Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0066–0095) T Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease Poster
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: CD4+ Foxp3– conventional T cells (Tconv) play a key role in the inflammatory process involved in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Recent studies, aided by a substantial advance in available technologies (RNA sequencing, multiparameter flow cytometry and mass cytometry), identified additional CD4+ T cell subpopulations that are expanded or dysregulated in RA. It notably included peripheral helper (TPH) T cells (PD-1hi CXCR5–) and cytotoxic HLA-DR+ CD27– CD4+ T cells (CD4+ CTLs). Regarding pro-inflammatory Tconv, a major remaining objective is to identify additional parameters that support their pathological functions, and then to focus on those that are therapeutically targetable. Among the receptors potentially capable of upregulating the Tconv response, SLAMFs (Signaling lymphocytic activation molecule) represent a family of nine receptors. In RA, our objectives were to determine whether SLAMF receptors are involved in the establishment of the Tconv pro-inflammatory response.
Methods: In RA, we used a multiparametric approach, including multiple flow cytometry panels, cells sorting, RNA sequencing, and various bioinformatics analysis to immuno-phenotyped Tconv from peripheral blood (PB) and synovial fluid (SF). SLAMFs expression was determine among four Tconv subpopulations with different activation status (naive, central memory, effector memory and terminally differentiated effector CD4+ T cells). To assess the inflammatory tropism of Tconv subpopulations, CCR5 expression was studied. The transcriptome of SLAMF4+ CCR5+ Tem was compared to that of their SLAMF4– counterpart using RNA sequencing. Unpaired and paired data were analyzed usinga parametric test or a non-parametric test according to data distribution. In analyses involving more than 2 comparisons, appropriate post-hoc comparisons were systematically used. Correlations between quantitative parameters were assessed using the Spearman test.
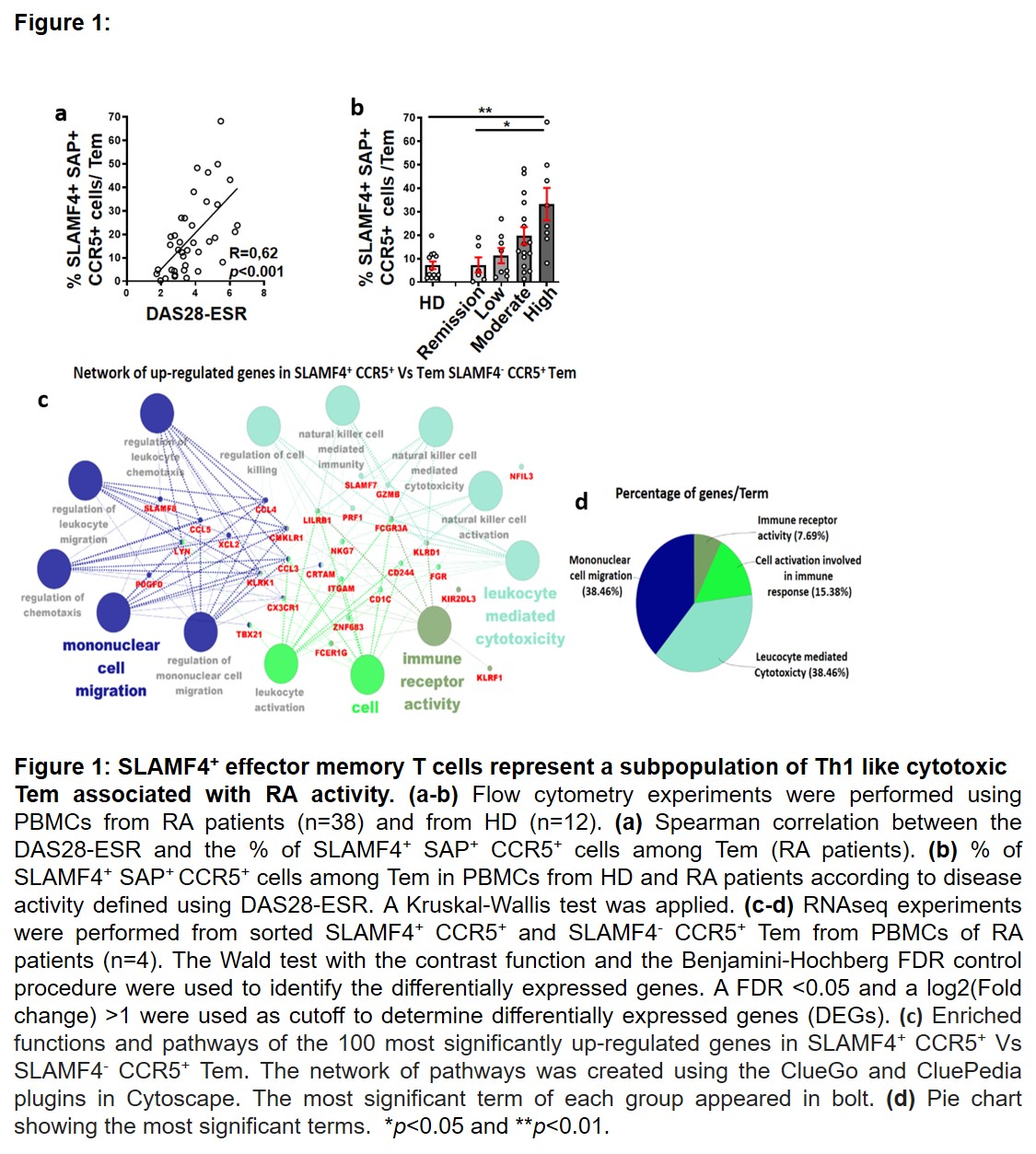
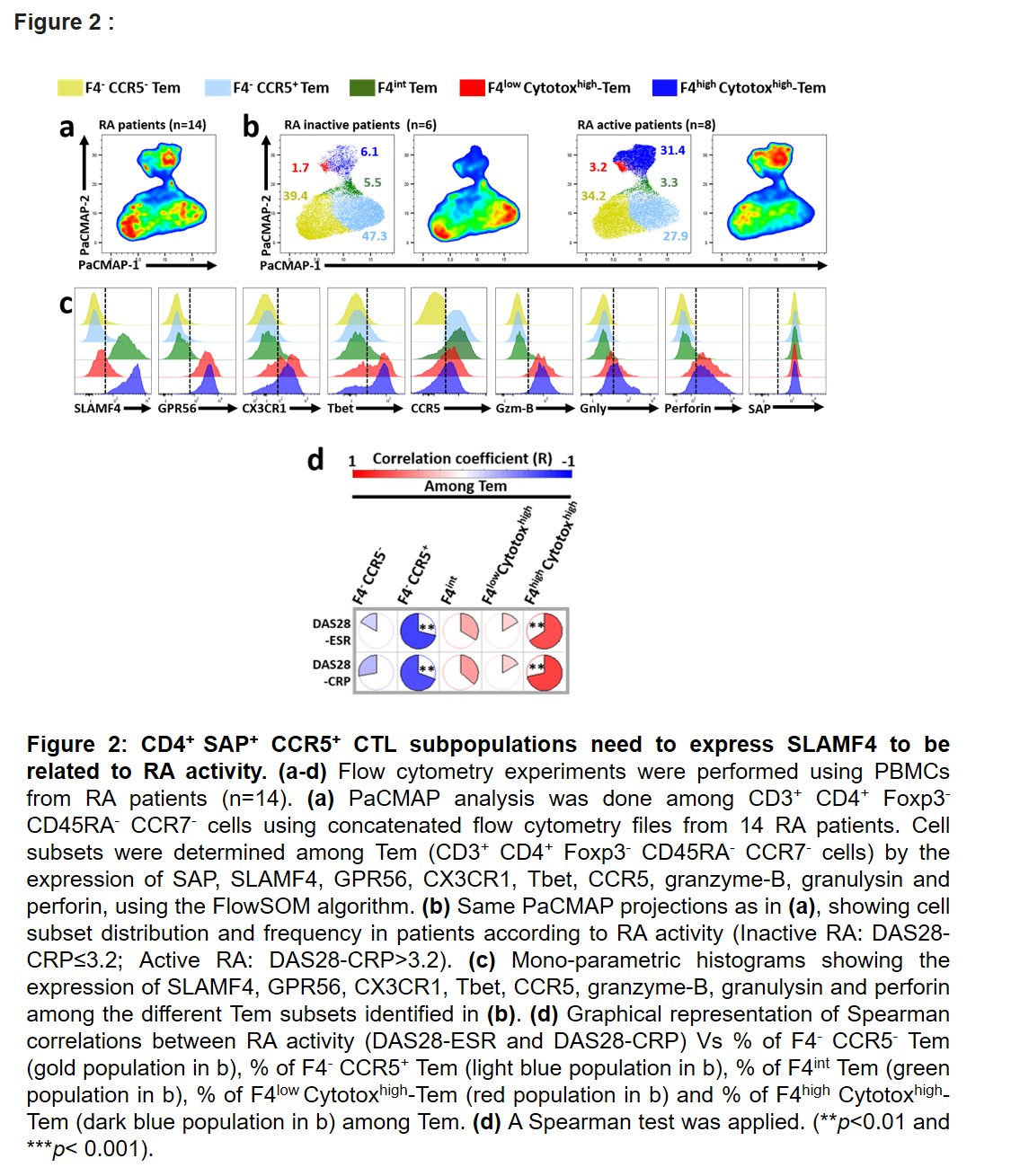
Results: In RA, the study of SLAMF expression among four Tconv subpopulations from peripheral blood (PB), showed that effector memory CD4+ T cells (Tem, Foxp3– CCR7– CD45RA–) overexpressed SLAMF4 in patients with active disease. This association was restricted to Tem co-expressing SAP and the chemokine receptor CCR5 (figure 1 a-b). Moreover, RNAseq experiments, followed by gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA),clearly identified that SLAMF4+ CCR5+ Tem from RA patients corresponded to a subpopulation of Th1-like CD4+ CTLs (figure 1 c-d). Based on the differential expression of cytotoxicity markers, multiparameter flow cytometry data identified distinct SAP+ CCR5+ cytotoxic Tem subpopulations. Remarkably, among them, only those highly expressing SLAMF4 were related to RA activity (figure 2). Finally, our data showed that in the synovial fluid (n=8), SLAMF4+ Tem represented the only CD4+ T cell subpopulation that maintained a significant expression of granzyme-B and perforin.
Conclusion: By providing a comprehensive immunoprofiling of the cytotoxic CD4+ T cell response in RA, our study identified SLAMF4high SAP+ CCR5+ CD4+ effector memory T cells as the main cytotoxic subpopulation involved in this disease.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lacaud M, Bouzidi H, breckler M, Lemeiter D, Semerano L, Boissier M, Bessis N, Biton J. SLAMF4 Orchestrates the Pathological Cytotoxic Response of CD4+ T Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/slamf4-orchestrates-the-pathological-cytotoxic-response-of-cd4-t-cells-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/slamf4-orchestrates-the-pathological-cytotoxic-response-of-cd4-t-cells-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/