Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (1945–1972) Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Autoimmune myositis involves a spectrum of rare autoimmune disorders characterized by inflammation and damage to skeletal muscles. The management of these challenging conditions often requires immunosuppressive therapies. Rituximab (RTX), a monoclonal antibody targeting CD20-positive B cells, has emerged as a promising therapeutic option for patients with autoimmune myositis who are refractory to or intolerant of conventional treatments.This meta-analysis aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of RTX treatment in patients with autoimmune myositis, encompassing polymyositis (PM), dermatomyositis (DM), juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM), antisynthetase syndrome (ASS), and immune-mediated necrotizing myositis (IMNM).
Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted using electronic databases:PubMed and Embaseto identify relevant studies published up to September 2022. Studies reporting on the efficacy and safety outcomes of RTX treatment in patients with autoimmune myositis were included, case reports or series with less than 3 subjects were excluded. Data were extracted, and a random-effects model was used to calculate pooled estimates for clinical response rates, subgroup analysis, and adverse events. This study was registered withPROSPERO 2022 CRD42022353740
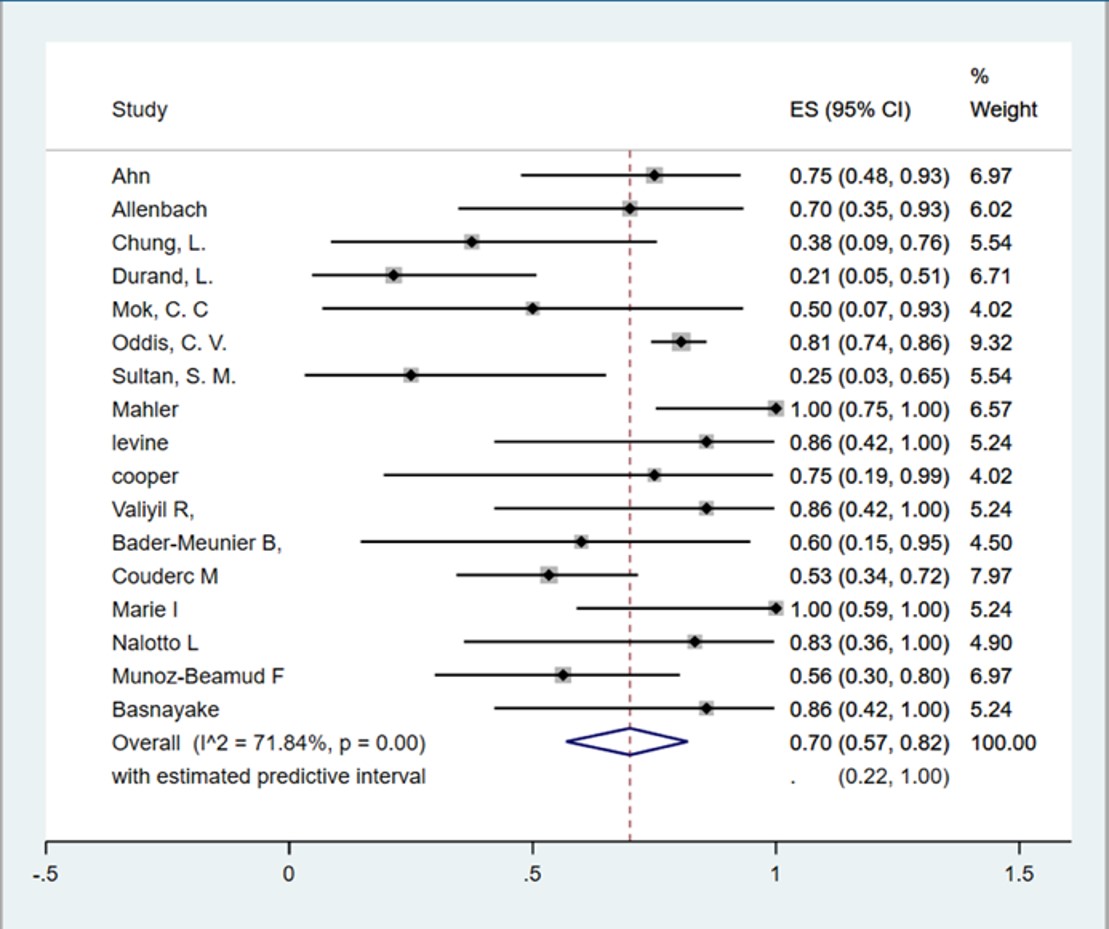
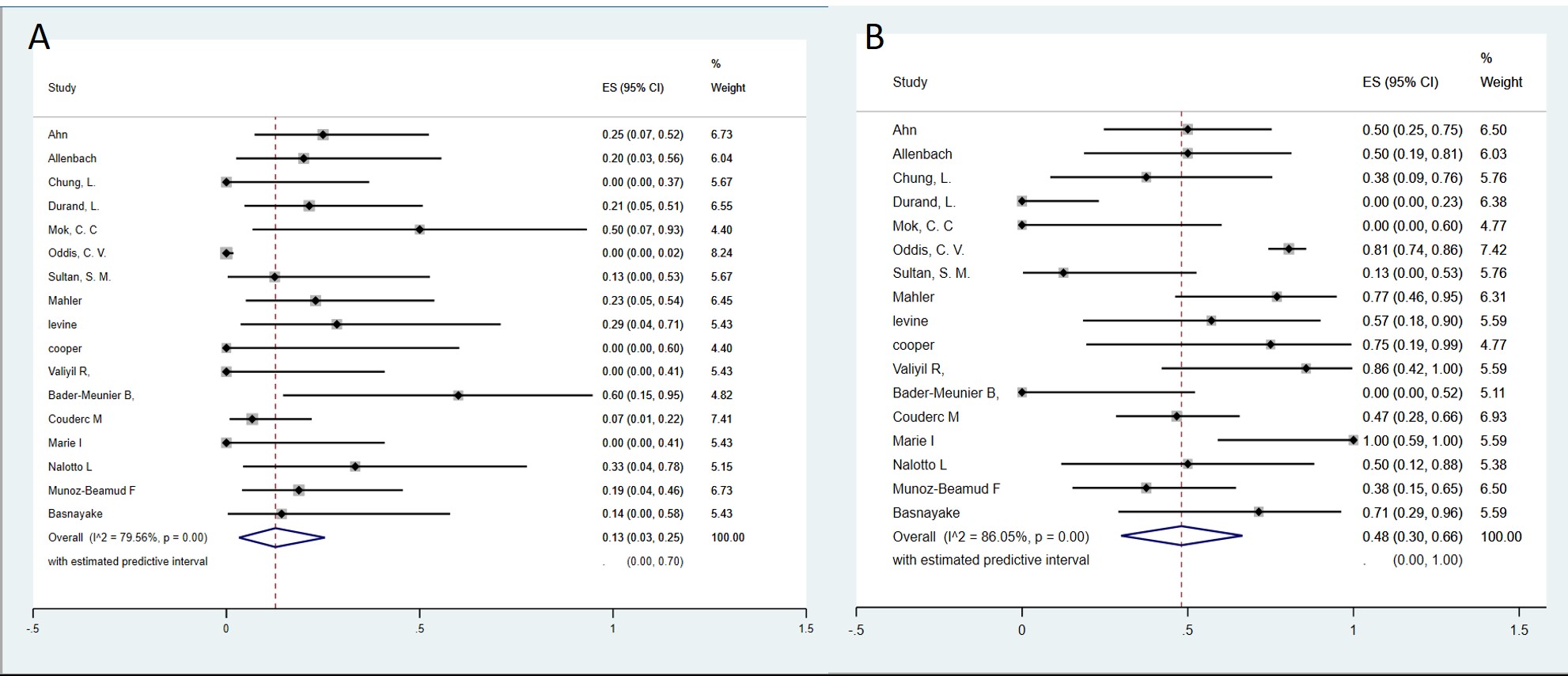
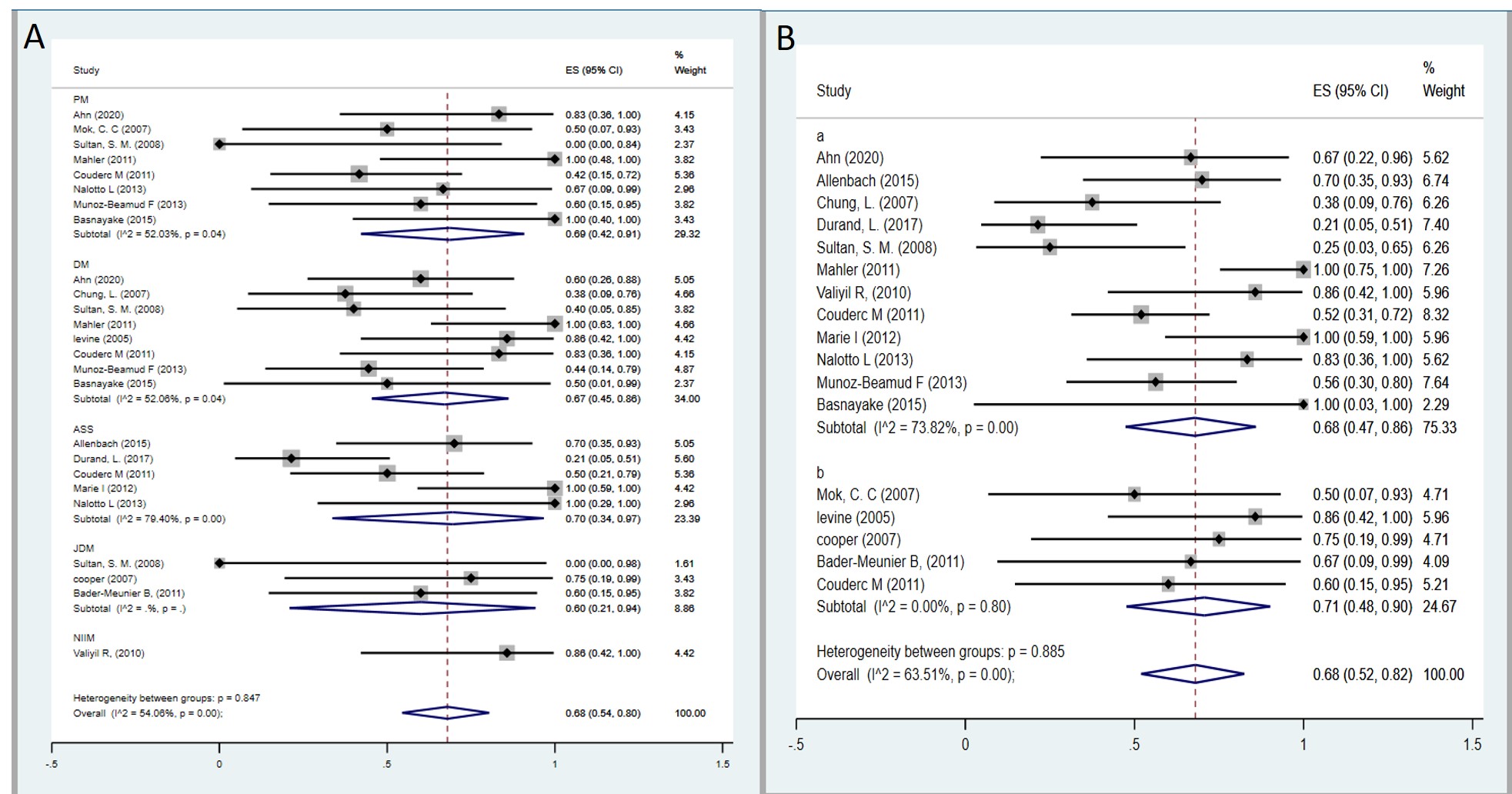
Results: A total of 17 studies, 1 RCT and 16 uncontrolled studies, involving 362 patients with autoimmune myositis were included in the meta-analysis. The pooled analysis demonstrated a notable overall clinical response rate of 70% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 57-82% I2=71.8%, p= < 0.001), Pooled complete remission rate after treatment with RTX was 13% (95% CI:3-25%, I2=79.5%, p=< 0.001), and partial remission rate was 48% (95% CI: 30–66%, I2=86.0%, p=< 0.001). Subgroup analyses showed high response rates in all typed of myositis PM 69% (95% CI: 42-91% I2=52.0%, p=0.04) DM 67% (95% CI: 45-86% I2=52.0%, p=0.04), ASS 70% (95% CI: 34-97% I2=79.4%, p=< 0.001), JDM 60% ( 95% CI: 21-94%) and NIIM (just one study) 86% ( 95% CI: 42-100%). Regarding RTX induction dose, subgroup analysis showed similar overall response with 1 g IV at days 0 and 14 days 68% (95% CI:47-86, I2=75.3% P=< 0.001) and 375 mg/m2 weekly for 4 weeks was 71% (95% CI:48–90, I2=24.6% P=0.80). Regarding safety, 120 adverse events were reported. The most reported adverse events from the 362 patients were infusion reactions in 67 (18.5%) and infections in 45 patients (12.4%).
Conclusion: The highly variable response and remission rates seen in this review warrant further controlled trials on RTX for autoimmune myositis. RTX demonstrates a favorable clinical response rate and muscle strength improvement. Potential adverse events, particularly infusion reactions and infections, should be considered. Further research is needed to optimize treatment protocols and assess long-term outcomes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Otalora Rojas L, Ramsubeik K, Sanchez-Ramos L, Motilal S, Singh J, S Kaeley G. Rituximab Treatment in Adult Patients with Idiopathic Inflammatory Myositis (IIM): A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rituximab-treatment-in-adult-patients-with-idiopathic-inflammatory-myositis-iim-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rituximab-treatment-in-adult-patients-with-idiopathic-inflammatory-myositis-iim-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/