) for all-cause mortality. The mean follow-up time for CV mortality was 8745 person-years with 121 death (0.3 per 100 person-years). The cut-point for SII was 710.99. There were 180 all-cause deaths in the group with SII > 711 vs. 98 in the group with SII < 711. Similarly, there was 79 cardiovascular deaths vs. 42 in the same groups, respectively. The logistic regression analysis, crude and multivariable, showed that SII predicts all-cause (OR 2.64, 95% CI 1.81, 3.85 p < 0.0001) and CV-mortality (OR 3.03 955 CI 1.76, 5,21, p < 0001 ). (Figures)
Conclusion: SII is a biomarker derived from variables that are ubiquitous in clinical practice and that can be obtained with a hand-held calculator. Our findings suggest that it is an efficient survival predictor, accounting for both all-cause and CV mortality in patients with RA. Further research to examine the performance of the SII as a predictor of other important RA outcomes would be of considerable interest.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Restrepo Suarez J, Del Rincon I, Lorenzo C, Escalante A. Systemic Immune Inflammation Index Predict All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/systemic-immune-inflammation-index-predict-all-cause-and-cardiovascular-mortality-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/systemic-immune-inflammation-index-predict-all-cause-and-cardiovascular-mortality-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/