Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: During the COVID-19 pandemic, Canadians adults with RA faced considerable uncertainty due to greater risk of infection, hospitalization, changing access to RA medications, and very limited access to in-person RA care due to stringent pandemic-related restrictions. We examined trends in perceived stress, physical, emotional, and social health, perceived disease activity and flares prior to and during the first two waves of COVID-19 in adults with RA.
Methods: Participants were enrolled in the Canadian Early Arthritis Cohort with available data. Descriptive statistics examined trends in Perceived Stress and PROMIS-29 from 6 months pre-pandemic (9/19-2/20) through Waves 1 (3/20-6/20) and Wave 2 (10/20-1/21). Disease activity was assessed using the RA-FQ, a validated PRO; scores ≥20 are consistent with inflammatory flares.
Results: A total of 858 visits were collected from 3/16/20 through 1/31/21 and compared with 956 pre-pandemic visits. Participants were mostly white (86%) women (72%) with a mean age of 55 years. Pre-pandemic mean PROMIS-29 scores were in the normal range. Monthly trends showed that pandemic impacts were greatest in April 2020 (Fig 1) where mean PROMIS-29 scores worsened for all domains except Participation (mean Δ -0.4); the largest changes were in Depression (Δ+4.8) and Anxiety (Δ+4.2)(p’s< .01). Compared with pre-pandemic visits, by April higher proportions had moderate-severe Anxiety (12% vs 23%), Depression (11% vs 23%), Fatigue (18% vs 25%), Sleep Disturbance (10% vs 19%), Pain (23% vs 40%), Participation (15% vs 21%) and Disability (25% vs 34%) (all p’s< 0.05). By July 2020, mean PROMIS-29 scores had improved for Depression (Δ -4.5), Anxiety (Δ -3.2), Fatigue (Δ -2.0) and Perceived Stress (Δ -0.7). The proportions of patients with moderate-severe symptoms (≥60) were similar to pre-pandemic for all domains except Pain, Function, Participation, and Sleep where 29%, 34%, 21% and 17%, respectively, continued to have moderate-severe impairments. Wave 2 scores were higher than pre-pandemic, but lower than Wave 1, with the largest changes in depression (p=.02) and anxiety (p=.06).
Mean RA-FQ increased from the pre-pandemic period, peaking in April 2020 and Dec 2020-Jan 2021 (Fig 2). More patients had RA-FQ scores consistent with disease fIares in April (45%) and December (35%) than in the pre-pandemic period.
Conclusion: Stringent COVID-19 pandemic restrictions impacted care across Canada in Waves 1 and 2 resulting in considerable stress, higher perceived disease activity and flares, and meaningfully worse physical and emotional health. More than 1/3 experienced moderate-severe anxiety, depression, fatigue, sleep disturbance, pain, and disability.
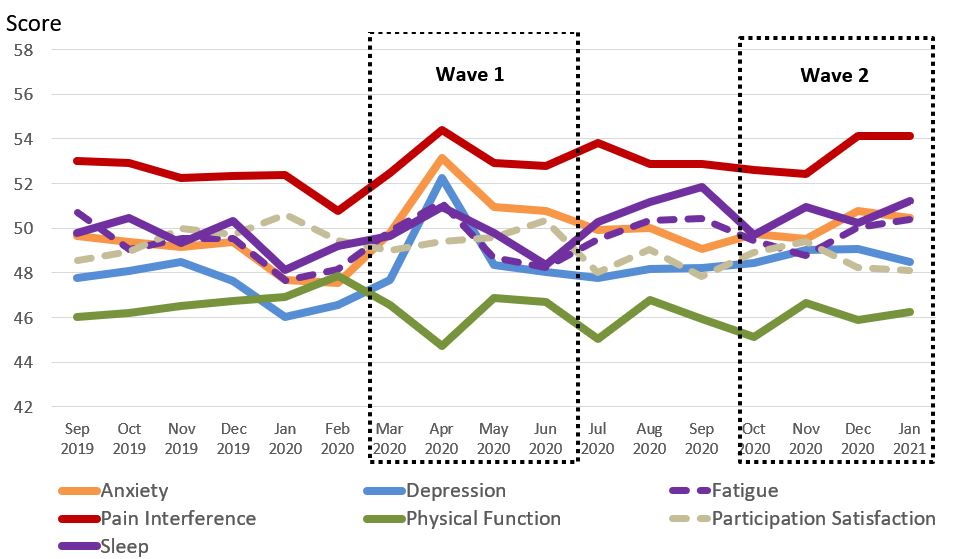 Figure 1. PROMIS_29 scores prior to and during the COVID_19 pandemic in Canadian RA patients.
Figure 1. PROMIS_29 scores prior to and during the COVID_19 pandemic in Canadian RA patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Schieir O, Bartlett S, Valois M, Bessette L, Boire G, Hazlewood G, Hitchon C, Keystone E, Pope J, Tin D, Thorne C, Bykerk V, Investigators C. Riding Multiple Waves of Uncertainty: Real World Canadian RA Patient Outcomes over 1 Year of COVID-19 Restrictions [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/riding-multiple-waves-of-uncertainty-real-world-canadian-ra-patient-outcomes-over-1-year-of-covid-19-restrictions/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/riding-multiple-waves-of-uncertainty-real-world-canadian-ra-patient-outcomes-over-1-year-of-covid-19-restrictions/

