Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Single-cell analysis has emerged as a powerful tool for investigating the transcriptomics and T-cell receptor (TCR) diversity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, there is limited information on the specificities, immunophenotype, and TCR diversity of antigen-specific T cells in RA using single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq). To address this knowledge gap, we conducted a pilot study to demonstrate the applicability of 10x single-cell sequencing for studying antigen-specific T cells.
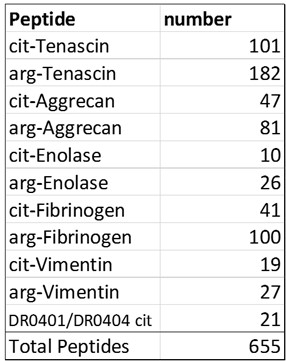
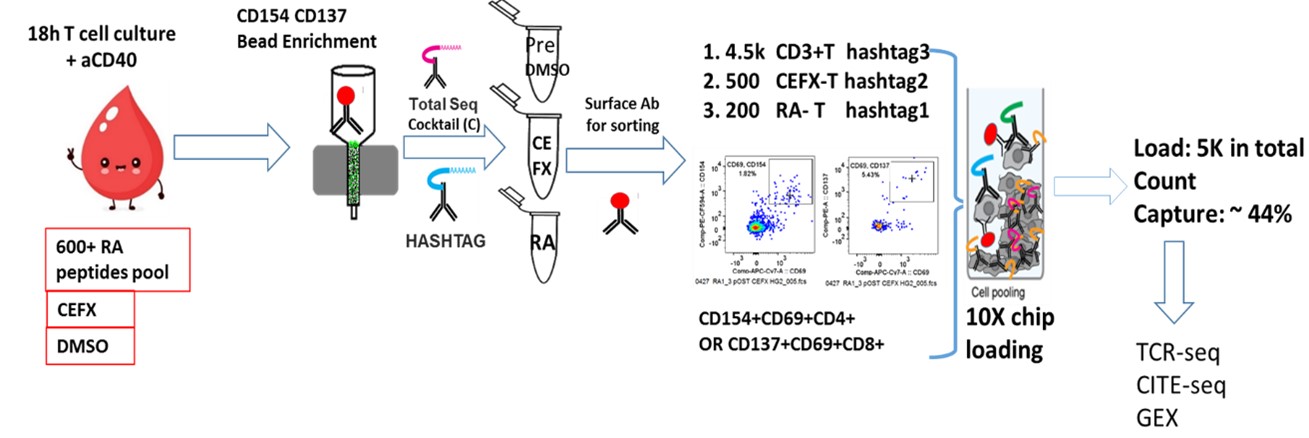
Methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were from patients with seropositive RA (n=3) and healthy control (HC) subjects (n=2). All individuals were HLA DRB1*0401 or 0404. Using an activation-induced marker (AIM) assay, PBMC were stimulated overnight with a pool of peptides derived from RA antigens (Table 1) or a peptide pool for viral antigens (CFEX). CD4+CD154+ and CD8+CD137+ cells were isolated to obtain paired scRNA-seq, cellular indexing of transcriptomes and epitopes by sequencing (CITE-seq), and TCR repertoire data. Specifically, we isolated RA antigen-specific T cells, CEFX antigen-specific T cells, and general CD3 T cells from the same subjects (Figure 1). The sorted cells were stained with the TotalSeq Human Universal Cocktail (BioLegend), hashtagged, and the captured single cells sequenced using the droplet-based 10x Chromium platform. Cell projection and graph-based clustering were performed using the Seurat package.
Results: A total of 11,053 cells, 6464 from RA and 4589 from HC subjects, were subjected to high-quality scRNA-seq analysis. Utilizing a graph-based clustering approach, we identified seven distinct clusters of cells, representing both RA and HC, which were visualized through integrated UMAPs< ![if !supportAnnotations] >[VG1]< ![endif] > combining multimodal data. Overlaying hashtags to the UMAP suggests that RA and CEFX T cells mostly mapped to cluster 4. Differential gene expression analysis and antibody expression of established lineage markers revealed that cells in cluster 4 express high levels of activation markers including CD71, CD28, CD38, HLA-DR and KLRG1, transcription factors including NR4A1, HLA-A, HLA-B and IFNG, and translation initiation factorEIF5A and EIF1. We applied a similar graph-based clustering method to RA and CEFX antigen-reactive T cells, leading to the identification of four major clusters: a cytotoxic CD8+ T cells (cluster 0), exhausted CD8+ T cells (cluster 1), activated CD4+ T cells (cluster 2), and IFN I signature CD4+ T cells (cluster 3). We observed high-quality TCR sequences in over 90% of the captured cells from each subject and significant private clonal expansions, with CD8 RA antigen-specific T cells displaying a higher degree of clonotypic expansion compared to CD4 populations. We also identified clonal sharing between RA antigen-specific T cells and the non-selected CD3 T cells in each subject.
Conclusion: Our findings highlight the power of multimodal single cell analysis to identify clonally expanded T cells in RA, characterize their phenotypic features at rest and upon activation, which may provide valuable insights into the antigen-specific T-cell responses and TCR dynamics associated with RA pathology.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
SONG J, Rims C, Dufort M, Linsley P, James E, Buckner J. Single-cell RNA Sequencing Analysis and Immune Profiling of Antigen-specific T Cells in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Healthy Controls [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/single-cell-rna-sequencing-analysis-and-immune-profiling-of-antigen-specific-t-cells-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-healthy-controls/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/single-cell-rna-sequencing-analysis-and-immune-profiling-of-antigen-specific-t-cells-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-healthy-controls/