Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: Osteoporosis & Metabolic Bone Disease – Basic & Clinical Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients have an increased risk of fractures due to factors such as chronic inflammation, use of glucocorticoids, and reduced muscle mass. While Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX) is commonly used to predict fracture risk in RA patients, it may not fully account for sarcopenia-related risks. The SARC-F questionnaire, a validated tool for screening sarcopenia has been found to predict fracture risk independently. This study aims to assess the potential benefits of integrating SARC-F score to improve fracture risk prediction in RA patients.
Methods: We enrolled patients > 40 years with validated RA (ACR-EULAR 2010 RA classification criteria) who attended our rheumatology clinic to perform a cross-sectional and descriptive study. We assessed sarcopenia risk using the SARC-F screening tool, which evaluates strength, assistance in walking, rising from a chair, climbing stairs, and falls. A score > 4 indicates high risk of sarcopenia. To identify sarcopenia based on muscle mass, we used dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA). According to the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People, 2nd Edition (EWGSOP2) criteria, sarcopenia was defined as having a muscle mass index of < 7.0 kg/m2 in men and <5.5 kg/m2 in women. Fracture risk was determined using the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX). We performed Kolmogorov-Smirnov, Chi-square, and Spearman tests and presented the data as percentages, frequencies, means and standard deviations (SD), medians, and interquartile ranges (IQR).
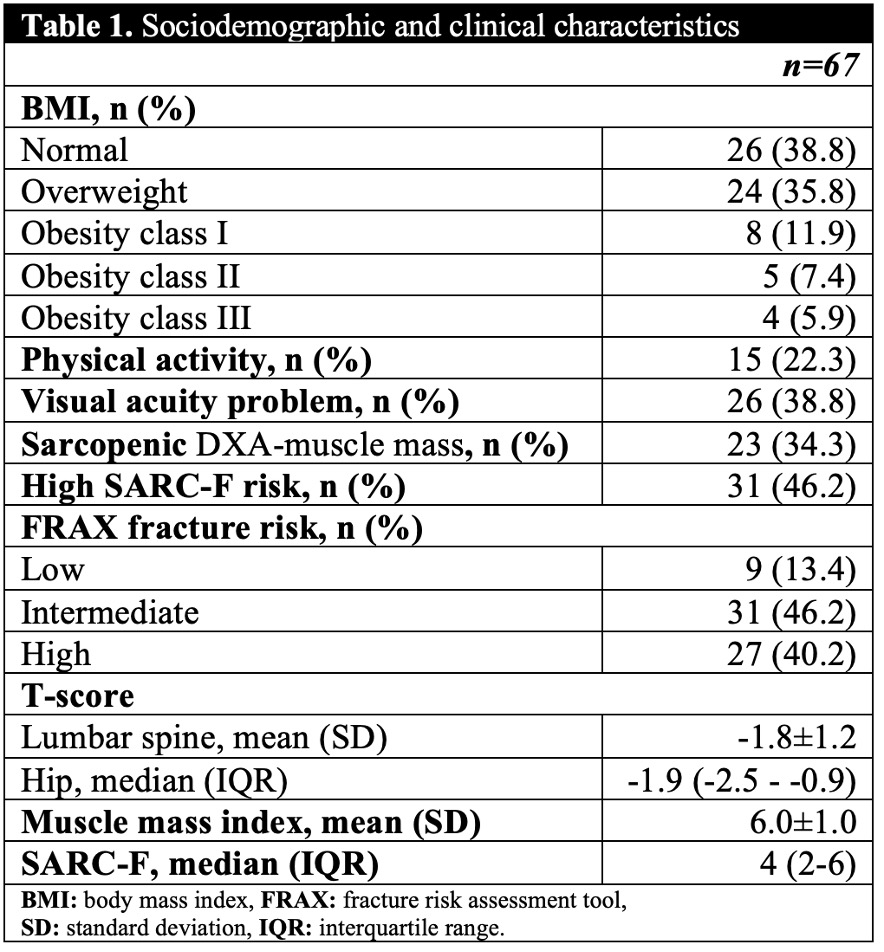
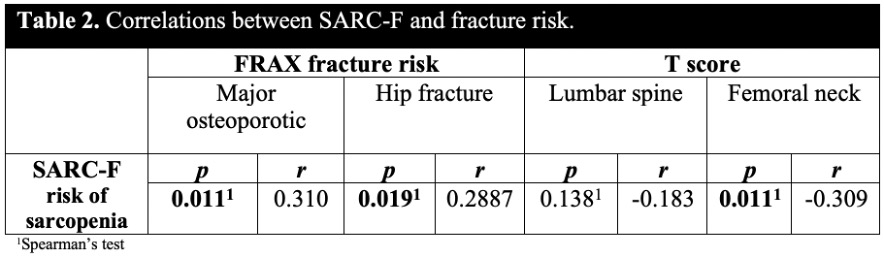
Results: 67 patients were included, comprising 63 (94.0%) women and 4 (5.9%) men, with a mean age of 63.52 ± 10.12 years. The patients’ sociodemographic and clinical characteristics are summarized in Table 1. The median SARC-F score was 4 (IQR: 2-6), and 31 (46.2%) of all patients had a score of >4 (high-risk of sarcopenia). A significant positive correlation was observed between SARC-F score and the risk of major osteoporotic fracture (MOF) (p = 0.019, r = 0.287) and hip fracture (HF) risk (p = 0.011, r = 0.310), as determined by FRAX scores. We also noted a significant negative correlation between SARC-F score and femoral neck T-score (p = 0.011, r = -0.309). Table 2. displays the correlation test results between SARC-F score, fracture risk, and T-scores. Among patients, 23 (34%) had sarcopenic DXA-muscle mass, with a mean muscle mass of 5.0 ± 0.3 kg/m². Compared to sarcopenic DXA-muscle mass index, SARC-F showed a sensibility of 70% and specificity of 90% to identify sarcopenia which is similar to what is described in literature. Table 3.
Conclusion: Higher SARC-F scores correlate with an increased risk of MOF and HF as determined by FRAX. A significant negative correlation exists between SARC-F score and femoral neck T-score, indicating that higher SARC-F scores are associated with lower bone mineral density. SARC-F may help identify patients at high risk of fractures, facilitating preventive interventions.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rodriguez-Flores A, Bardan-Inchaustegui A, Ponce M, Rodriguez G, Carrazco Chapa A, De Hoyos-Perez V, Cervantes Charles G, Damian Peñaloza A, Cortez Lopez C, SKINNER TAYLOR C, Negrete Lopez R, Cardenas-de la Garza J, Galarza-Delgado D. Strengthening Fracture Risk Prediction in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Integrating a Self-report Sarcopenia Screening Tool (SARC-F) and Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX) Scores [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/strengthening-fracture-risk-prediction-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-integrating-a-self-report-sarcopenia-screening-tool-sarc-f-and-fracture-risk-assessment-tool-frax-scores/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/strengthening-fracture-risk-prediction-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-integrating-a-self-report-sarcopenia-screening-tool-sarc-f-and-fracture-risk-assessment-tool-frax-scores/