Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: RA – Animal Models Poster
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The semaphorin family is a large group of proteins initially described in axon guidance. However, semaphorins also play a role in other processes involved in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) such as the regulation of immunity, angiogenesis, apoptosis and cell migration and invasion. Previously we demonstrated that semaphorin 3B (Sema3B) expression is reduced in the synovial tissue and synovial fluid of RA compared to undifferentiated arthritis patients and reduces the invasive capacity of RA fibroblast like synoviocytes (FLS). Here, we validated initial findings in an independent cohort of patients and determined the role of Sema3B in an in vivo model of arthritis
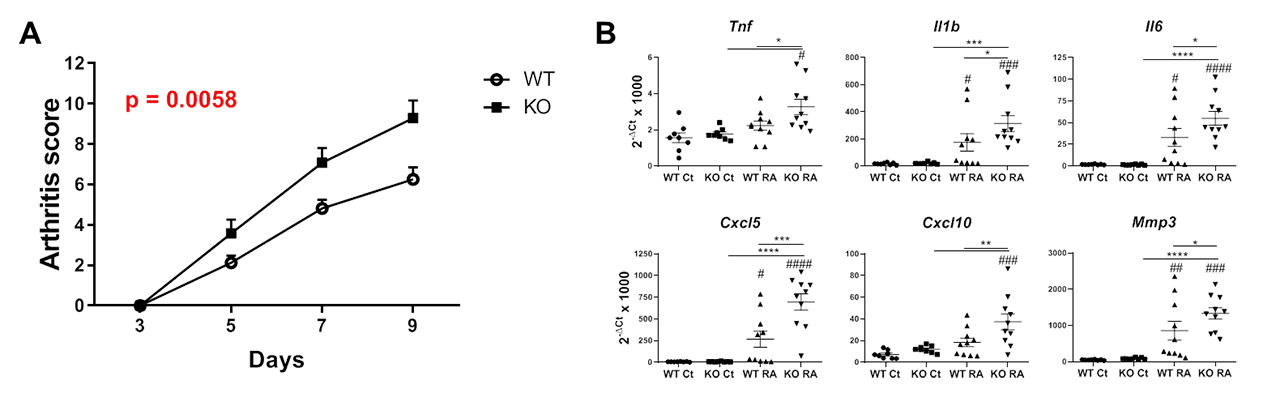
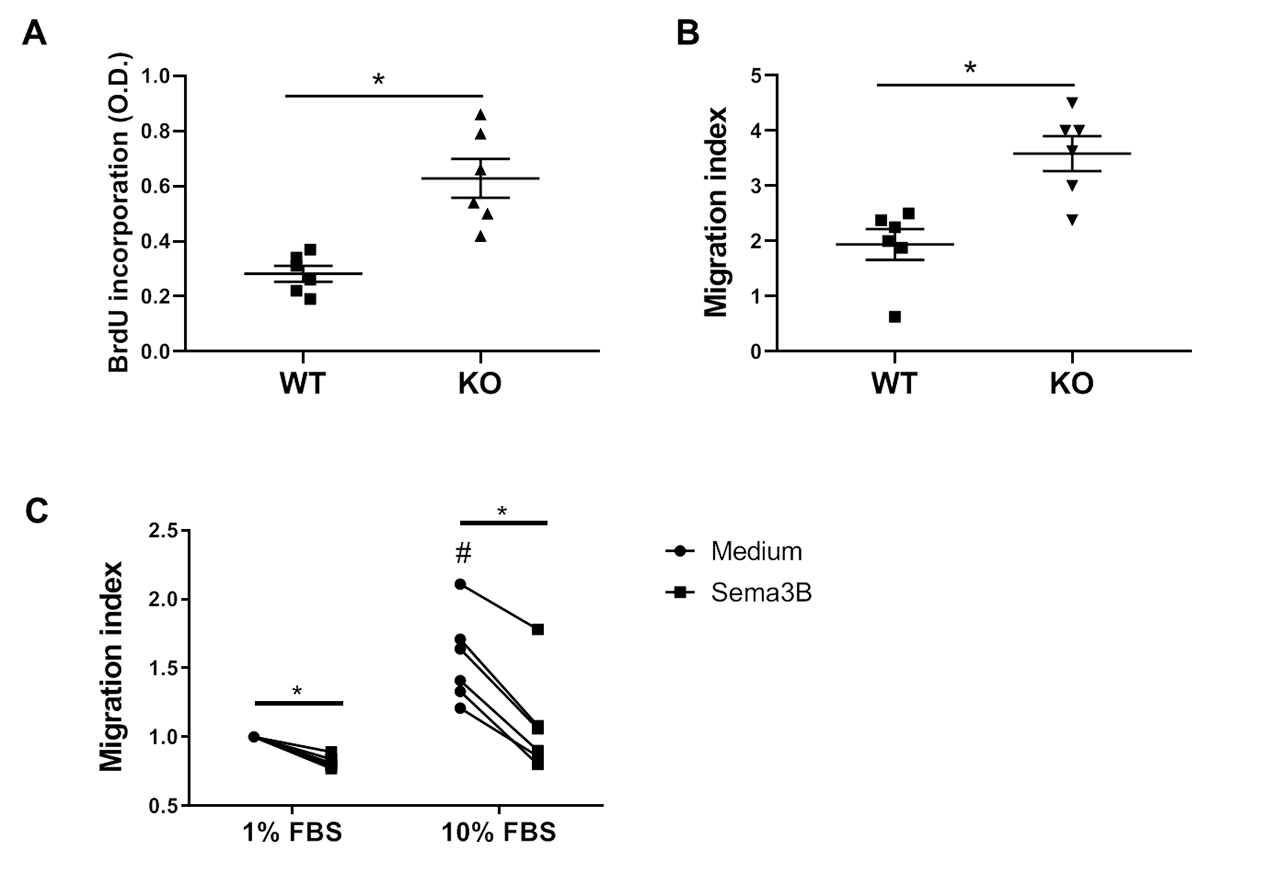
Methods: Sema3B expression in healthy control (HC, n=10), RA (n=10) and arthralgia patient (n=8) synovial tissue and serum was determined by qPCR and ELISA. Arthritis was induced in wild type (WT) and Sema3B-deficient mice (Sema3B KO) mice (n=10 for both) by intraperitoneal injection of 100 ml of K/BxN serum on day 0 and day 2. Mice were sacrificed on day 9 after serum transfer. mRNA expression in total joints and murine fibroblast-like synociocytes (mFLS) was determined by qPCR. mFLS proliferation and migration were determined using BrdU and wound closure assays, respectively.
Results: mRNA levels of Sema3B were significantly lower in the synovial tissue of RA patients compared to arthralgia patient (p=0.0205). Importantly, serum levels of Sema3B were also reduced in RA patients compared to HC and arthralgia patients (p=0.034 and p=0.0241, respectively) The clinical severity of serum-induced arthritis was significantly higher in Sema3B KO mice compared to WT mice (p=0.0015). This was associated with a higher joint and mFLS expression of the inflammatory mediators IL-1β, TNF, IL-6, CXCL-5 and CXCL-10 and the matrix metalloproteinases MMP-2 and MMP-3 (p-values ranging between p< 0.05 and p< 0.001). Functional experiments demonstrated a significantly higher proliferation and migration capacity (p=0.034 and p=0.0313, respectively) in the mFLS from Sema3B KO compared to WT mice. Importantly, the administration of recombinant mouse Sema3B abrogated the enhanced migratory capacity of Sema3B KO mFLS (p=0.044).
Conclusion: Our data confirm our previous results demonstrating that Sema3B expression is reduced early in RA onset and provide evidence that Sema3B has a protective role in a mouse model of arthritis. Therefore, Sema3B administration could be a novel therapeutic strategy for the treatment of RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Igea A, Carvalheiro T, Malvar Fernandez B, Rodriguez-Trillo A, McGarry T, Conde C, Veale D, Fearon U, Gonzalez A, Radstake T, Reedquist K, Garcia S. Sema3B Expression Is Reduced in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients and Has a Protective Role in a Murine Model of Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sema3b-expression-is-reduced-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-and-has-a-protective-role-in-a-murine-model-of-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sema3b-expression-is-reduced-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-and-has-a-protective-role-in-a-murine-model-of-arthritis/