Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: B Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease Poster
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
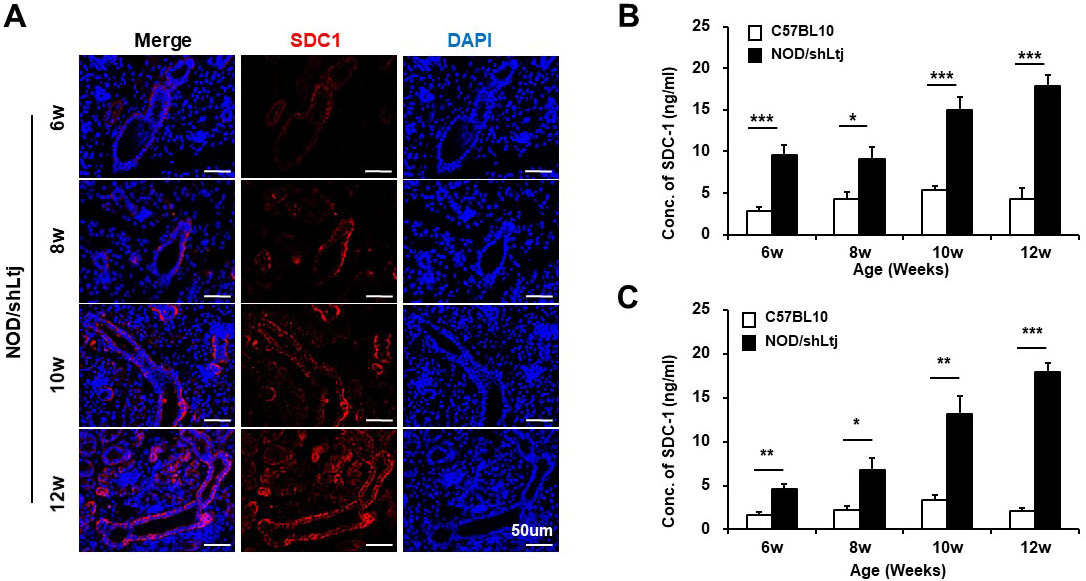
Background/Purpose: Primary Sjögren’s syndrome (pSS) is a prototypical autoimmune disorder with lymphocytic infiltration of exocrine and non-exocrine epithelia, where complex interactions between innate and adaptive immunity and glandular epithelial cells play a critical role in the pathogenesis of pSS. Infiltrating B cell within salivary gland ducts can trigger the development of lymphoepithelial lesions, and conversely, the salivary glandular epithelial cells (SGECs) can induce chemotaxis of B cells and provide chronic activation signals to glandular B cells. Syndecan-1 (SDC-1) is a transmembrane heparan sulfate proteoglycan predominantly expressed on epithelial cells and binds to and regulates heparan sulfate (HS)-binding molecules, such as chemokines. CXCL13 is a B-cell chemokine produced by immune cells, such as T follicular helper cells, and non-immune cells, SGECs. In this study, we sought to elucidate the role of SDC-1 in the pathogenesis of pSS by examining the expression of SDC-1 and B-cell chemokines in a mouse model of pSS, the association between SDC-1 and B-cell chemokines, and the effects of HS treatment on tissue inflammation.
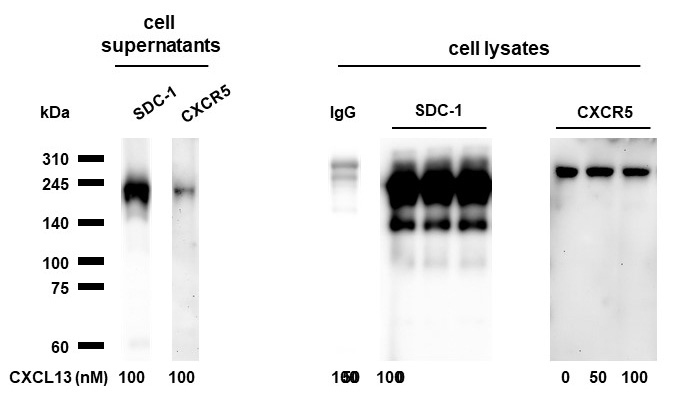
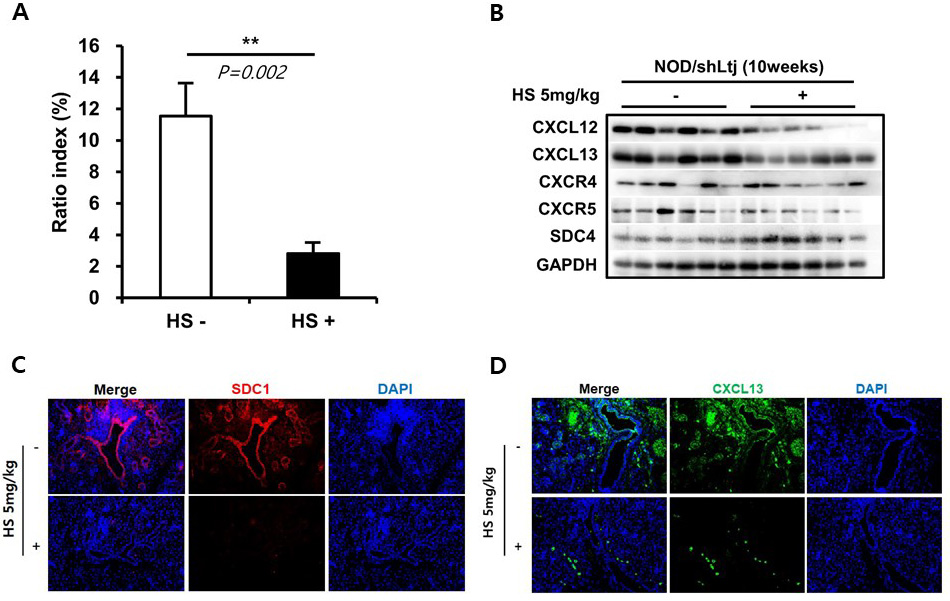
Methods: Female NOD/ShiLtJ mice between 6 and 12 weeks of age and sex-, and age-matched C57BL10 mice were used. The inflammation of the submandibular glands (SMGs) was assessed by the ratio index (RI, ratio of the area of inflammation to the total SMG area). SDC-1 levels in SMGs and blood were analyzed using dot blot method. The expression of B-cell chemokines was analyzed by western blotting. Immunoprecipitation assay was performed for SDC-1 and CXCL13 coassociation. Additionally, glandular inflammation and changes in the expression of SDC-1 and CXCL13 were examined following intraperitoneal administration of HS at 5 mg/kg three times per week in 6- to 10-week-old mice.
Results: Periductal inflammatory cell infiltration was detected in 0% of the 6-week-old, 60% of 8-week-old, and all of the 10-week-old and 12-week-old NOD/ShiLtJ mice. The mean RIs were 0.0, 0.7, 9.5, and 14.2 in the 6-, 8-, 10-, and 12-week-old NOD mice, respectively. The expression of SDC-1 in the SMGs and blood of mice were significantly increased in NOD/ShiLtJ mice, compared to controls. The concentration of SDC-1 in the SMGs and blood of NOD/ShiLtJ mice began to increase significantly from the age of 6 weeks (SMGs, 4.6 ± 0.6 vs. 1.6 ± 0.4, P=0.021; Blood, 9.6 ± 1.4 vs. 2.8 ± 0.6, P< 0.001). The concentration of SDC-1 of SMGs and blood began to be significantly higher from the age of 10 weeks (6-week-old vs. 10-week-old mice; SMGs, 4.6 ± 0.6 vs. 13.2 ± 2.0, P =0.034; Blood, 9.6 ± 1.4 vs. 15.0 ± 1.6, P =0.025). The expression of CXCL12, CXCL13, CXCR4, and CXCR5 was increased in SMGs of NOD/ShiLtJ mice. Colocalization of SDC-1 and CXCL13 was confirmed by immunofluorescent staining. Immunoprecipitation studies demonstrated that SDC-1 formed complexes with CXCL13. Mice treated with HS for 4 weeks showed significant improvement in the tissue inflammation (RI, P=0.002) and expression of SDC-1, CXCL13 and CXCR5, compared to controls.
Conclusion: These results suggest that SDC-1 plays an important role in the pathogenesis of pSS by inducing B-cell chemotaxis through CXCL13-HS interaction.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lee S, Lee N, Lee E, Jang J, Kim G, Nam E. Syndecan-1 Plays a Role in the Pathogenesis of Sjögren’s Syndrome by Inducing B-cell Chemotaxis Through CXCL13-heparan Sulfate Interaction [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/syndecan-1-plays-a-role-in-the-pathogenesis-of-sjogrens-syndrome-by-inducing-b-cell-chemotaxis-through-cxcl13-heparan-sulfate-interaction/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/syndecan-1-plays-a-role-in-the-pathogenesis-of-sjogrens-syndrome-by-inducing-b-cell-chemotaxis-through-cxcl13-heparan-sulfate-interaction/