Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2089–2094) Patient Education/Community Service – Interprofessional Poster
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Immunogobulin G4-Related Disease (IgG4-RD) is a rare chronic immune-mediated fibroinflammatory disorder that often manifests with tumor-like masses and/or enlargement of multiple organs. In order to guide future communications for people living with IgG4-RD, our objective was to examine the emotions expressed in social media discussions regarding IgG4-RD.
Methods: Data from YouTube and Reddit conversations from January 2017 to March 2023 were accessed using R packagestuber, for YouTube, and RedditExtractoR, for Reddit. The top viewed YouTube videos and their comments were searched using the terms “IgG4-RD” or “IgG4-Related Disease”. Resulting words from the video comments were used for sentiment analysis. Because IgG4-RD does not have its own subreddit,the subreddit r/Autoimmune was used for the Reddit analysis. We applied the same search terms to the top eight most commented subreddit threads for the analysis because these were the only IgG4-RD-related posts with comments. Data were separated into two groups: posts and comments on posts. Text was analyzed by classifying words within the Emotional Dynamic Classification System (EmoLex). Each word was assigned a positive or negative sentiment; each sentiment has four exclusive possible emotions associated with them. Depending on the sentiment, the word was assigned one to four negative or positive emotions. Only words with strong associations according to the EmoLex’s Association Score were included.
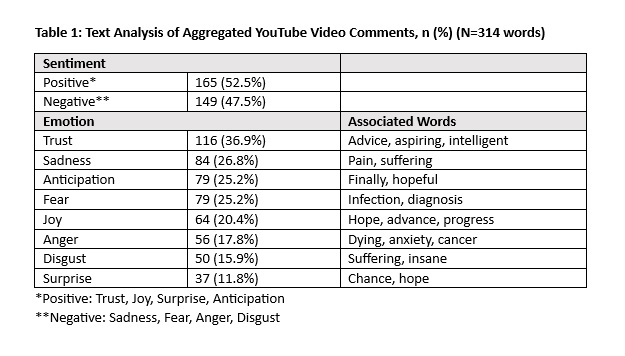
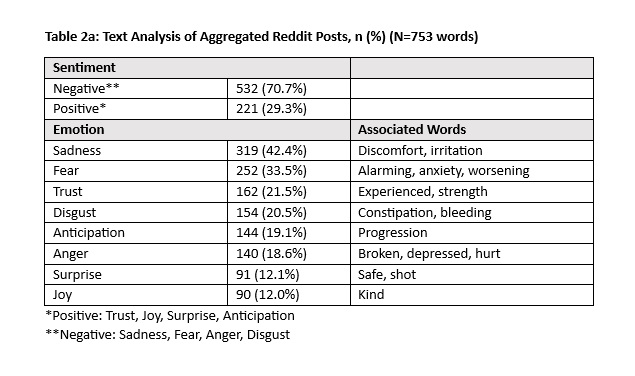
Results: Comments from seven YouTube videos, all created by or featuring physicians, were included in the analysis, with a total of 314 words analyzed. Fifty-three (165/314) words from comments had a positive sentiment (Table 1). Trust (37%) was the emotion most frequently associated with the text, followed by sadness (27%), anticipation (25%), fear (25%) and joy (20%). Advice and intelligence were words used evoking trust in the comments. Pain and hopeful evoked the emotions sadness and anticipation in the comments, respectively (Table 1). For Reddit, eight posts and their comments were included in the analysis. Posts had a total of 753 words and comments had 585 words. Posters to the subreddit were either recently diagnosed with IgG4-RD or seeking information on getting a diagnosis. Seventy-one percent (532/753) of words in these posts expressed negative sentiment (Table 2a). The top negative emotions for posts were sadness (42%), fear (34%), and disgust (21%) based on words like discomfort and anxiety (Table 2a). Trust was the only positive emotion associated with more than a fifth of the words (22%). Aggregated comment emotions were similar to those of YouTube comments, with trust as the most frequently associated emotion (42%), followed by anticipation (31%), sadness (28%), and fear (27%) (Table 2b).
Conclusion: Social media discussions of IgG4-RD provide insight into the patient experience. People living with IgG4-RD may benefit from patient-centered educational and supportive resources that focus on trust of health care providers and address negative emotions associated with the disease journey.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rivera E, Gavigan K, Hernandez D, Picone M, Cordova A, Dougherty L, Davidson K, LaMoreaux B, Amatucci A, Nowell W. Social Listening Analysis of IgG4-Related Disease Social Media Discussions [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/social-listening-analysis-of-igg4-related-disease-social-media-discussions/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/social-listening-analysis-of-igg4-related-disease-social-media-discussions/