Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (1776–1795) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Basic Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The inflammatory process characterizing Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) is mainly driven by interleukin (IL)-23/IL-17 axis and IL-9 overexpression, in presence of T helper (Th)17 and Th9 expansion (Veale DJ, The Lancet. 2018).Recently, a correlation between IL-9 and Glucocorticoid-induced Tumor Necrosis Factor-related receptor (GITR), whose ligand (GITRL) is expressed on antigen presenting cells, was described. Specifically, the activation of GITR/GITRL promotes Th9 and Th17 differentiation and alters Treg functions fueling inflammation (Tian J, Front Immunol. 2020). Considering the role of Th9 and Th17 in PsA and the proinflammatory function of GITR, we aimed to study the effects of GITR/GITRL interaction in PsA.
Methods: Eighteen patients fulfilling the 2006 classification criteria for PsA (CASPAR) and 10 healthy controls (HC) were enrolled in this study; all gave their informed written consent to participate. The study complied with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the local Ethics Committee. Patients had an active disease and were naïve to biologicdisease modifying antirheumatic drug (bDMARDs). Blood samples were collected from all participants. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated and GITR/GITRL expression was determined by flow-cytometry in different cell subsets. An in vitro functional assay with a recombinant GITR agonist was performed to assess the effect of GITR activation on Th9 and Th17 expansion and Treg functions. Cells were stimulated with anti-CD3-CD28 monoclonal antibodies (mAb) too. The frequency of T cells was studied by flow-cytometry while the expression of cytokines and transcription factors was assessed by qRT-PCR. Data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism version 8.0.1; p values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
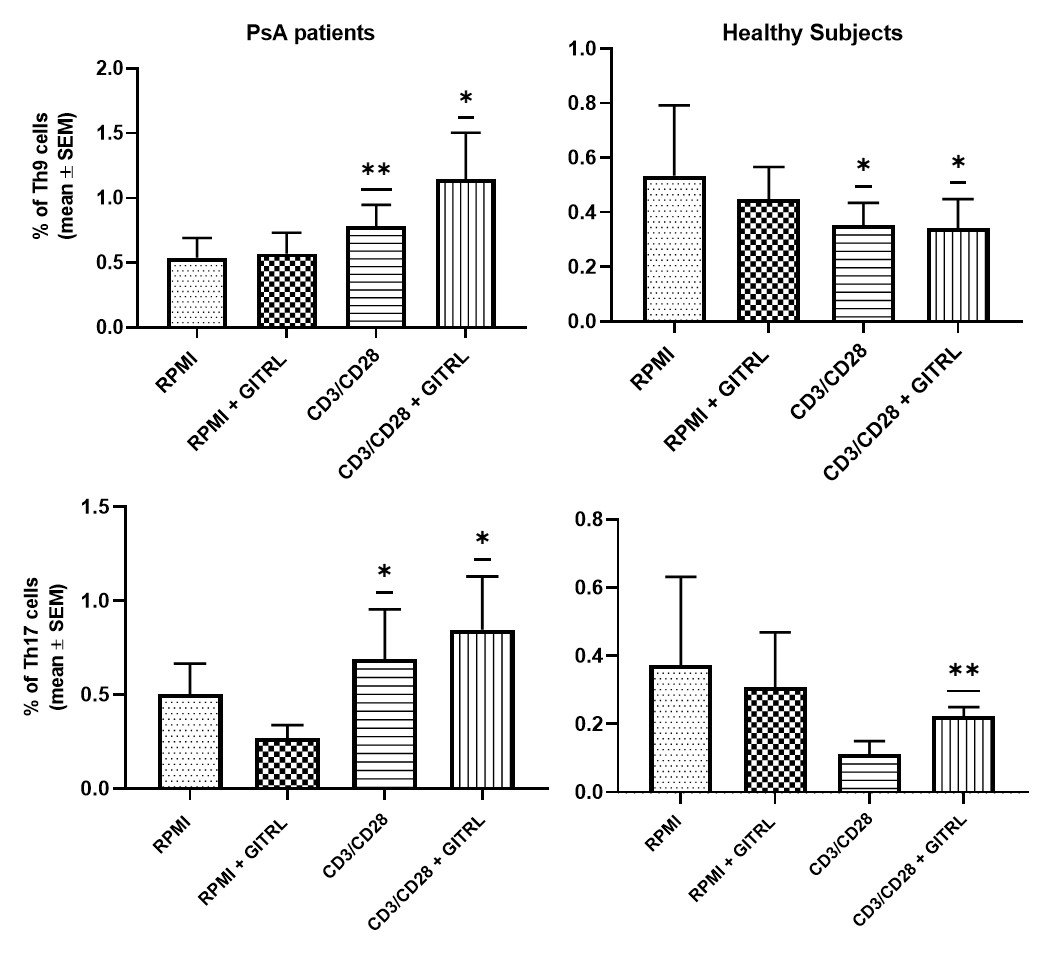
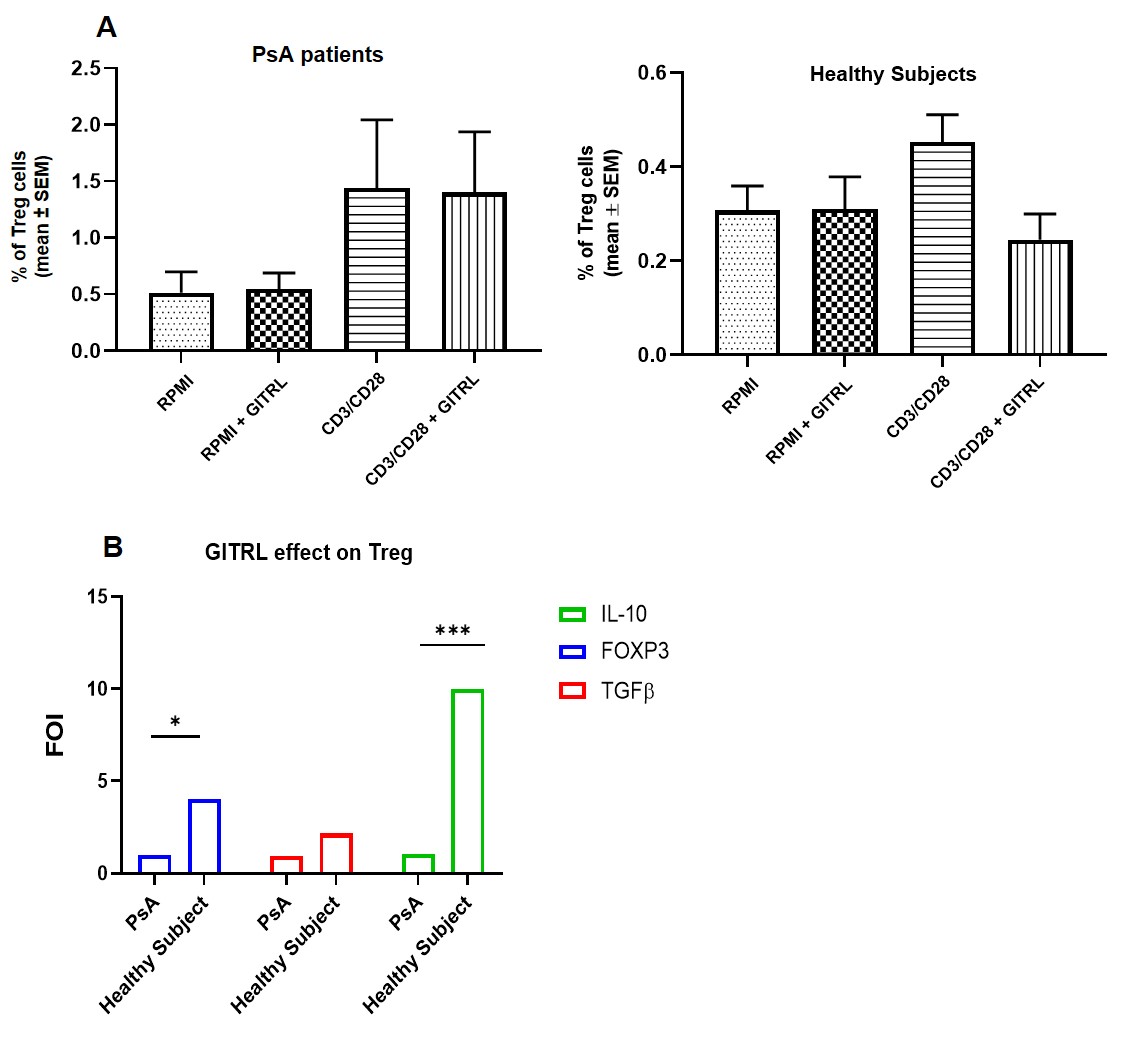
Results: An enhanced expression of GITR among CD4+ T cells was detected both pre and after in vitro stimulation with anti-CD3-CD28 mAb. In particular, although not statistically significant, Th17 and Th9 demonstrated an increased GITR expression after stimulation. GITRL was found upregulated on monocytes (CD14+), dendritic cells (CD11c+) and B cells (CD19+) in PsA patients, even if no differences in cell frequency were detected between PsA and HC. The expression of HLA-DR was assessed as a positive control without evidencing any difference between PsA and HC. An expansion of both Th9 and Th17 was found after stimulation with anti-CD3-CD28 (p< 0.05); the proliferation of these subsets was further increased in presence of recombinant GITR agonist (p< 0.05) (Figure 1). Treg from PsA were expanded compared with HC after stimulation with anti-CD3-CD28 mAb. The addition of GITRL did not further modulate Treg proliferation. However, in presence of GITR agonist the mRNA expression of NF-kB, FOXP3, TGFb and IL-10 was reduced in Treg from PsA patients, with a statistically significant difference for both IL-10 and FOXP3 (p< 0.05) (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Our data support a novel role for GITR/GITRL axis in modulating the inflammatory process behind PsA through the expansion of Th9 and Th17 and the simultaneous suppression of Treg functions, unravelling a possible future target of therapy in PsA.
Frequency of Th9 and Th17 analysed in four different conditions: RPMI, RPMI + GITRL, CD23/CD28 activation beads, CD3/CD28 + GITRL in PsA patients (left panel of the figure) and in healthy controls (right panel of the figure), respectively.
*p<0.05
A. Frequency of Treg analysed in four different conditions: RPMI, RPMI + GITRL, CD23/CD28 activation beads, CD3/CD28 + GITRL in PsA patients (on the left) and in healthy controls (on the right), respectively.
B. mRNA expression of IL_10, FOXP3 and TGFβ after GITRL stimulation in PsA patients and healthy subjects analyzed by qRT-PCR.
*p<0.05
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rizzo C, La Barbera L, Lo Pizzo M, Mohammadnezhad L, Camarda f, Dieli F, Ciccia F, Guggino G. Role of GITR/GITRL Interaction in Modulating T Helper 9, T Helper 17 and T Regulatory Response in Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/role-of-gitr-gitrl-interaction-in-modulating-t-helper-9-t-helper-17-and-t-regulatory-response-in-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/role-of-gitr-gitrl-interaction-in-modulating-t-helper-9-t-helper-17-and-t-regulatory-response-in-psoriatic-arthritis/