Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Basic Science Poster
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
The measurement of disease activity is mainly dependent on the patient-reported outcome measures in ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patients. Current inflammatory biomarkers have insufficient sensitivity and specificity to assess the disease activity and treatment response, especially after treatment with anti-TNF-α agents. Interleukin(IL)-37 is an anti-inflammatory cytokine, induced by TNF-α, and inhibits the proliferation of Th-17 cells. In AS patients, serum IL-37 level was higher in controls, and associated with CRP level and ESR. We aimed to estimate whether serum IL-37 levels reflect disease activity, and change according to the anti-TNF agent in active AS patients.
Methods:
Patients were recruited from the PLANETAS study (NCT01220518). Active AS patients with BASDAI ≥4 and visual analogue scale score for spinal pain were ≥4 were treated with infliximab originator or infliximab biosimilar, CT-P13. The serum levels of IL-37 were measured at week 0 and week 30 with specific ELISA. Other demographic, laboratory and clinical variables were evaluated simultaneously. Responders was defined as those satisfying Assessment in SpondyloArthritis International Society (ASAS 20/40) response.
Results:
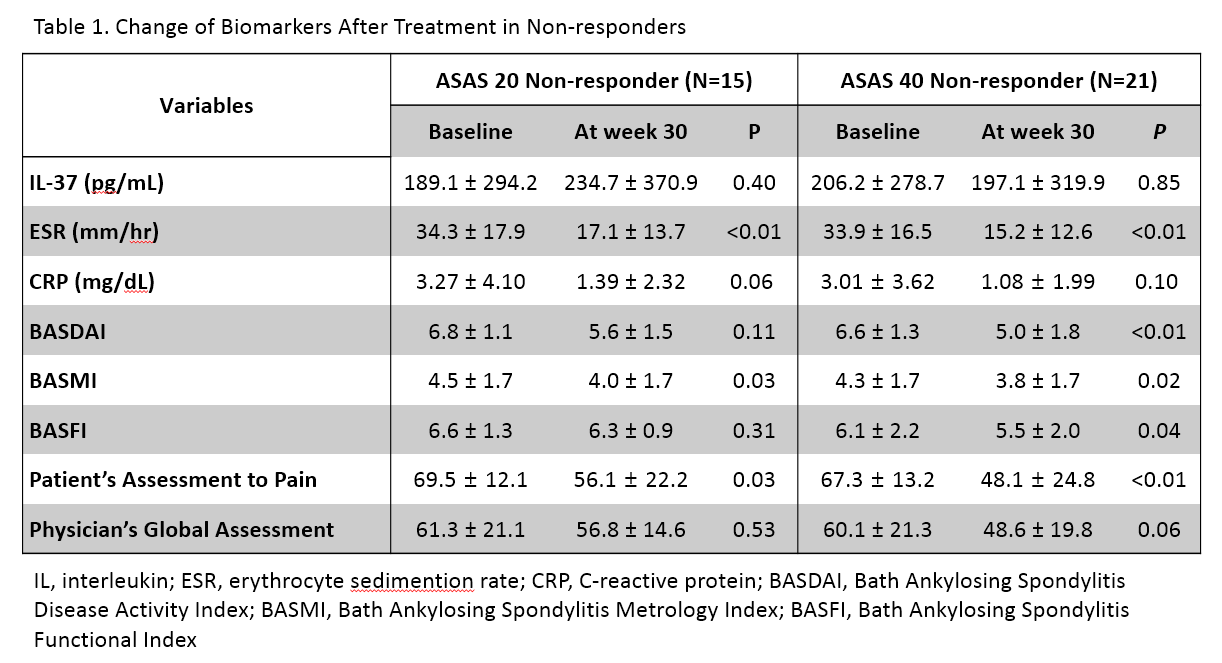
Among 250 patients, 50 patients (43 males) agreed to provide their serum samples for further study. The median age of patients was 40 years old (Interquartile range [IQR], 33.8-49.5), and the median BASDAI score was 6.7 (IQR 5.3-7.9). A significant correlation between IL-37 and CRP levels (Spearman’s rho [r]=0.39, p<0.01) and BASDAI (r= 0.31, p=0.04) was observed at the baseline, but not at week 30. When calculating the overall differences (Δ) of parameters between baseline and week 30, ΔIL-37 was correlated with ΔCRP (r=0.36, p=0.02), ΔBASFI (r= 0.34, p=0.02) and ΔBASDAI (r = 0.32, p=0.03). In ASAS 20/40 responders, all the disease activity markers were significantly improved after 30 weeks of treatment. Notably, most clinical parameters except IL-37 level were decreased in both responders and non-responders. However, there was no change of serum IL-37 level in non-responders. The ROC curves for response revealed that the area under curve (AUC) value for ΔIL-37 (AUC=0.74) was similar to that for ΔESR (AUC=0.71, p=0.64) and superior than that for ΔCRP (AUC=0.54, p<0.01).
Conclusion:
Serum IL-37 levels correlated with disease activity in active AS patients. Changes in serum IL-37 levels after treatment depends on the clinical response to anti-TNF agents. Further study is required to see if earlier change of IL-37 levels after infliximab infusion can identify patients who are likely to respond to infliximab treatment.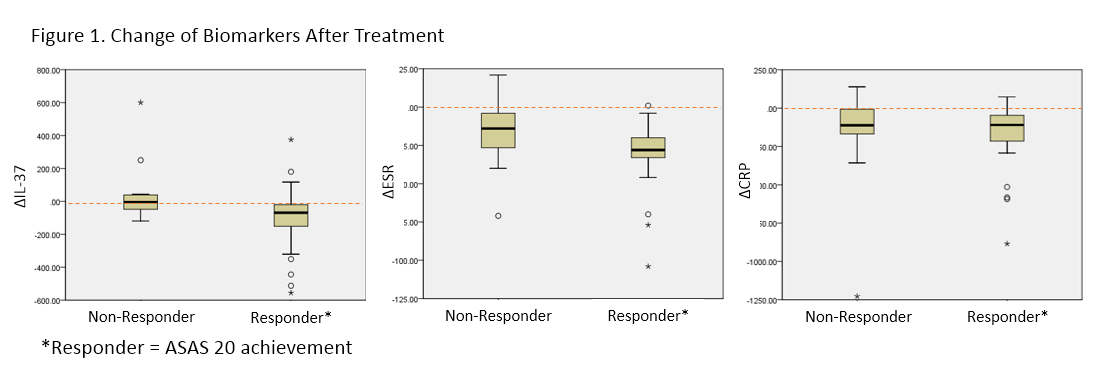
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ahn GY, Kang SM, Kang J, Nam B, Kwon HH, Kim TH, Yoo DH. Serum IL-37 Is an Efficient Biomarker of Disease Activity and Treatment Response in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-il-37-is-an-efficient-biomarker-of-disease-activity-and-treatment-response-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-il-37-is-an-efficient-biomarker-of-disease-activity-and-treatment-response-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis/
