Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Abstracts: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes I: Breathe: RA-ILD
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: Predictors of progressive pulmonary fibrosis (PPF) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease (ILD) are unclear but may be due to inflammation or fibrosis. Therefore, we investigated serologic and clinical predictors of PPF in RA-ILD.
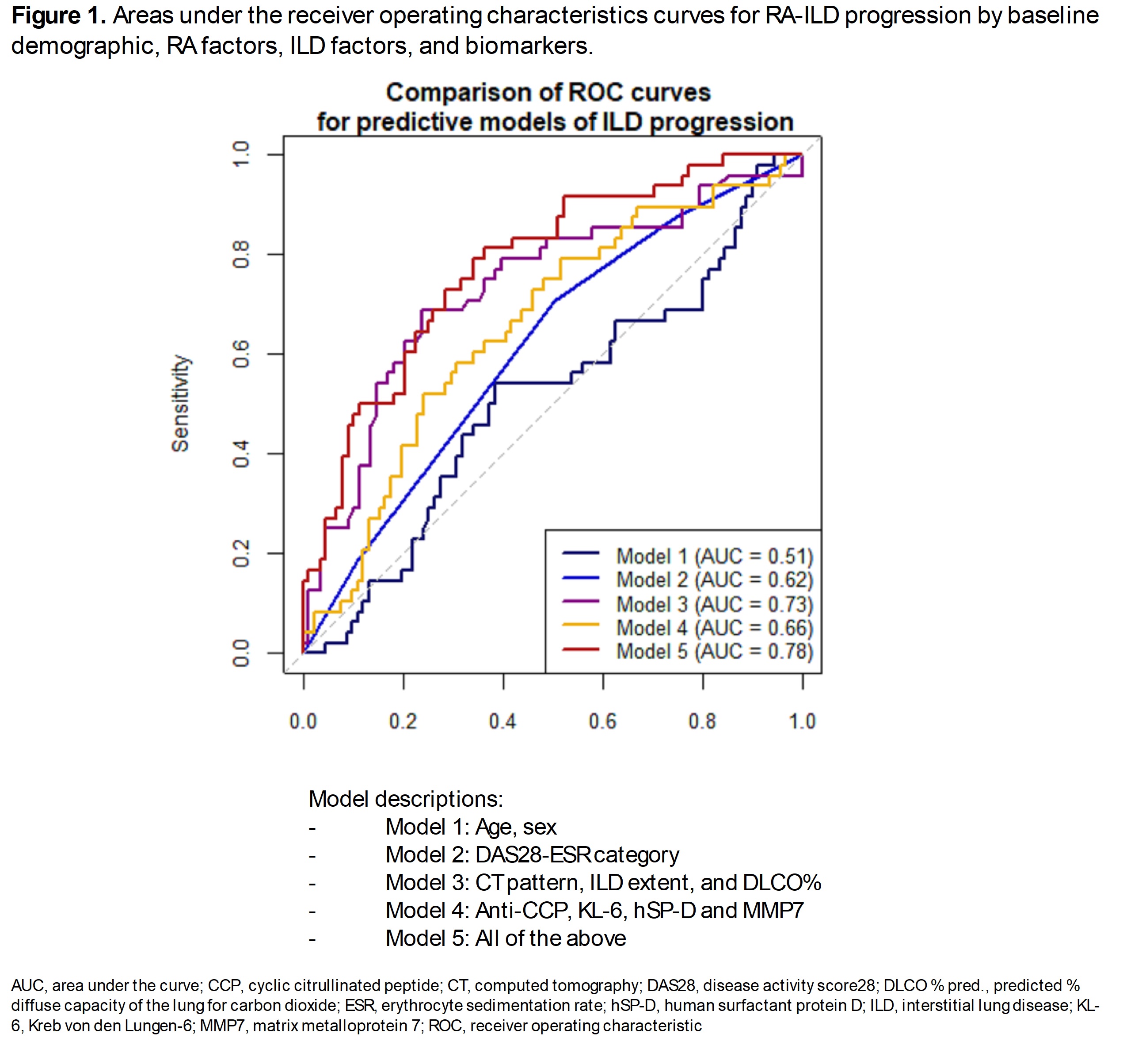
Methods: We investigated predictors of RA-ILD progression in the Korean RA-ILD (KORAIL) cohort, a prospective, longitudinal observational study that enrolled RA patients based on the 1987 ACR or 2010 ACR/EULAR criteria and ILD on chest computed tomography (CT) scans from January 2015 to July 2018 and followed them for 3 years. Pulmonary function tests (PFTs) and chest CT scans were conducted annually, and the extent of ILD on the chest CT was independently scored by two radiologists. ILD progression was defined as the presence of both physiological and radiological evidence of disease progression, adapted from the 2023 ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT definition of PPF. Baseline biomarkers included autoantibodies, inflammatory markers, and pulmonary damage markers. Cox regression was used to estimate hazard ratios for progression, adjusting for age and sex. Then, we compared performance of prediction models with significant predictors from each domain (model 1 to 5, as indicated in Figure 1) using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves.
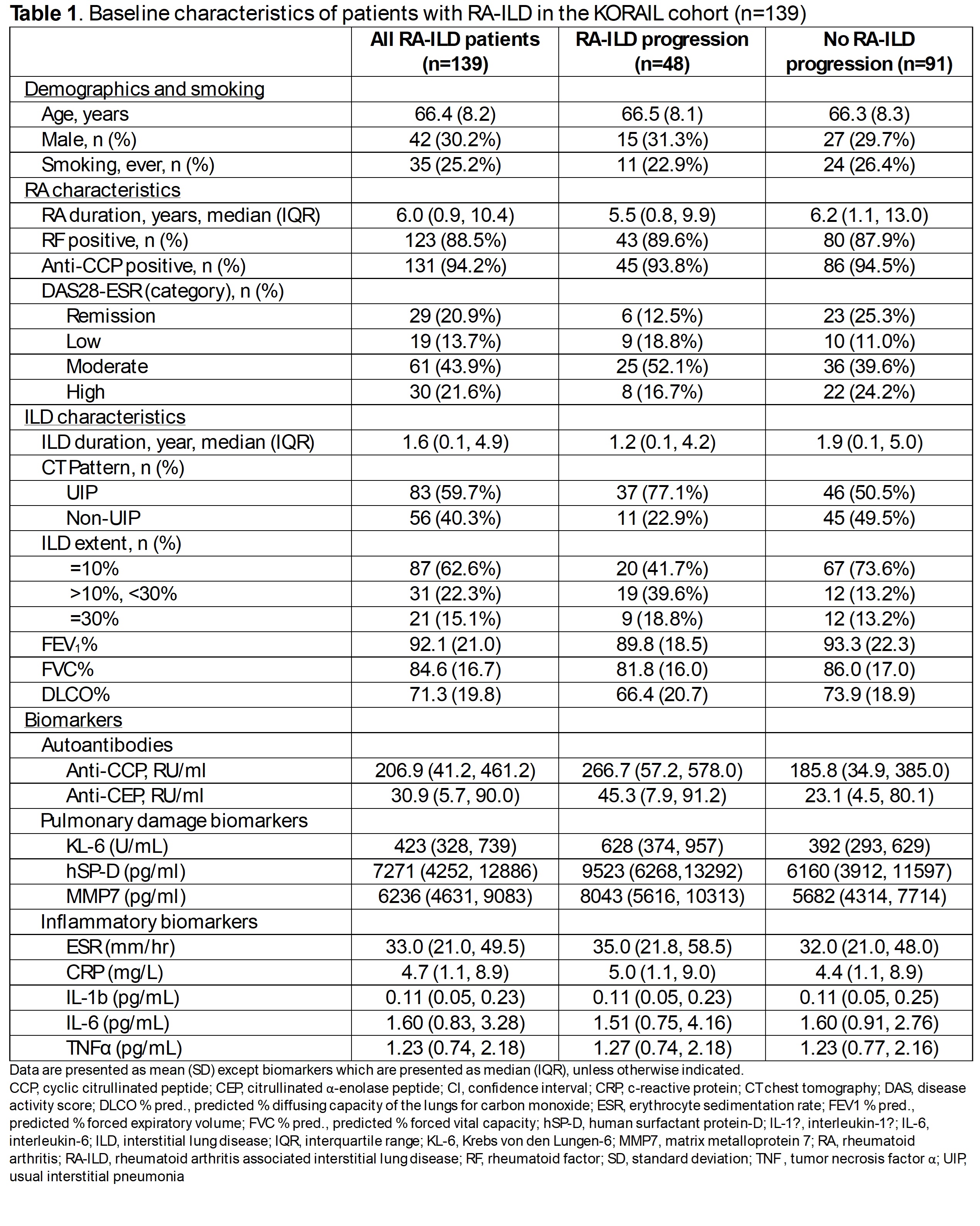
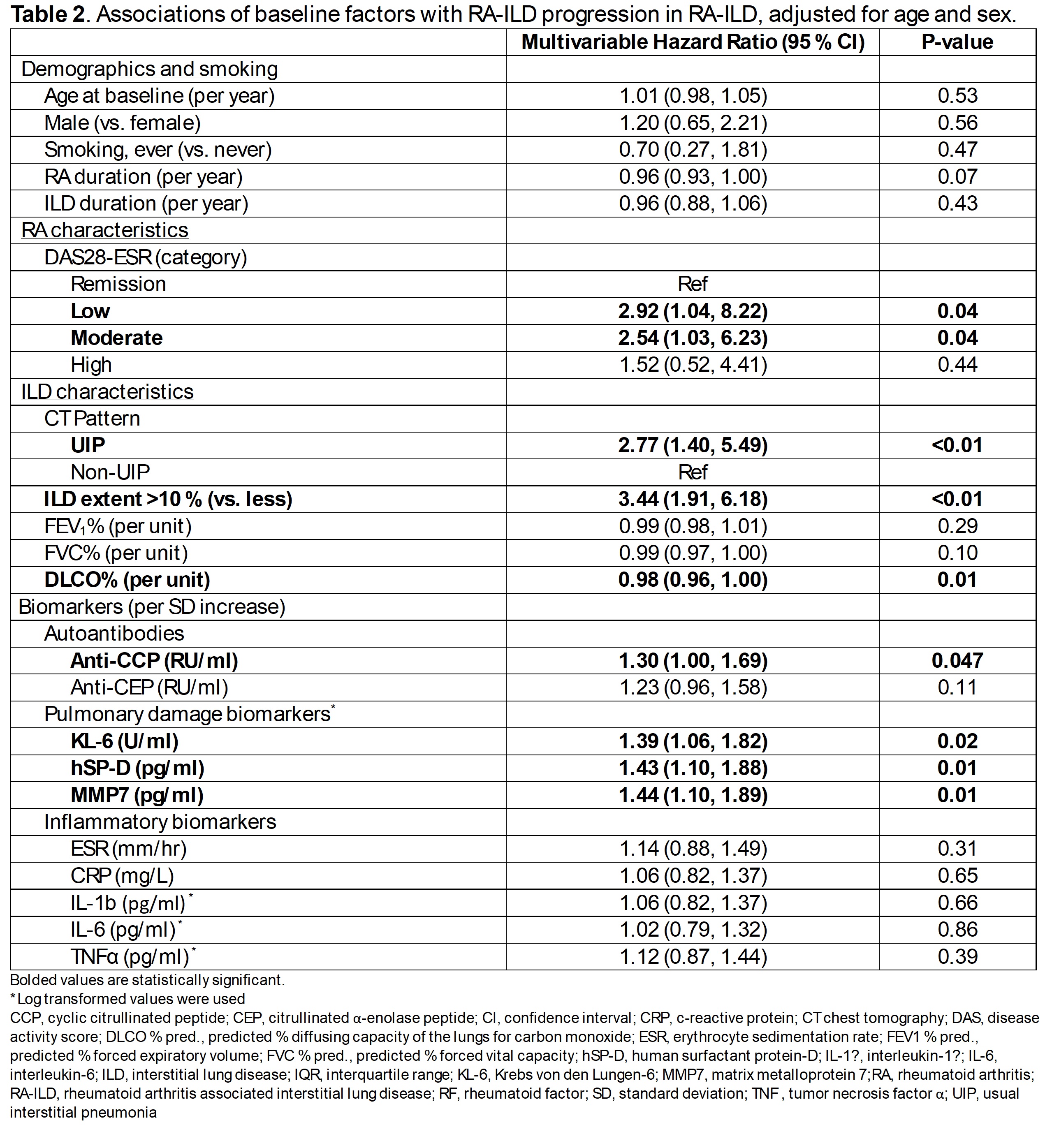
Results: We analyzed 139 RA-ILD patients (mean age 66.4 [SD 8.2] years, 31% male, 77% usual interstitial pneumonia [UIP] pattern). During a median follow-up period of 2.9 (IQR 2.6, 3.4) years, 35% (n=48) of patients had ILD progression (Table 1). UIP pattern was strongly associated with progression compared to non-UIP (HR 2.77, 95%CI 1.40-5.49). Additionally, ILD extent of >10% was strongly associated with progression (HR 3.44, 95%CI 1.91-6.18) (Table 2). In addition, anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP, HR 1.30 per SD increase, 95%CI 1.00-1.69), Krebs von den Lungen-6 (KL-6, HRs 1.39 per SD increase, 95%CI 1.06-1.82), human surfactant protein D (hSP-D, HR 1.43 per SD increase, 95%CI 1.10-1.88), and matrix metalloprotein 7 (MMP7, HR 1.44 per SD increase, 95% CI 1.10-1.89) levels were associated with progression. However, no inflammatory biomarkers were associated with progression. Compared to participants in DAS28-ESR remission, participants in low (HRs 2.92, 95% CI 1.04-8.22) and moderate disease activity (HRs 2.54, 95% CI 1.03-6.23) had higher risk of progression. In the ROC analysis, the ILD characteristics model (model 3) had an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.73, compared to 0.66 for the biomarker model (model 4) (Figure 1). The combined model (model 5) that included all factors associated with ILD progression had an AUC of 0.78.
Conclusion: In this prospective cohort that applied the recent PPF definition to RA-ILD, we identified traditional predictors of progression that included UIP pattern, ILD extent, lower DLCO, and the pulmonary damage biomarkers KL-6, hSP-D, and MMP7. In addition, we identified RA disease activity and anti-CCP antibody levels as novel RA-related predictors of progression. The model combining these factors had high predictive performance, so may be clinically useful to risk stratify for treatment consideration once externally validated.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chang S, Paudel M, McDermott G, Zhang Q, Ha Y, Lee J, Kim M, Park C, Kim J, Ha J, Chung S, Lee S, Kang E, Lee Y, Choe J, Park Y, Lee E, Sparks J. Serologic and Clinical Predictors of Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis-associated Interstitial Lung Disease Progression: A Prospective Longitudinal Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serologic-and-clinical-predictors-of-progressive-pulmonary-fibrosis-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-progression-a-prospective-longitudinal-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serologic-and-clinical-predictors-of-progressive-pulmonary-fibrosis-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-progression-a-prospective-longitudinal-cohort/