Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Excessive cholesterol accumulation in macrophages underlies foam cell formation, initiation and progression of atherosclerosis. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) oxidation and unregulated uptake by macrophages are critical in foam cell development. Cholesterol loading capacity (CLC) is the ability of serum to deliver cholesterol to cells and is related to foam cell formation. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) serum increased cholesterol content in macrophages and promoted foam cell formation significantly more than control serum. We here explore factors in the serum of patients with RA and mechanisms through which they interact and influence CLC on macrophages.
Methods: In a cross-sectional observational cohort of 104 patients with RA, CLC was measured as intracellular cholesterol content in human THP-1-derived macrophages after incubation with patient serum. LDL oxidation was measured as oxidized phospholipids on apoB100-containing particles (oxPL-apoB100). Antibodies against oxidized LDL (anti-oxLDL), proprotein convertase subtilisin/Kexin type-9 (PCSK9) and high-sensitivity CRP were also quantified. All analyses adjusted for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk score, obesity, total LDL, statin use, age at diagnosis, and anti-oxLDL IgM.
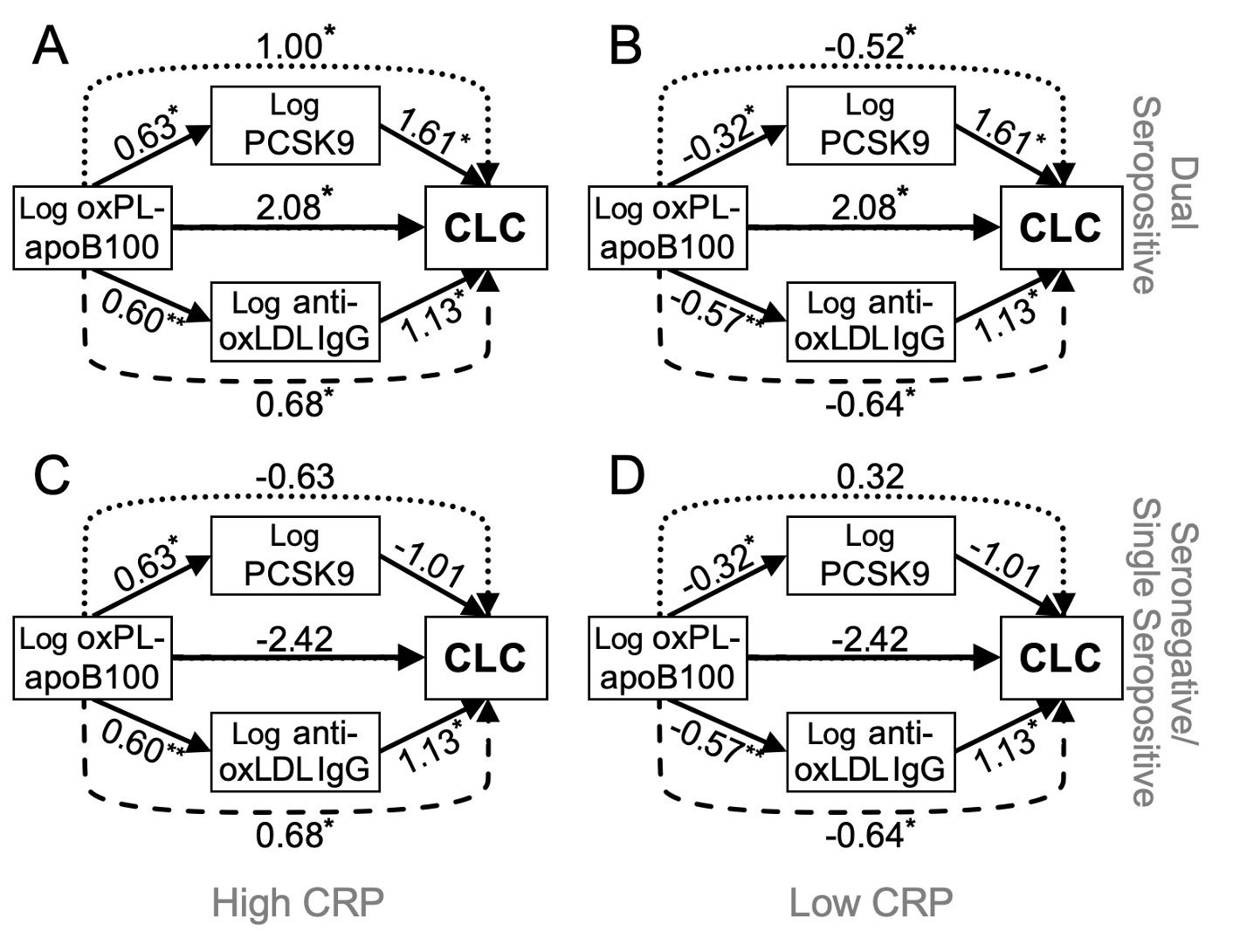
Results: OxPL-apoB100, anti-oxLDL IgG and PCSK9 positively associated with CLC (all p< 0.020). OxPL-apoB100 directly influenced CLC only in dual rheumatoid factor and anti-citrullinated protein antibody positive patients (unstandardized b [95% bootstrap confidence interval]=2.08 [0.38-3.79]) and independently of CRP (Figure 1). An indirect effect of oxPL-apoB100 on CLC through anti-oxLDL IgG increased along with level of CRP (index of moderated mediation=0.55 [0.05-1.17]). CRP also moderated yet another indirect effect of oxPL-apoB100 on CLC through upregulation of PCSK9, but only among dual seropositive patients (conditional indirect effect=0.64 [0.13-1.30]).
Conclusion: Oxidized LDL can directly influence CLC in dual seropositive RA patients, regardless of CRP. This suggests that targeting LDL oxidation in addition to inflammation may enable a more comprehensive reduction of atherosclerotic risk in these patients. Two additional and independent pathways—via anti-oxLDL IgG and PCSK9—may further mediate the effects of oxPL-apoB100 on CLC depending on CRP level and seropositivity status. If externally validated, these findings may have clinical implications for cardiovascular risk prevention.
oxPL-apoB100: oxidized phospholipids on apolipoprotein B100 particles, anti-oxLDL: antibodies against malondialdehyde LDL, PCSK9: proconvertase subtilisin/kexin type-9, CLC: cholesterol loading capacity, CRP: C-reactive protein, Seronegative: rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA) negative, Single seropositive: RF or ACPA positive, Dual seropositive: both RF and ACPA positive, SD: standard deviation.*p<0.05, **p<0.01.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Karpouzas G, Papotti B, Ormseth S, Palumbo M, Hernandez e, Adorni M, Zimetti F, Budoff M, Ronda N. Serum Cholesterol Loading Capacity on Macrophages Is Dependent on Oxidized Low-density Lipoprotein and Regulated by Seropositivity and C-reactive Protein in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-cholesterol-loading-capacity-on-macrophages-is-dependent-on-oxidized-low-density-lipoprotein-and-regulated-by-seropositivity-and-c-reactive-protein-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-cholesterol-loading-capacity-on-macrophages-is-dependent-on-oxidized-low-density-lipoprotein-and-regulated-by-seropositivity-and-c-reactive-protein-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/