Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2095–2140) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: High-density lipoprotein (HDL), known for its anti-atherogenic reverse cholesterol transport function, also transports miRNAs between cells, altering cellular function. We found that compared to control subjects, patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) – a type of inflammatory arthritis (IA) – have increased plasma HDL-bound miR-1246, which increased macrophage IL-6 expression. Previous reports indicate that HDL is enriched in the synovial fluid of patients with RA versus osteoarthritis (OA). We hypothesize that in IA the higher concentration of synovial HDL promotes joint inflammation by delivering a higher cargo load of miR-1246 to synovial fibroblasts and enhancing the release of inflammatory cytokines. The purpose of this study is to determine if HDL and HDL-miR-1246 is enriched in IA versus OA synovial fluid and increases synovial fibroblast proinflammatory cytokine expression.
Methods: Synovial fluid and plasma were collected consecutively from 15 IA (10 RA and 5 with immune-checkpoint inhibitor-induced IA) and 4 OA patients who underwent arthrocentesis for routine care. Nuclear magnetic resonance was used to measure the synovial fluid and plasma lipoproteins. Synovial fluid HDL was isolated by fast protein liquid chromatography. Synovial fluid miR-1246 and synovial fluid HDL-miR-1246 were measured by qPCR and normalized to a spike-in miRNA and DNA mimic standard to determine miRNA concentration. RA synovial fibroblasts were activated with LPS for 24-hours then washed and treated with a miR-1246 mimic or antagomir for 24-hours. Cellular IL-6 expression was measured by qPCR.
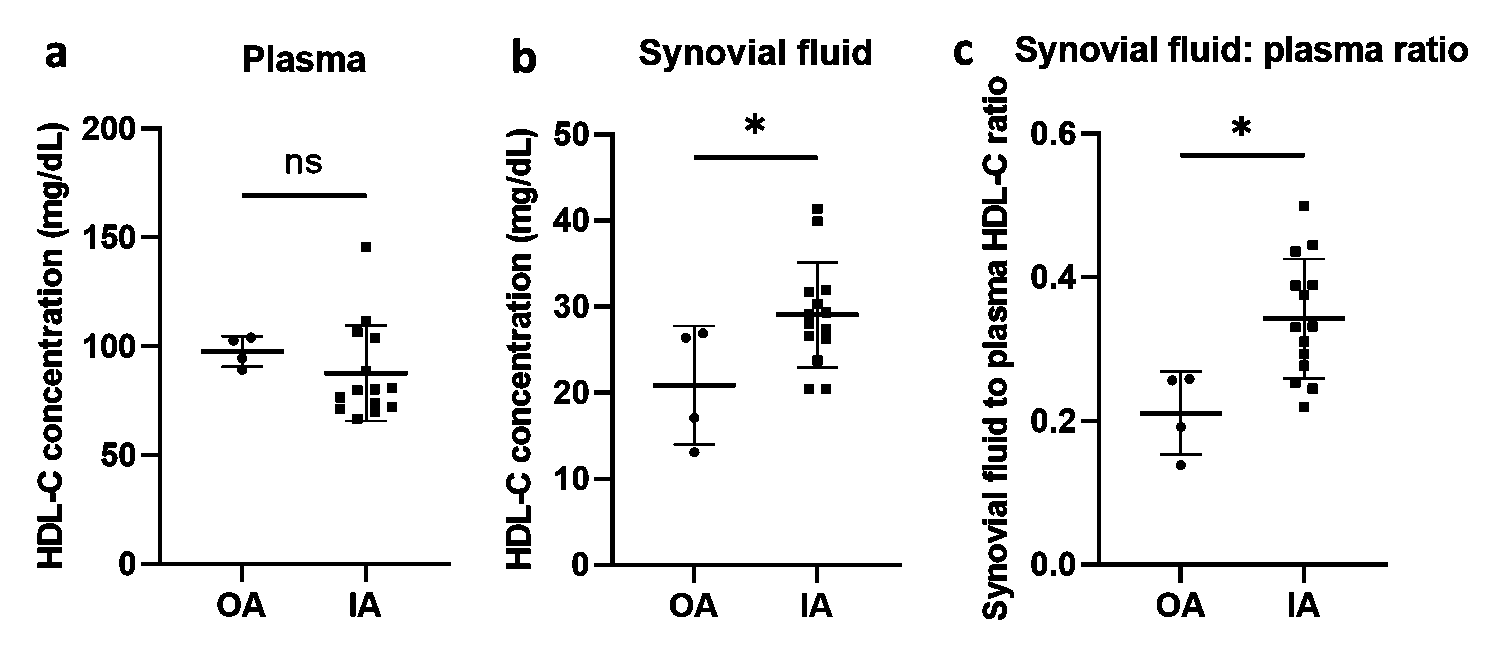
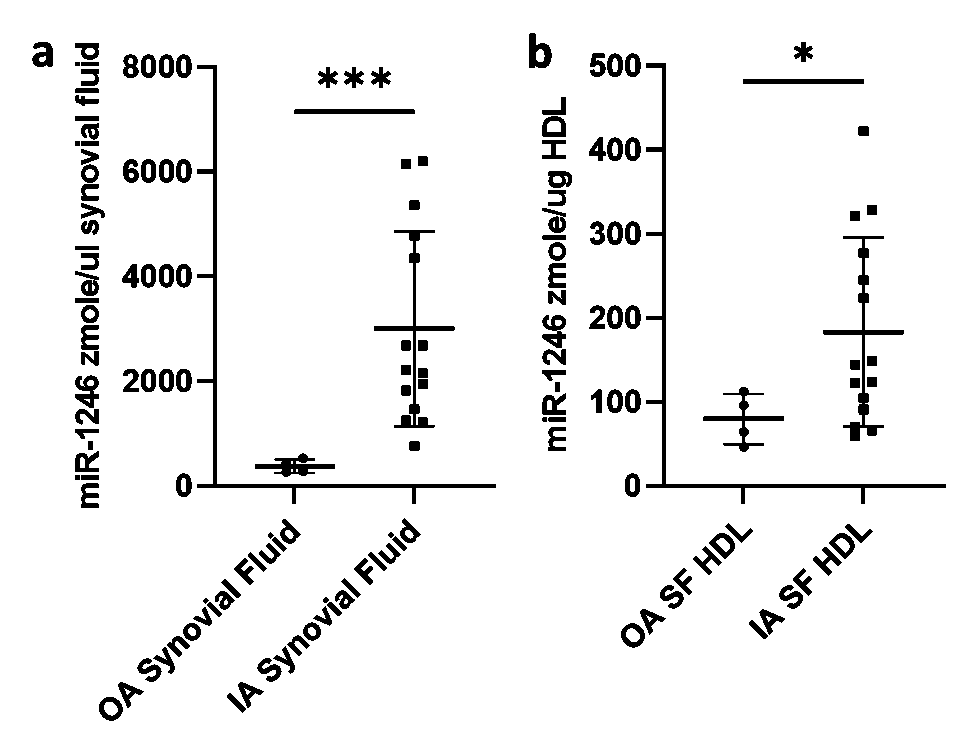
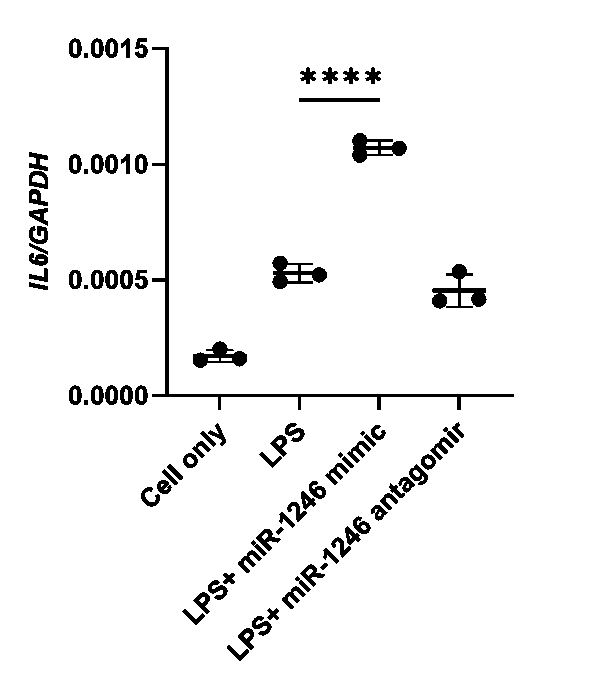
Results: HDL-cholesterol (HDL-C) concentration was similar in IA versus OA plasma (P=0.19). However, synovial fluid HDL was enriched 1.4-fold in IA (29 mg/dl ± 6.1 mg/dl) versus OA (21mg/dl ± 6.9mg/dl) (P=0.04). Similarly, the ratio of synovial fluid to plasma HDL-C was 1.6-fold enriched in IA versus OA patients (P=0.02) (Figure 1). Synovial fluid miR-1246 concentrations were increased 7.9-fold in IA (3000 zmol/uL ± 1860 zmol/uL) versus OA patients (379 zmol/uL ± 126 zmol/uL, P=0.0005). Synovial fluid HDL miR-1246 concentrations were also increased 2.3-fold in IA (183 zmol/ug HDL ± 113 zmol/ug HDL) versus OA patients (80 zmol/ug HDL ± 30 zmol/ug HDL, P=0.049) (Figure 2). Treatment of activated synovial fibroblasts with miR-1246 increased IL-6 expression 2.0-fold (P< 0.0001, Figure 3).
Conclusion: HDL is concentrated in synovial fluid and enriched in miR-1246 in patients with IA versus OA. miR-1246 is proinflammatory to synovial fibroblasts. These data suggest that the HDL may enhance IA synovial inflammation by transport of proinflammatory miRNAs. Future studies will be dedicated to examining HDL-mediated transfer of miR-1246 to synovial fibroblasts and its effect in vivo.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Posey O, Wu Q, Phothisane A, Pham C, Parks D, Akk A, Michell D, Vickers K, Ormseth M. Synovial Fluid High-density Lipoprotein (HDL)-miR-1246 Is Enriched in Patients with Inflammatory Arthritis Compared to Osteoarthritis and Increases Synovial Fibroblast IL-6 Expression [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/synovial-fluid-high-density-lipoprotein-hdl-mir-1246-is-enriched-in-patients-with-inflammatory-arthritis-compared-to-osteoarthritis-and-increases-synovial-fibroblast-il-6-expression/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/synovial-fluid-high-density-lipoprotein-hdl-mir-1246-is-enriched-in-patients-with-inflammatory-arthritis-compared-to-osteoarthritis-and-increases-synovial-fibroblast-il-6-expression/