Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Wnt-1 inducible signaling pathway protein 2 (WISP-2/CCN5) is an adipokine that has been described as an important mediator of canonical Wnt activation in adipogenic precursor cells. In osteoarthritis (OA), the most common form of arthritis, chondrocytes exhibit aberrant and increased production of pro-inflammatory mediators and matrix-degrading enzymes such as IL-1β and MMP-13. Although recent evidence suggests a role for Wnt signaling in OA physiopathology, little is known about the involvement of WISP-2 in cartilage degradation. In this study, we investigate the role of WISP-2 in cartilage inflammation and catabolism modulation.
Methods: For loss of function experiments, we silenced WISP-2 with siRNA in human T/C-28a2 chondrocytes and OA human primary chondrocytes. We determined mRNA and protein expression levels of catabolic and pro-inflammatory markers by RT-qPCR and western blot. We also assessed the protein expression levels of relevant factors involved in WNT/b-catenin signaling pathway by western blot.
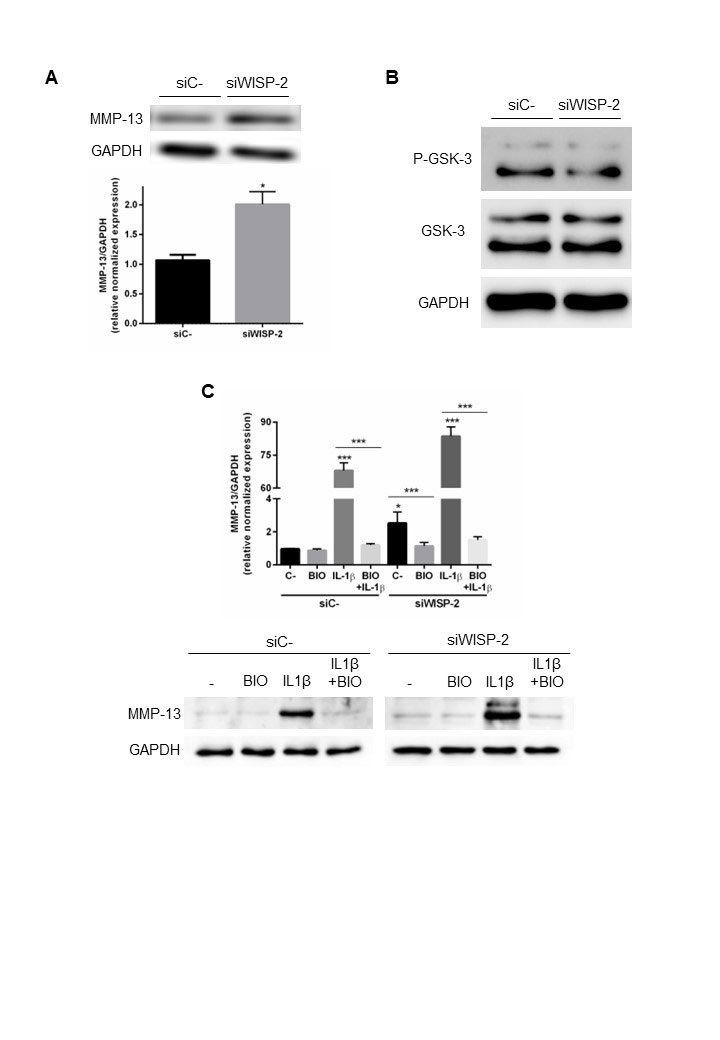
Results: We investigated the catabolic and pro-inflammatory effects of WISP-2 gene silencing on cartilage ECM breakdown mediators and several cytokines and chemokines. WISP-2 gene knockdown increased MMP-13, ADAMTS-5, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-1β expression levels in human T/C-28a2 chondrocytes or OA human primary chondrocytes. We also tested WISP-2 as an activator of canonical Wnt signaling. To investigate Wnt/β-catenin signaling activation we addressed GSK-3 phosphorylation in WISP-2-silenced T/C-28a2 chondrocytes. Upon WISP-2 silencing there is a significant decrease in GSK-3 phosphorylation, suggesting that the accumulation and translocation of β-catenin to the nucleus, and the expression of downstream target genes, are compromised.
Since IL-1β has been implicated in cartilage degradation, we determined the effect of WISP-2 silencing on IL-1β-stimulated T/C-28a2 or human primary OA chondrocytes. IL-1β induced mRNA expression of MMP-13, ADAMTS-5, IL-6, and IL-8, while WISP-2 knockdown further increased IL-1β-induced expression of those genes.
To investigate the involvement of Wnt/β-catenin signaling, we transfected T/C-28a2 cells or human primary OA chondrocytes with siWISP-2 and treated them with IL-1β in the presence or not of selective GSK-3 inhibitor BIO. Activation of canonical Wnt signaling by BIO significantly decreased the expression of MMP-13, as well as ADAMTS-5, IL-6, and IL-8. Moreover, BIO treatment blocked the IL-1β-induced expression of the catabolic markers. Blocking GSK-3 with BIO almost completely suppressed the IL-1β-mediated upregulation of MMP-13, ADAMTS-5, IL-6, and IL-8 in siWISP-2-transfected cells.
Conclusion: In conclusion, here we have shown for the first time that WISP-2 may have relevant roles in modulating the turnover of extracellular matrix in the cartilage and that its downregulation may detrimentally alter the inflammatory environment in OA cartilage. We also proved the participation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in these processes. Thus, targeting WISP-2 might represent a potential therapeutical approach for degenerative and/or inflammatory diseases of the musculoskeletal system, such as osteoarthritis.
A. Human T/C_28a2 chondrocytes were transfected with negative control (siC-, 10 nM) or siRNA against WISP_2 (siWISP_2, 10 nM) for 48 hours. Determination of human MMP_13 protein expression by western blot in human OA chondrocytes. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Densitometric analysis was also shown. B. Determination of phosphorylated GSK_3 protein expression by western blot in human OA chondrocytes transfected with negative control (siC-, 10 nM) or siRNA against WISP_2 (siWISP_2, 10 nM) for 48 h. GAPDH was used as a loading control. C. Chondrocytes were transfected with negative control (siC-, 10 nM) or siRNA against WISP_2 (siWISP_2, 10 nM) in the presence or not of IL_1β (0.5 ng/mL) for 24 h in combination with 1 μM BIO. Determination of human MMP_13 protein expression by western blot in human primary OA chondrocytes. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Densitometric analysis was also shown.
Values are the mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01,***p < 0.001 vs. siC-)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ruiz-Fernández C, González-Rodríguez M, Francisco V, Ait Eldjoudi D, Cordero-Barreal A, Farrag Y, Pino J, González-Gay M, Mera A, Lago F, Gualillo O. Silencing of WISP-2 Induces Inflammatory Mediators and Catabolic Factors in Cartilage [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/silencing-of-wisp-2-induces-inflammatory-mediators-and-catabolic-factors-in-cartilage/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/silencing-of-wisp-2-induces-inflammatory-mediators-and-catabolic-factors-in-cartilage/