Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: There is limited information about sex-related differences in efficacy of biologics in axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA). We hypothesized that females with axSpA are less likely to respond to biologics compared to men with axSpA. We aimed to compare the efficacy of biologics among men and women with axSpA both from clinical trials and real-world studies
Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted using electronic databases, including PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library, and screening the EU clinical trial registry to identify relevant studies published until November 2023. Clinical trials and real world studies reporting BASDAI50, ASDAS, ASAS-40 disease indices were included. The studies included patients with both radiographic and non-radiographic axSpA treated with different biologic therapies (TNF-i, and IL-17-i) for 6 months to 1 year. The risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane risk of bias tool. Two independent reviewers screened the articles, and the senior author did conflict resolution. Data were extracted and analyzed using R Statistical Software meta package (v4.2.1; R Core Team 2022) to calculate odds ratios for male vs female treatment responses (95% CI).
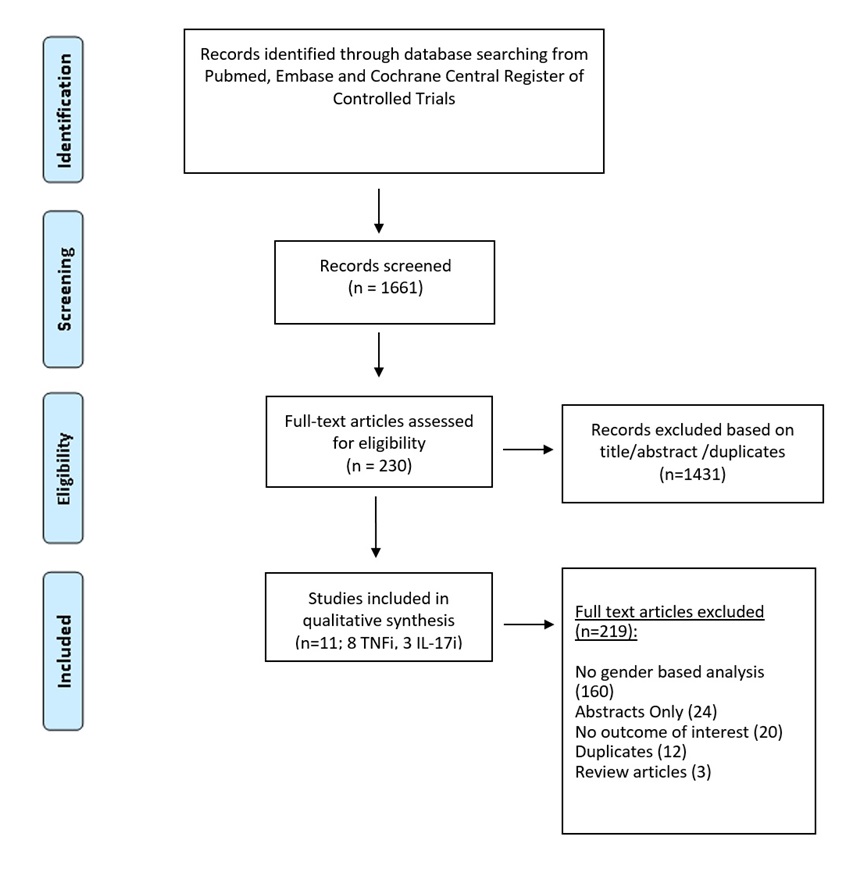
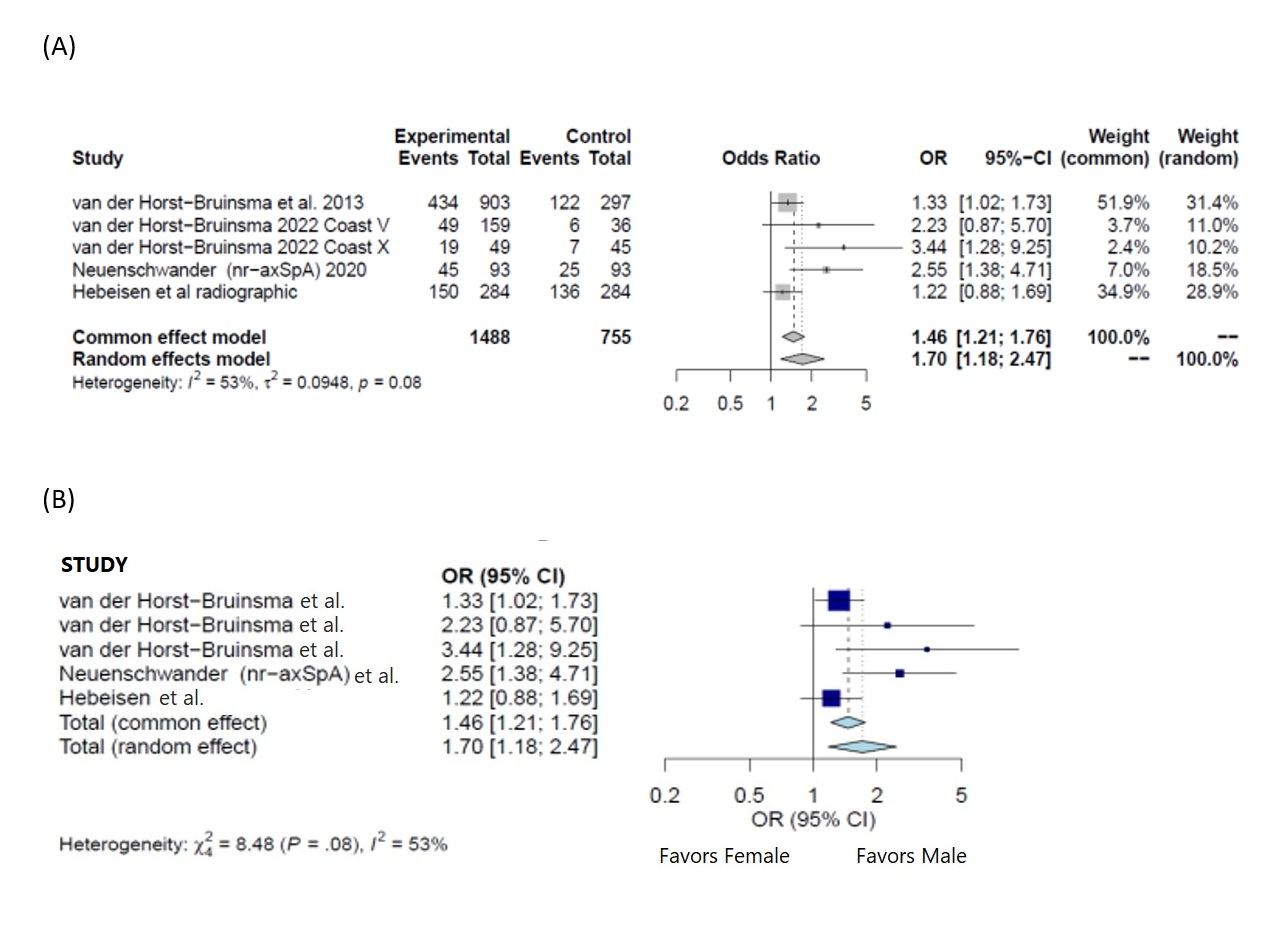
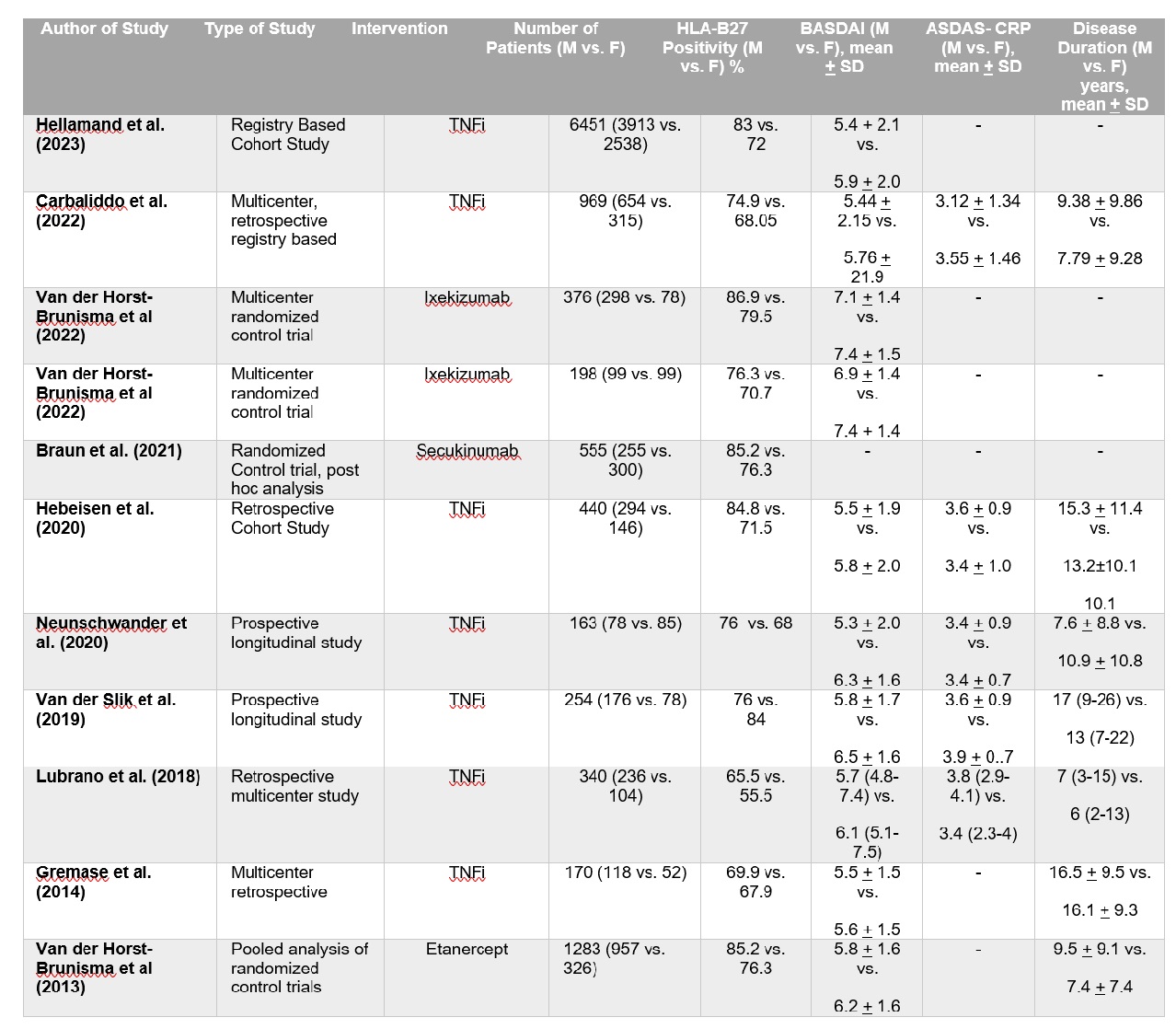
Results: We screened 1665 articles and included 11 studies, 8 of TNFi and 3 of IL-17i as shown in PRISMA flow diagram (Figure 1.0). Total number of patients with axSpA were 11,199, of which 4121 (36.8%) were females. The baseline gender based characteristics of the studies are shown in Table 1. HLA-B*27 positivity was more common in males, pooled OR 1.58 (95% CI:1.45-1.72). BASDAI 50 response, pooled OR 1.91 ( 95% C1: 1.45: 2.49) and ASDAS low disease activity response, pooled OR of 1.70 ( 95% C1: 1.18-2.47) showed significantly higher odds for male response to the therapy in both common effect and random effect model as shown in the figure 2 (a) and (b), five studies each. There was no gender based difference in ASAS40 responses in seven studies with, OR 1.00 (95% CI: 0.59-1.71). The data for ASDAS-ID, ASAS20 responses were not analyzed owing to heterogeneity in the reported outcomes.
Conclusion: Male patients with axSpA treated with biologics achieved higher BASDAI50 response and were more likely to achieve ASDAS low disease activity compared to females with axSpA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chaudhary H, Pamuk O, Abi Doumeth S, Daoud A, Shamim M, Magrey M. Sex- related Differences in Efficacy of Biologics in Axial Spondyloarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sex-related-differences-in-efficacy-of-biologics-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sex-related-differences-in-efficacy-of-biologics-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/