Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: RA Treatments & Their Safety (1674–1710)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: T-cell priming and T-cell-dependent B-cell responses require an intact cluster of differentiation (CD)40/CD40L pathway. CD40 is expressed on the surface of B-cells, dendritic cells, antigen-presenting cells, and non-immune cell types; its ligand, CD40L (CD154), is expressed on the surface of activated T-cells, platelets, and other cell types. Blockade of CD40/CD40L interaction has been shown to ablate primary and secondary T-cell dependent antibody response (TDAR). We hypothesized that KPL-404, an anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody which inhibits interaction between CD40 and CD40L, would block T-cell dependent, B-cell-mediated autoimmunity in this Phase 1 study in healthy participants.
Methods: This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, first-in-human study of KPL-404 in healthy participants was designed with two single-ascending-dose arms: single intravenous (IV) doses of 0.03 mg/kg, 0.3 mg/kg, 1 mg/kg, 3 mg/kg, or 10 mg/kg and single subcutaneous (SC) doses of 1 mg/kg or 5 mg/kg. The primary objective was safety and tolerability of KPL-404; secondary and exploratory objectives included pharmacokinetic (PK) parameters, TDAR inhibition, and receptor occupancy (RO). To evaluate TDAR inhibition, participants post-KPL-404 administration were immunized with 1 mg intramuscular injection of the test antigen Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin (KLH) on day 4 and day 29 to elicit a primary and secondary Immunoglobulin (Ig) response, respectively. To evaluate RO, free and total CD40 receptor levels (percent change from baseline) on B-cells (whole blood) were measured using flow cytometry.
Results: There were no dose-limiting or dose-related safety findings in healthy participants after KPL-404 administration. One unrelated serious adverse event (patella fracture following a fall) occurred in the 10 mg/kg IV arm. The PK profile of KPL-404 in serum after IV or SC administration had low to moderate variability between individuals; elimination was dose-dependent and consistent with target-mediated drug disposition (TMDD) (Figure 1). For participants receiving 10 mg/kg IV, full receptor occupancy was observed through day 71 (Figure 2), complete TDAR suppression was observed through Day 57 (Figure 3), and anti-drug antibodies to KPL-404 were suppressed for at least 57 days; the suppression of antibody responses to the drug itself is an independent indicator of target engagement and pharmacodynamic effect. For participants receiving 5 mg/kg SC, full receptor occupancy was observed through day 43 (Figure 2), and complete TDAR suppression was observed through Day 29 (Figure 3). The TDAR response to KLH antigen correlated with the observed full RO.
Conclusion: The safety and tolerability data and the PK/PD profile of KPL-404 support further investigation of KPL-404 in a broad range of autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis. These data support the optionality for studying chronic KPL-404 dosing in patients with subcutaneous and/or intravenous administration.
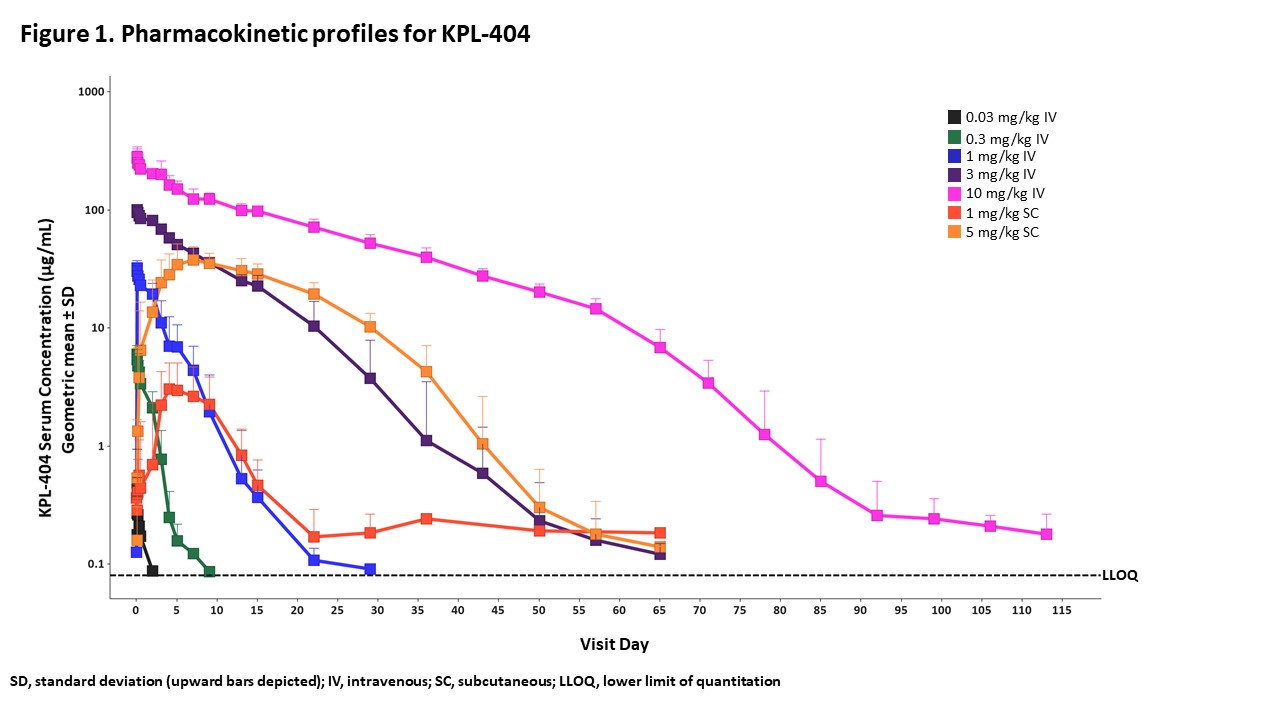 Figure 1. Pharmacokinetic profiles for KPL_404
Figure 1. Pharmacokinetic profiles for KPL_404
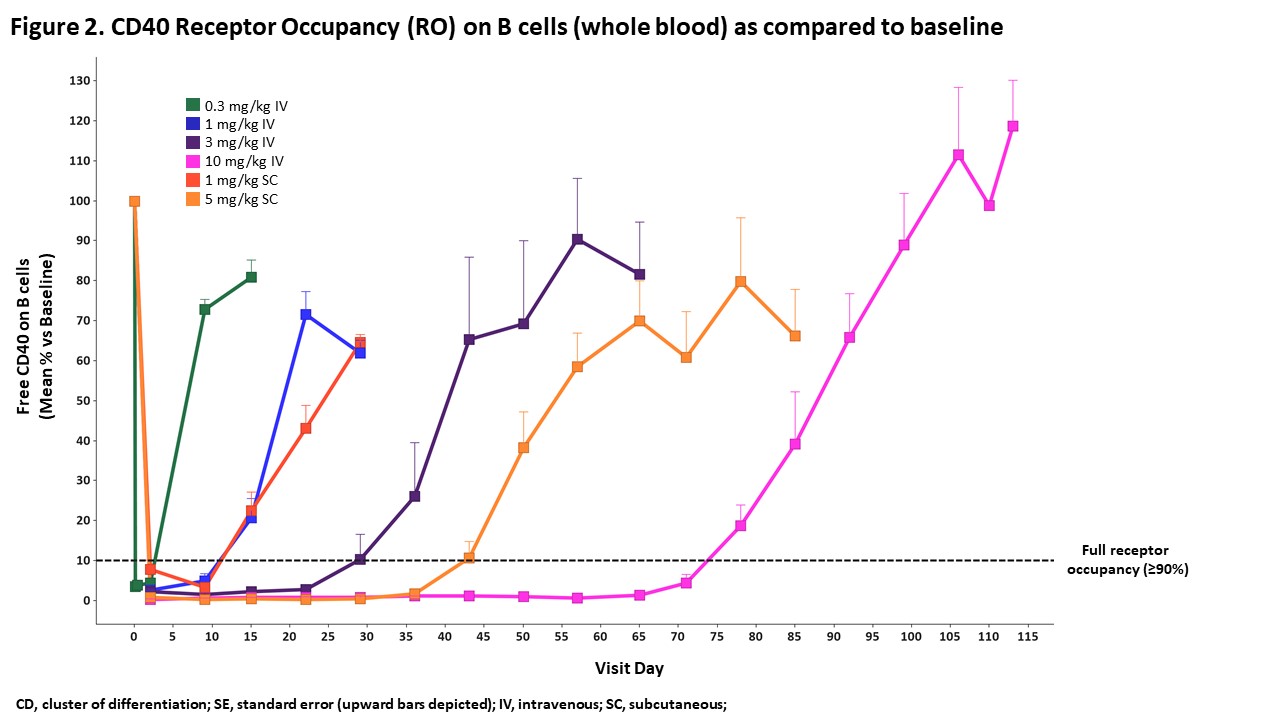 Figure 2. CD40 Receptor Occupancy (RO) on B cells (whole blood) as compared to baseline
Figure 2. CD40 Receptor Occupancy (RO) on B cells (whole blood) as compared to baseline
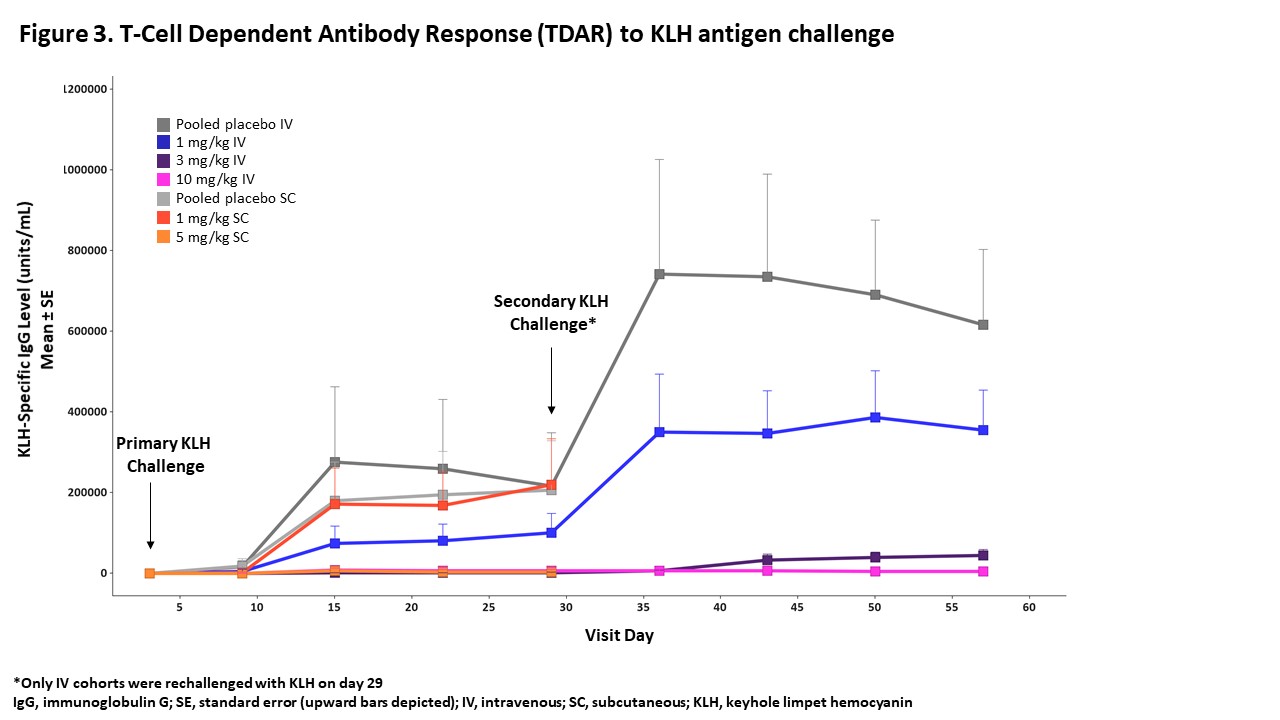 Figure 3. T-Cell Dependent Antibody Response (TDAR) to KLH antigen challenge
Figure 3. T-Cell Dependent Antibody Response (TDAR) to KLH antigen challenge
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Samant M, Wheeler A, Jiang G, Njenga M, Spiers M, Pano A, Paolini J. Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, Receptor Occupancy, and Suppression of T-cell-Dependent Antibody Response in a Phase 1 Study with KPL-404, an anti-CD40 Monoclonal Antibody [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-tolerability-pharmacokinetics-receptor-occupancy-and-suppression-of-t-cell-dependent-antibody-response-in-a-phase-1-study-with-kpl-404-an-anti-cd40-monoclonal-antibody/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-tolerability-pharmacokinetics-receptor-occupancy-and-suppression-of-t-cell-dependent-antibody-response-in-a-phase-1-study-with-kpl-404-an-anti-cd40-monoclonal-antibody/
