Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (1776–1795) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Basic Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In psoriatic arthritis (PsA) aberrant activation/migration of specific T cell subpopulations (Th17/Th9/MAIT cells) in the joint synovium induce synovial inflammation and pannus formation. Several T cell cytokines such as IL-9, IL-17A/IL-17F, IL-22 and IL-23 play critical roles in the pathogenesis of PsA. IL-23 does not have any biological effect on synovial cells (FLS) and IL-17 does not activate the JAK/STAT signaling system. IL-9 and IL-22 have regulatory roles on proliferation of FLS; and as well JAK-1 and 3 are activated by IL-9; and JAK1/TYK2 by IL-22. Here to determine the functional significance of these signaling proteins on pannus formation we hypothesized that IL-9/IL22 induced JAK/STAT signaling regulates the proliferative cascades of FLS in PsA. We studied the regulatory role IL-9 induced JAK-1,3 and IL-22 induced JAK1/TYK2 on FLS biology.
Methods: FLS from PsA (n=10) were cultured as per our standardized protocol (Cytokine.2012;60:38-42) with rIL-9 (10ng/ml) and rIL-22 (100ng/ml). Proliferation was measured by MTT assay and CFSE dilution assay. IL-6, IL-8 and MMP3 levels were determined by ELISA. Immunoblot studies were done to assess JAK1/pJAK1, TYK2/pTYK2, STAT1/pSTAT1, STAT3/pSTAT3. Further to determine the molecular mechanisms of JAK inhibitors (JAKi) these experiments were done in the presence or absence of specific JAKi (JAK-inhibitor, Upadacitinib).
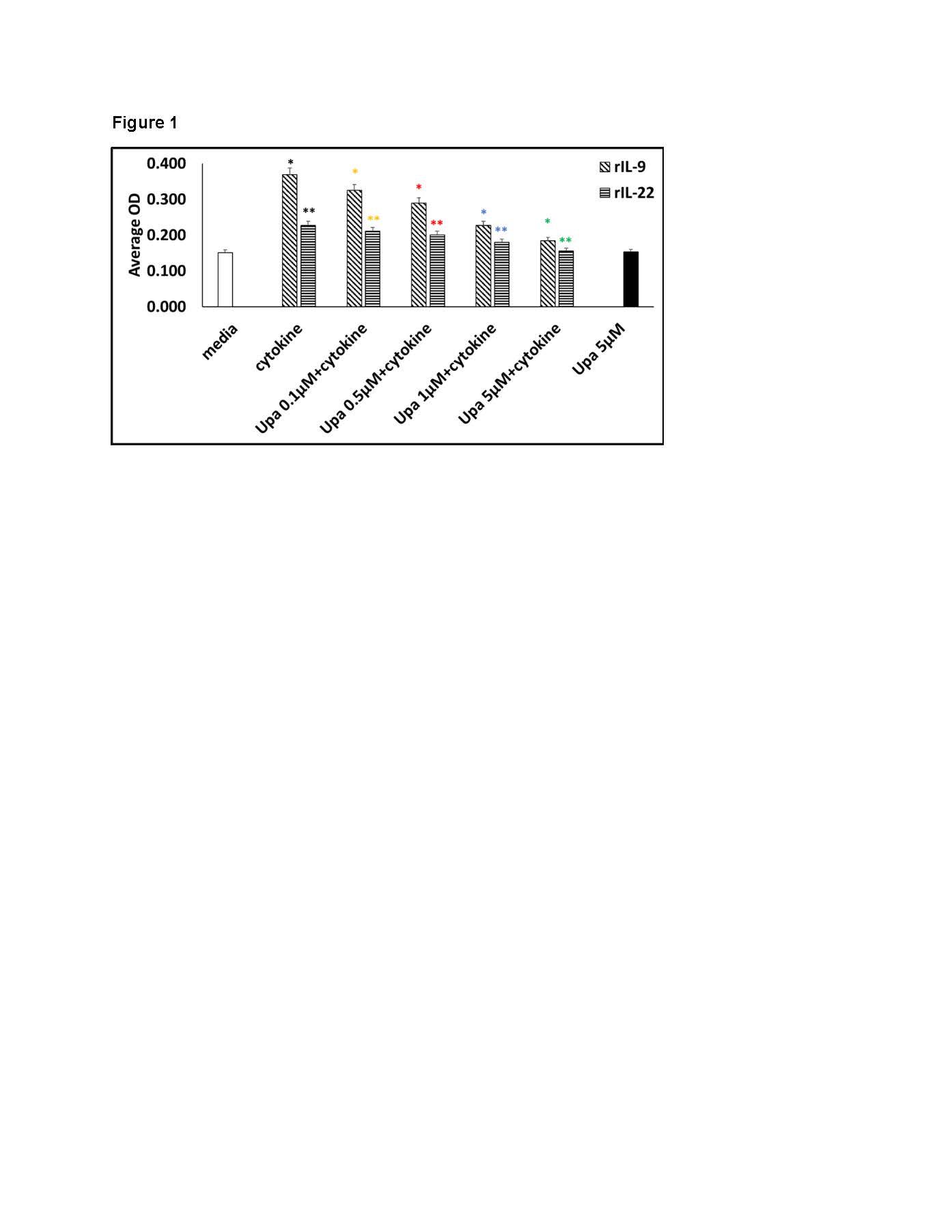
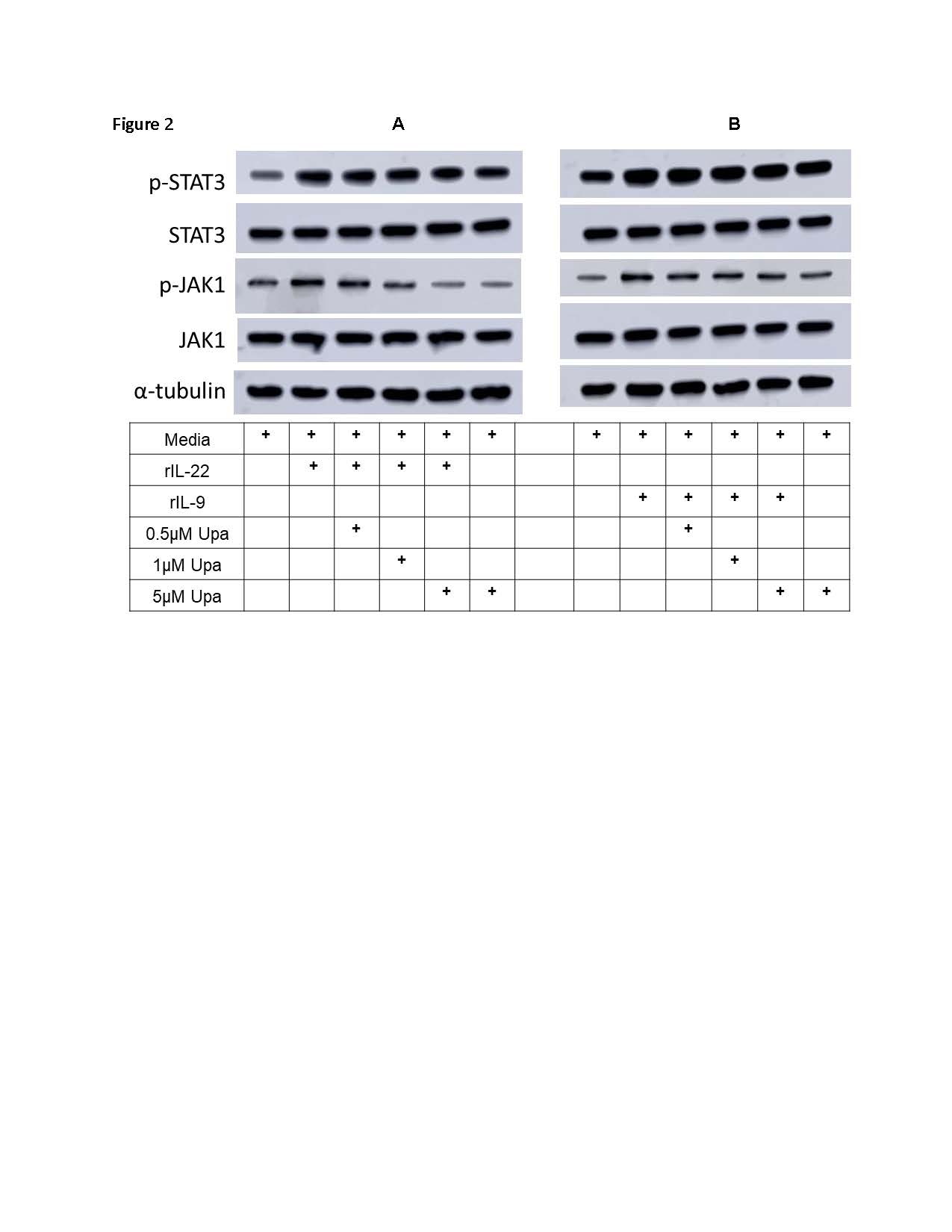
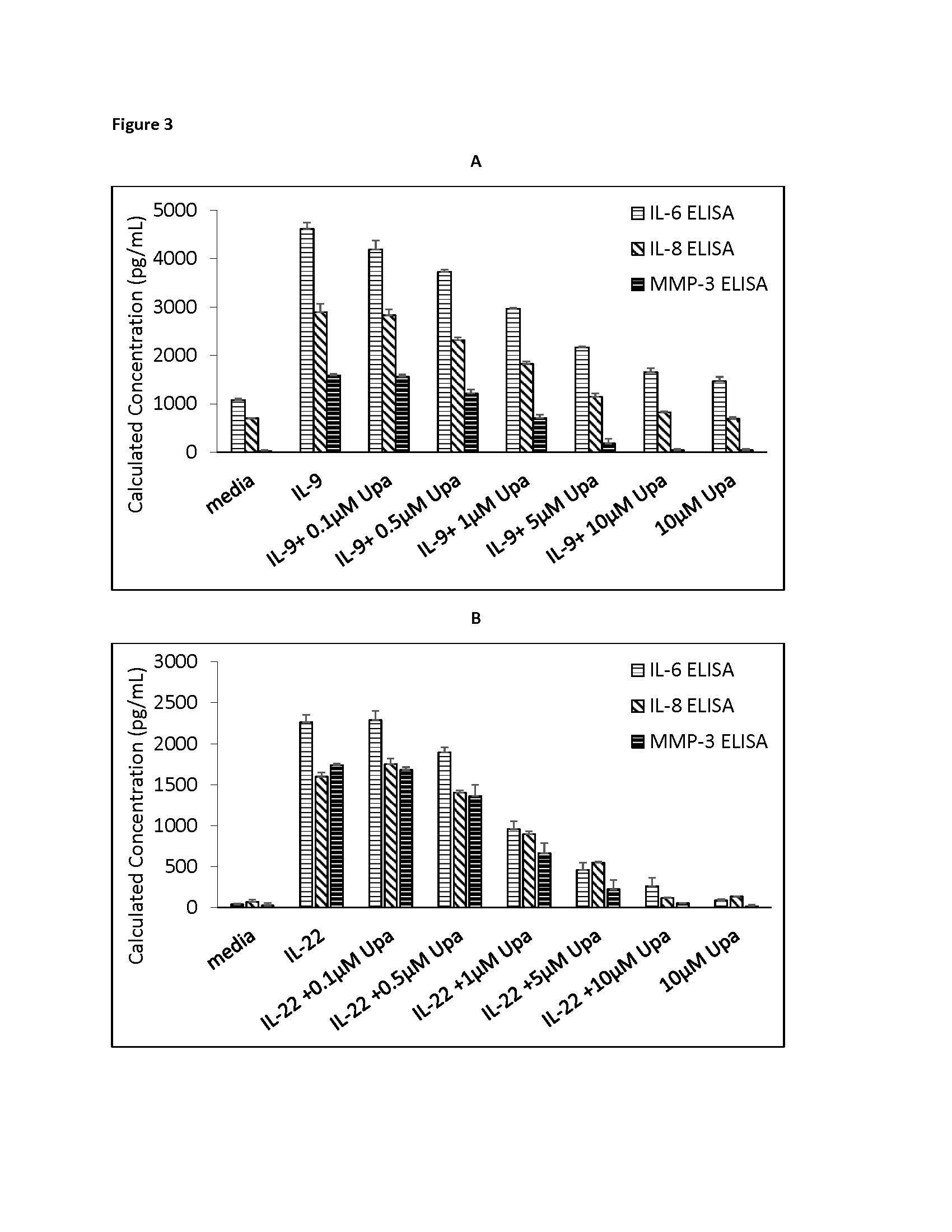
Results: In cultured FLS we observed that rIL-22 and rIL-9 induced increased phosphorylation of JAK1/TYK2 and JAK1/JAK3 respectively compared to the culture media only, (p< 0.01). rIL9/rIL22 also phosphorylated STAT3/RORγt. We observed that the critical events in PsA such as (i) proliferation of FLS (ii) IL-6, IL-8 and MMP-3 production by FLS are induced by rIL-22 and rIL-9 and those were regulated by JAK1/TYK2 and JAK-1,3 respectively. Further pan-JAK inhibitors and other specific JAK-1 and TYK2 inhibitors blocked these effects significantly (p< 0.01). Details of some these observations on the regulatory role of JAK-1 are shown in the Figure 1. Figure-1 demonstrates that rIL-9r/rIL-22 induced proliferation of FLS could be inhibited by blocking JAK-1 with JAKi (upadacitinib) by MTT assay; Figure-2 shows the regulatory role of rIL-22 on JAK/STAT phosphorylation in FLS and Figure-3 demonstrates regulatory role of JAK-1 on FLS in respect to local cytokine and metalloproteinase production.
Conclusion: JAK/STAT signaling system of T cells and its regulatory role in the pathogenesis of psoriatic disease is well established.This study provides a novel insight about the role for JAK-1 and TYK2 signaling on pannus formation and demonstrates novel therapeutic targets for treatment of psoriatic disease.
MTT assay results show that rIL-9/rIL_22 induced proliferation of FLS is inhibited by a specific JAK_1 inhibitor (upadacitinib). IL-9 and IL_22 increases FLS proliferation significantly compared to culture media (p<.001, t-test). Upadacitinib at several concentrations show significant inhibition of IL-9/IL_22 induced FLS proliferation compared to IL-9/IL_22 induced proliferation (p<.001).
(A) immunoblot study of FLS demonstrates that rIL_22 induced phosphorylation of JAK_1 and STAT_3 were inhibited by specific JAK_1 inhibitor, upadacitinib.
(B) immunoblot study of FLS demonstrates that rIL-9 induced phosphorylation of JAK_1 and STAT_3 were inhibited by specific JAK_1 inhibitor, upadacitinib.
(A) rIL-9 induced IL-6, IL-8, MMP3 secretion by FLS was inhibited by JAK_1 inhibitor, upadacitinib. FLS were cultured with rIL-9 and several doses of upadacitinib. ELISA assay of culture supernatants showed significant inhibition of IL-6, IL-8 and MMP3 levels.
(B) rIL_22 induced IL-6, IL-8, MMP3 secretion by FLS was inhibited by JAK_1 inhibitor, upadacitinib. FLS were cultured with rIL_22 and several doses of upadacitinib. ELISA assay of culture supernatants showed significant inhibition of IL-6, IL-8 and MMP3 levels.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Raychaudhuri S, Abria C, Raychaudhuri S. Regulatory Role of JAK-1/TYK2 Signaling on the Pannus Formation: Novel Mechanisms for JAK Inhibitors in Psoriatic Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/regulatory-role-of-jak-1-tyk2-signaling-on-the-pannus-formation-novel-mechanisms-for-jak-inhibitors-in-psoriatic-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/regulatory-role-of-jak-1-tyk2-signaling-on-the-pannus-formation-novel-mechanisms-for-jak-inhibitors-in-psoriatic-disease/