Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I: Diagnosis (0323–0356)
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Antibodies to Ro60 (SSA) or Ro52 (SSB) have been described as one of the defining autoantibodies in Sjogren syndrome but they are also commonly observed in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Sjogren syndrome and SLE frequently coexist and share common pathogenesis and clinical features. We aim to examine the clinical significance of Ro positivity in an Australian SLE cohort.
Methods: Patients from the Australian Lupus Registry and Biobank, all fulfilling SLE classification criteria, were studied according to their baseline anti‐Ro positivity status (either Ro60 or Ro52 or both). Comparison between Ro+ve and Ro‐ve patients was made using descriptive statistics. Clinical associations of Ro positivity with patient and disease characteristics were studied using logistic regression.
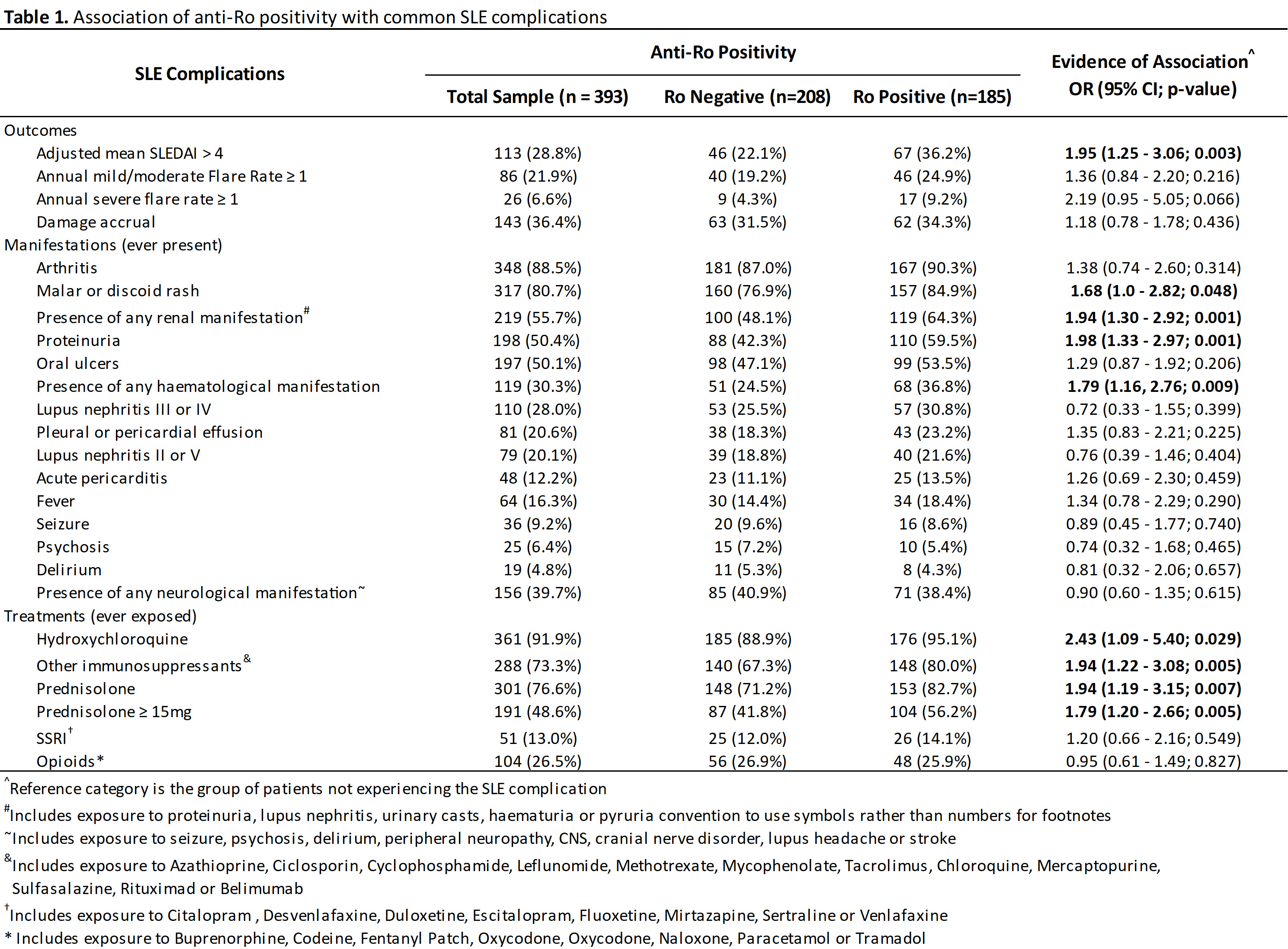
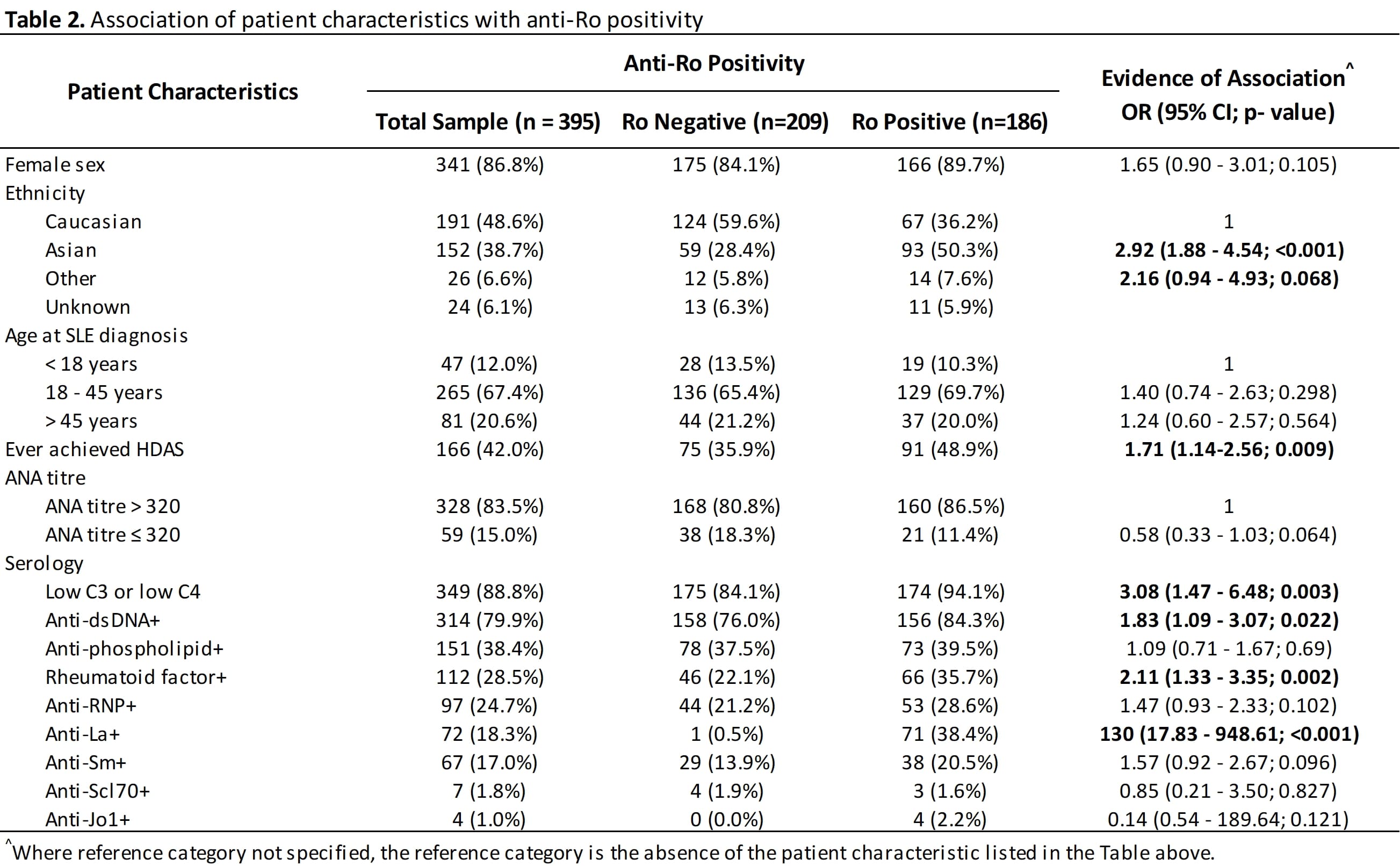
Results: 393 patients were studied; 47.1% have positive anti‐Ro status. Ro+ patients were more likely to be non‐Caucasians (Asian OR 2.92, 95% CI 1.88‐4.54, p< 0.001), and have significant association with positive serology other than the well‐recognised association with anti‐La (SSB) and rheumatoid factor, including positivity to anti‐dsDNA and hypocomplementemia. There were no association with positive antiphospholipid antibodies. Ro positive SLE patients were more likely to have High Disease Activity Status (HDAS) (OR 1.68, 95% CI 1.12‐2.52, p=0.012) and increased likelihood of high adjusted mean SLEDAI (greater than 4) (OR 1.95, 1.25‐3.06, p=0.003). Interestingly there was no difference in damage accrual between the two groups.
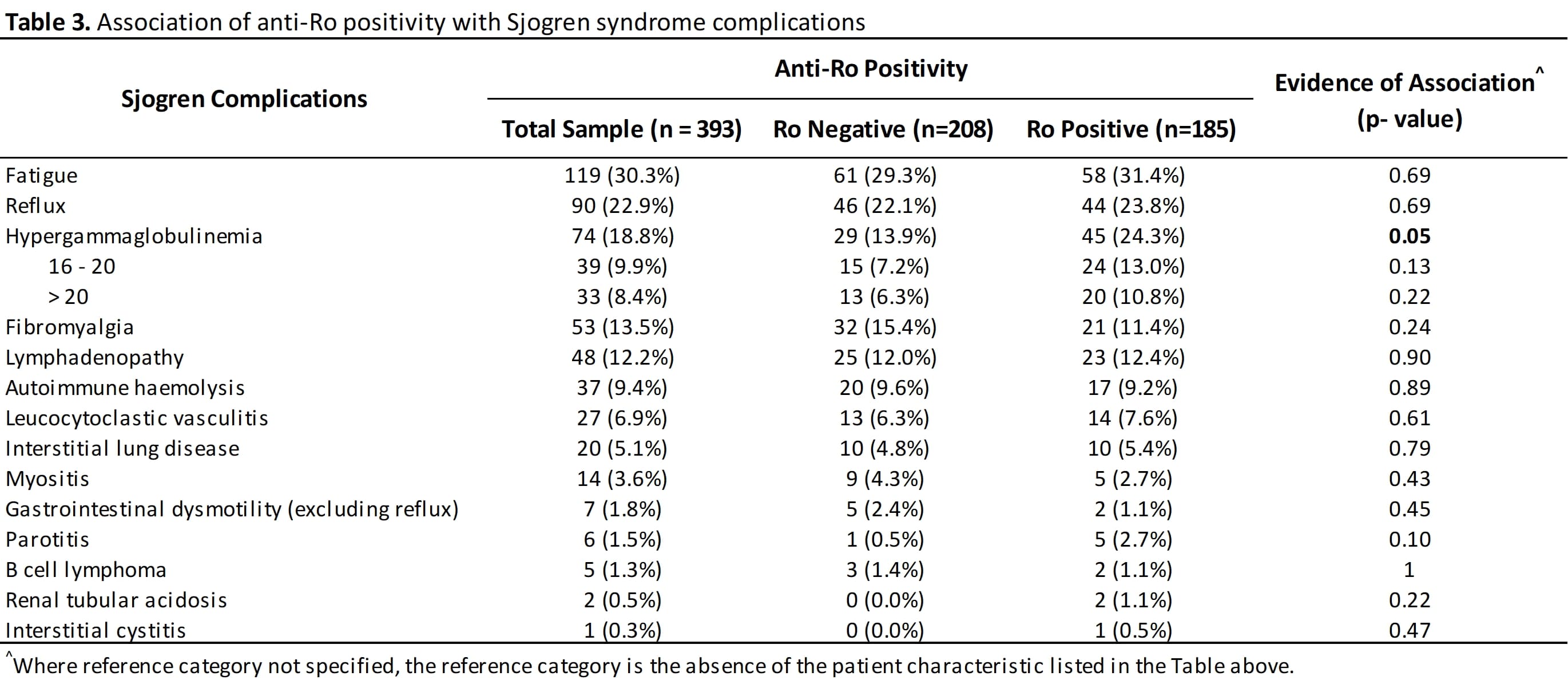
25.8% of the Ro positive cohort have associated sicca symptoms that may qualify them for diagnosis of Sjogren syndrome. Consistent with the observation that their overall disease activity is higher, Ro+ SLE patients are more likely to have to have malar or discoid rash (OR 1.68, 95%CI 1‐ 2.82, p=0.048), haematological manifestation (OR 1.79, 95% CI 1.16‐2.76, p=0.009), renal disease (OR for proteinuria was 1.98, 95% CI 1.33‐2.97, p=0.0010) (See table 1). Maximum urine proteinuria creatinine ratio was higher in Ro+ve SLE patients (p< 0.001). The minimum lymphocyte and neutrophil counts were also significantly lower in Ro+ve SLE patients (p=0.004 and p=0.001 respectively). Sjogren features such as parotitis, leucocytoclastic vasculitis, interstitial lung disease, and interstitial cystitis were seen in this lupus cohort but did not occur frequently enough to show a difference between Ro+ve and Ro‐ve groups. Hypergammaglobulinemia occurred significantly more frequently (OR 1.77, 1.00 ‐3.16, p‐0.05).
Ro+ patients were more likely to be treated with prednisolone (OR 1.94, 1.19‐3.15, p=0.007) and immunosuppressants (OR 1.94, 1.22‐3.08, p=0.005).
Conclusion: Ro positivity is seen frequently in SLE patients. Overlapping lupus and Sjogren features are seen in many patients, and Ro positivity can be used as a biomarker to denote a more severe disease phenotype.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Liao K, De Silva T, Bonin J, Koelmeyer R, Hoi A. Ro Positivity Is an Under‐Recognised Poor Prognostic Marker in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ro-positivity-is-an-under%e2%80%90recognised-poor-prognostic-marker-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ro-positivity-is-an-under%e2%80%90recognised-poor-prognostic-marker-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-patients/