Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2022
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III: Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: The prompt identification of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) at risk of or in flare strongly influences the prognosis of the disease. Cell-bound complement activation products (CB-CAPs) have been studied as biomarkers of SLE activity. Despite growing knowledge, experience with CB-CAPs in the Latin American population is scarce. Therefore, this study aims to explore the behavior of CB-CAPs to determine lupus activity in SLE Colombian patients.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study of 30 adult SLE patients (ACR/EULAR 2019 criteria) and 24 technical controls. Subjects were recruited from two centers in Medellín, Colombia, between September 2021 – January 2022. We used the non-serological SELENA/SLEDAI index (SELENA/SLEDAIns) to define activity as follows: inactive (0 points), mild/moderate (1-6 points), and severe (≥7 points) activity. We determined by flow cytometry the median fluorescence intensity (MFI) of the C3d and C4d bound to erythrocytes (E-C3d, E-C4d), reticulocytes (R-C3d, R-C4d), B lymphocytes (B-C3d, B-C4d), T CD4 (TCD4-C3d, TCD4-C4d), and T CD8 (TCD8-C3d, TCD8-C4d) lymphocytes. Descriptive correlations and an exploratory analysis of the accuracy of CB-CAPs to identify severe activity were performed.
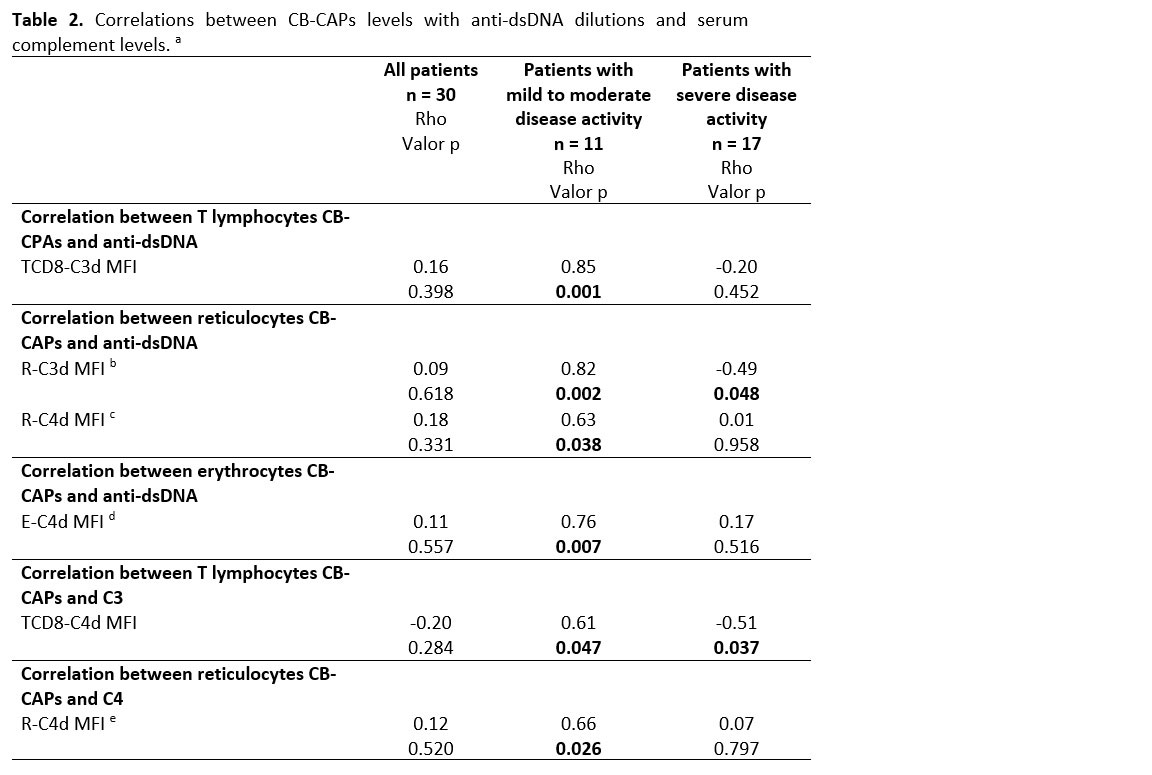
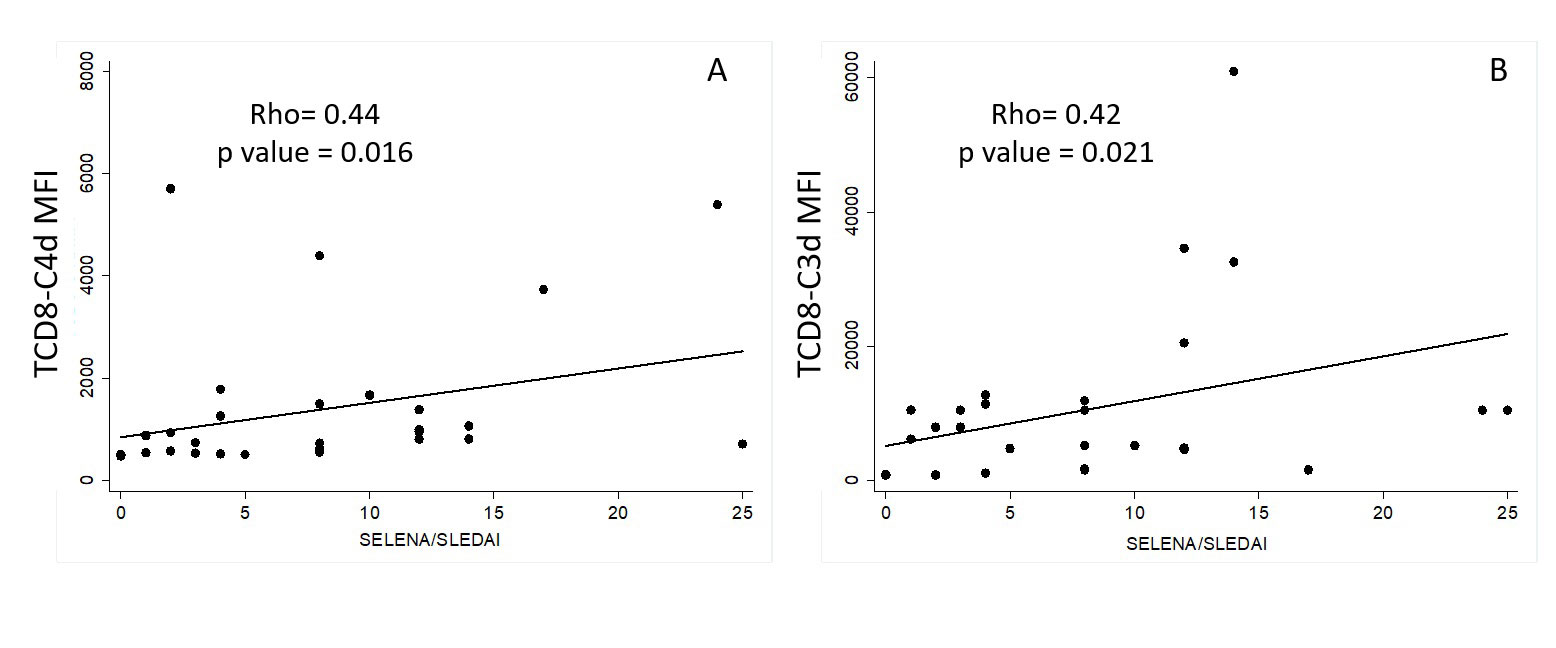
Results: Table 1 shows the demographic and clinical characteristics of the SLE patients. Two inactive subjects, 11 with mild disease activity and 17 with severe activity, were included. Table 2 shows correlations between CB-CAPs with anti-dsDNA dilutions and serum complement. There was a statistically significant correlation between clinical SELENA-SLEDAIns with the TCD8-C4d MFI and TCD8-C3d MFI (figure 1). The results showed a negative correlation between C3 levels and SELENA-SLEDAIns for all patients (Rho= -0.57; p=˂0.001) and patients with severe disease activity (Rho= -0.65; p=0.004). In the case of C4, the correlation was -0.51 (p=0.004) for the 30 SLE subjects. Spearman correlation coefficients were not significant between anti-dsDNA by IIF and SELENA/SLEDAIns in none of the groups. The R-C4d had the highest sensitivity (75%), the best specificity (64%), and the area under the ROC curve (0.7 CI 95% 0.53-0.87). Therefore, R-C4d MFI was the CB-CAP with the best performance to discriminate lupus severe activity (SELENA/SLEDAIns ≥7 points).
Conclusion: This is the first time that TCD8-C4d and TCD8-C3d MFI demonstrated significant correlations with lupus disease activity. Previously, T-C4d was correlated with activity in an ethnical minority. To our knowledge, there are no data on this biomarker in large and diverse cohorts, which places a gap in the knowledge and an opportunity for future investigations. As we did, other authors have demonstrated the utility of R-C4d as a lupus disease activity biomarker.
a. Taken at the time of recruitment.
b. Low complement was defined as either C3 or C4 levels below the normal range established at each of the laboratories.
a. Spearman’s correlation coefficient was used to determine the correlation between CB-CAP levels with anti-dsDNA, C3, and C4.
b. C4d-/ C3d+ reticulocytes.
c. C4d+/ C3d- reticulocytes.
d. C4d+/ C3d+ erythrocytes.
e. C4d+/ C3d+ reticulocytes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Muñoz Urbano M, Quintero-González D, Rojas M, Rodelo J, León Álvarez A, Gonzalez L, Vásquez G. Role of Cell-Bound Complement Fragments as Biomarkers to Determine Disease Activity in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/role-of-cell-bound-complement-fragments-as-biomarkers-to-determine-disease-activity-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/role-of-cell-bound-complement-fragments-as-biomarkers-to-determine-disease-activity-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/