Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0066–0095) T Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease Poster
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in systemic sclerosis (SSc). We aimed to identify features of circulating immune cells associated with SSc-ILD to develop biomarkers and to find treatment targets of SSc-ILD.
Methods: We employed single cell RNA-seq (scRNAseq) using cryopreserved peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from 20 SSc patients without ILD and 38 SSc patients with ILD and implemented covarying neighborhood analysis (CNA) to identify cell features associated with SSc-ILD. Detailed surface maker expression was also examined using mass cytometry (CyTOF) with a 39-marker panel using PBMC from 18 controls, 53 SSc patients with ILD and 29 SSc patients without ILD. Differentiation paths and inducing factors were explored through RNA velocity analysis and in-vitro culture.
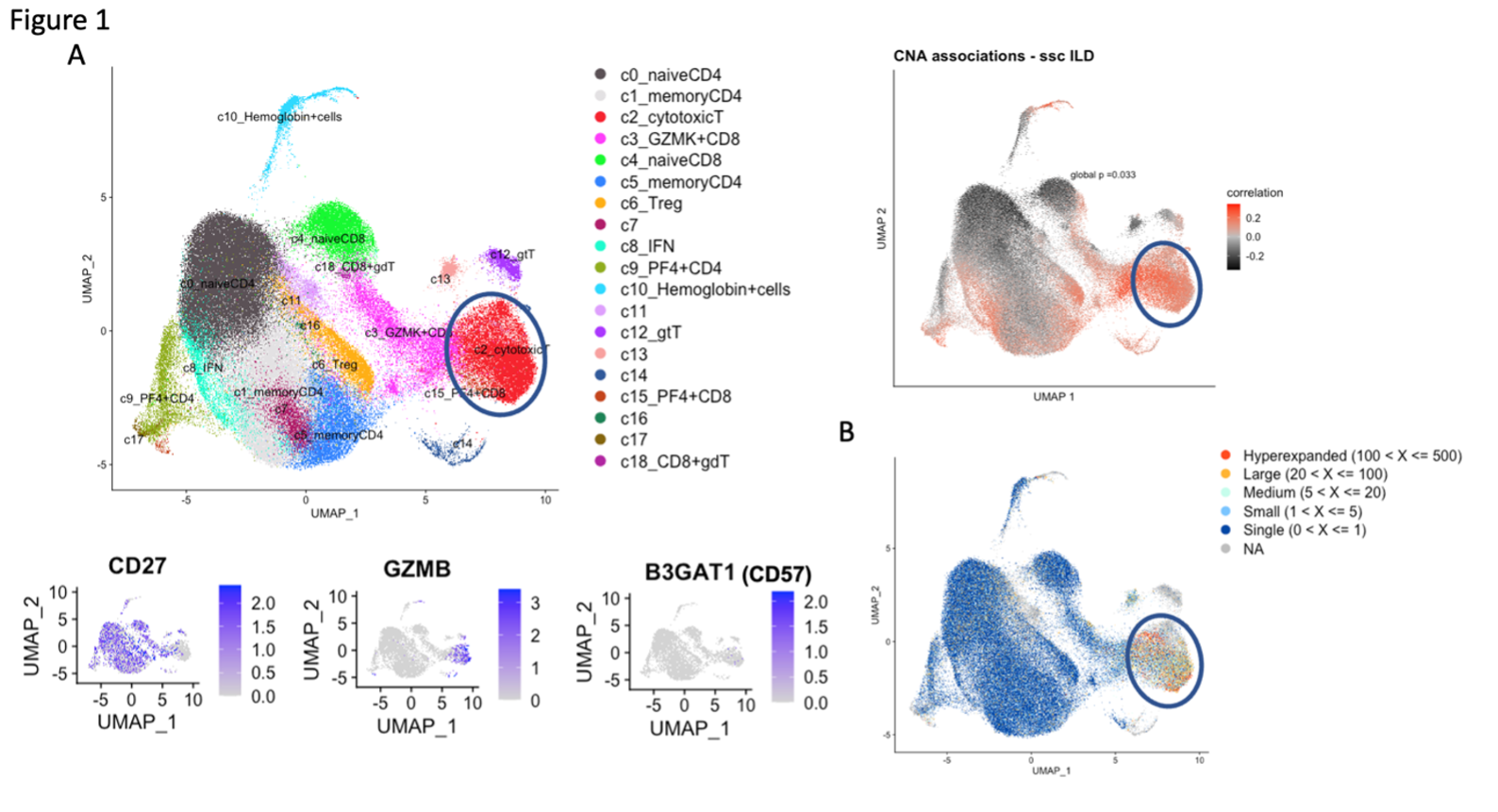
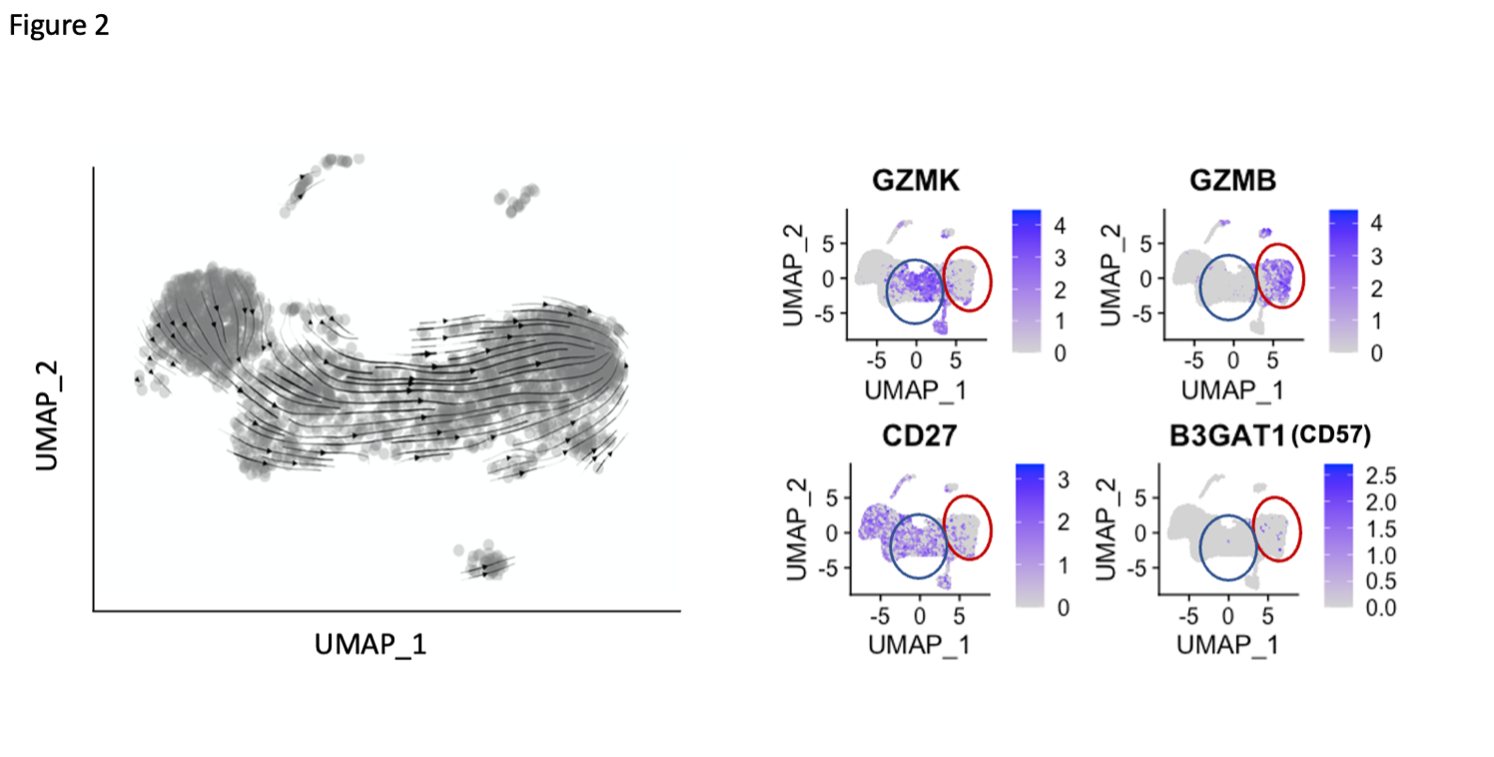
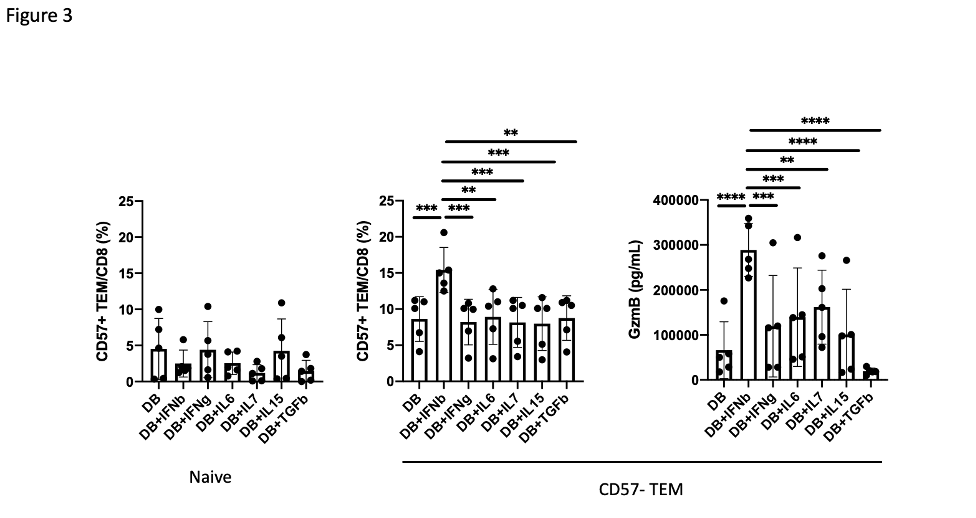
Results: A broad analysis of the scRNAseq dataset across mononuclear cells highlighted a significant enrichment in a specific CD8 T cell phenotype, captured as CD8 T cell cluster 2, in patients with ILD compared to those without ILD. This cluster expressed CD8A and GZMB but not CD27 or GZMK (Figure 1A). T cell receptor repertoire analysis indicated cluster 2 was clonally expanded, suggesting the antigen recognition of this CD8 T cell population in SSc-ILD (Figure 1B). In parallel, analysis of an overlapping set of PBMC samples by mass cytometry demonstrated that CD57+ CD27- CD56- CD45RO+ CCR7- effector memory CD8 T cells (CD57+ TEM) were significantly increased in the SSc-ILD cohort (Control: 0.74%, SSc without ILD: 1.42%, SSc with ILD: 2.71%), suggesting that a similar CD8 T cell population associated with SSc-ILD was captured by scRNAseq and mass cytometry. In contrast to CD57+ TEM cells, TEMRA were not statistically different between SSc patients with and without ILD. Independent flow cytometry analysis confirmed that CD57+ TEM highly expressed GZMB but not GZMK. On the contrary, CD57- CD27+ TEM (CD57- TEM) expressed GZMK but not GZMB, indicating there are two distinct populations in CD8 TEM. RNA velocity analysis of CD8 T cell clusters suggested that CD57+ TEM may differentiate from CD57- TEM (Figure 2). In-vitro culture experiments demonstrated that type I IFN facilitates differentiation from CD57- TEM to CD57+ TEM that highly produce GZMB (Figure 3).
Conclusion: ScRNAseq and mass cytometry analyses revealed that a cytotoxic effector memory CD8 T cell subset is expanded in SSc-ILD, and that a type I IFN signal may drive differentiation towards this phenotype.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cao Y, Sasaki T, Ainsworth R, Taylor K, Bottini N, Elahee M, Kim E, Boin F, Rao D. Single Cell RNA-seq and Mass Cytometry Reveal a Cytotoxic CD8 Effector T Cell Population Associated with Interstitial Lung Disease in Systemic Sclerosis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/single-cell-rna-seq-and-mass-cytometry-reveal-a-cytotoxic-cd8-effector-t-cell-population-associated-with-interstitial-lung-disease-in-systemic-sclerosis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/single-cell-rna-seq-and-mass-cytometry-reveal-a-cytotoxic-cd8-effector-t-cell-population-associated-with-interstitial-lung-disease-in-systemic-sclerosis-patients/