Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In the US, there is up to a 14-year delay in axSpA diagnosis, which is likely greater for nr-axSpA.1 Impediments to timely diagnosis of nr-axSpA are unknown. This two-phased study used a grounded theory analytical approach to understand the healthcare journey leading to nr-axSpA diagnosis and factors contributing to diagnostic delay.
Methods: Adults with nr-axSpA fulfilling the eligibility criteria of rheumatologist-confirmed diagnosis of nr-axSpA, chronic back pain for ≥3 months starting before age 45, and presence of characteristic SpA symptoms were recruited from February-May 2020 via the Spondylitis Association of America newsletter, social media channels, and from back pain patient databases. In the qualitative component of the study, semi-structured telephone interviews with 25 patients and 15 rheumatologists were conducted to identify barriers and overarching themes. For the quantitative component, patients completed a detailed online questionnaire.
Results: Quantitative analysis was conducted on 125 patients (mean age, 43.5 years [range: 18-73 years]; female 74%; white 84%, LatinX 3%, and black 2%; bachelor’s or advanced degree in 72%). Half of patients had seen ≥4 different healthcare providers (HCPs) before seeing a rheumatologist (Figure 1) and 50% saw ≥2 rheumatologists before receiving the nr-axSpA diagnosis. The interval from symptom onset to nr-axSpA diagnosis ranged between ≤2 years in 40% to ≥11 years in 25% (Figure 2). Both qualitative interviews and quantitative survey responses found that patients often perceived their symptoms as a typical consequence of activity or their age (Table 1). When patients did seek medical care, clinicians frequently minimized, overlooked, or misinterpreted signs and symptoms of inflammatory disease, particularly in young and female patients. Survey participants perceived these issues as leading barriers to timely diagnosis.
Conclusion: Patients with nr-axSpA often see multiple HCPs before arriving at the diagnosis. While rheumatologists play a critical role in diagnosis, disease recognition by clinicians in other specialties is key for early referral. Findings suggest that both patients and clinicians may be unfamiliar with inflammatory back pain, and nr-axSpA—particularly in young, or female patients, or in those with normal x-rays. Education on the cardinal features, epidemiology, burden, and benefits of timely diagnosis of nr-axSpA is warranted for providers who commonly manage back pain.
- Deodhar A, et al. Arthritis Rheum 2016;68:1669-1676.
 Figure 1. Health Encounters Leading to nr-axSpA Diagnosis
Figure 1. Health Encounters Leading to nr-axSpA Diagnosis
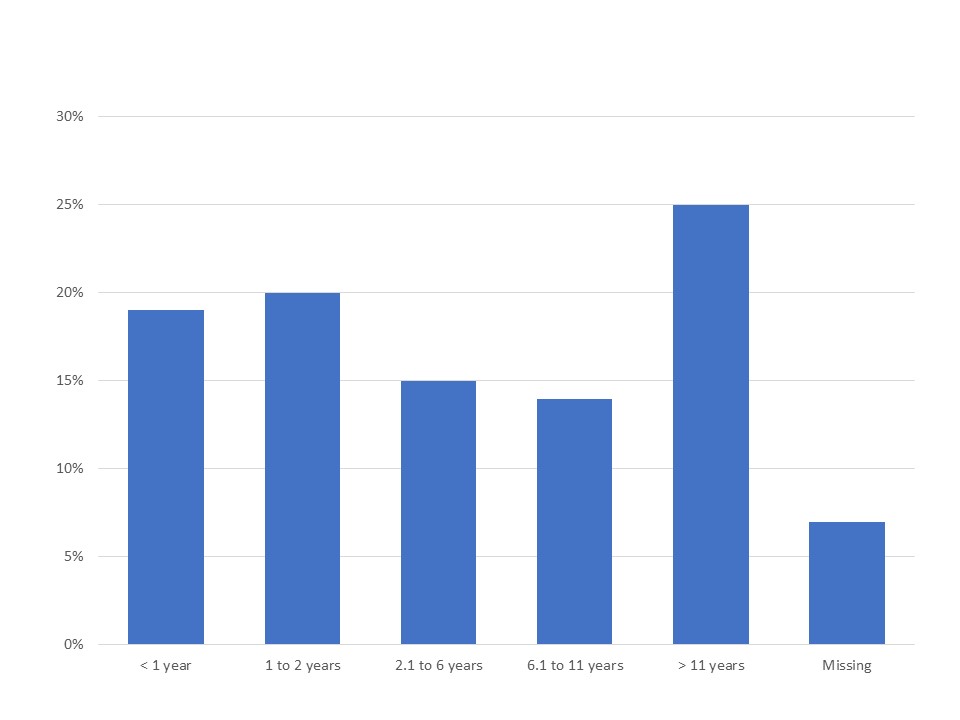 Figure 2. Duration of nr-axSpA Symptoms Before Diagnosis Established (N = 125)
Figure 2. Duration of nr-axSpA Symptoms Before Diagnosis Established (N = 125)
 Table 1. Barriers to nr-axSpA Diagnosis – Comparison of Qualitative and Quantitative Findings
Table 1. Barriers to nr-axSpA Diagnosis – Comparison of Qualitative and Quantitative Findings
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kiwalkar S, Deodhar A, Howard R. “Rheum to Diagnosis”: Uncovering Impediments to Accurate Diagnosis of Non-radiographic Axial Spondylarthritis (nr-axSpA) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rheum-to-diagnosis-uncovering-impediments-to-accurate-diagnosis-of-non-radiographic-axial-spondylarthritis-nr-axspa/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rheum-to-diagnosis-uncovering-impediments-to-accurate-diagnosis-of-non-radiographic-axial-spondylarthritis-nr-axspa/
