Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: MicroRNA (miRNA), a short endogenous noncoding RNA, has a major role in the degradation and translational repression of a specific gene through its binding to 3′ UTR of such target mRNA. While biological contribution of miRNA has been reported, its impact on the genetics of human complex traits, especially in the context of miRNA-target gene networks, has not been assessed.
Methods: We developed a novel analytical method that comprehensively evaluates enrichment of genome-wide association study (GWAS) signals in miRNA-target gene networks. We obtained GWAS results of the 19 human complex traits, that comprises in total >1.75 million subjects. The association signals of the SNPs (i.e. p-values) were converted into the gene-based or miRNA-based association signals, adjusted by local linkage disequilibrium structures and gene/miRNA sizes. Relative enrichment of the association signals between miRNAs and target genes predicted by the multiple public databases (miRDB, miRmap, PITA, and TargetScan) was evaluated through permutation test (x10,000 iterations).
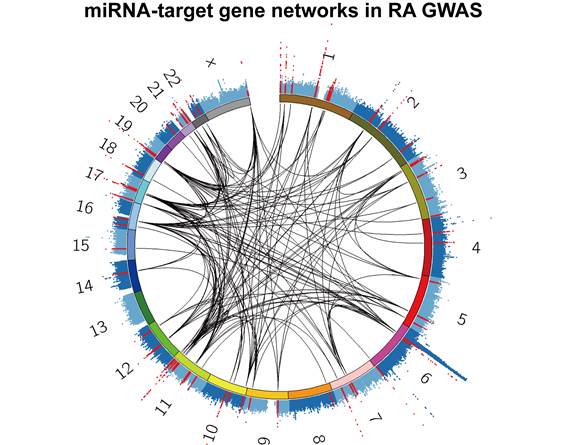
Results: Of the 19 evaluated human complex traits, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and adult height showed significant enrichment of the association signals in miRNA-target gene networks (P < 0.05/19 = 0.0026; Figure 1). RA demonstrated the most significant results with 1.77-fold relative enrichment compared to the null hypothesis (P = 1.7x10-4�GFigures 1 and 2). Our method also provides a list of miRNA and target gene pairs with excess genetic association signals, part of which included drug target genes.
Conclusion: Our method clearly indicated significant impacts of miRNA-target gene networks on the genetics of human complex traits, especially implying their important roles in biology and drug discovery of RA.
Figure 1 GWAS signal enrichment in miRNA-target gene networks.
Figure 2 miRNA-target gene networks in RA GWAS
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Okada Y, Tanaka T. Significant Impact of Microrna-Target Gene Networks on the Genetics of Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/significant-impact-of-microrna-target-gene-networks-on-the-genetics-of-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/significant-impact-of-microrna-target-gene-networks-on-the-genetics-of-rheumatoid-arthritis/