Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Imaging outcomes in ongoing cohort studies are typically evaluated across multiple reading rounds by several readers. Often, only scores from the most recent reading round are used, disregarding valuable data from previous rounds and potentially introducing selection bias by excluding participants lost to follow-up. Using an integrated analysis is an alternative incorporating scores from multiple readers and rounds. This method provides a more truthful reflection, but may introduce additional variability, potentially reducing the estimates’ precision. Therefore, we assessed if an integrated analysis, using available imaging data over time from different reading rounds, affects the precision of change estimates in early axSpA, using a completers analysis as reference.
Methods: Patients with chronic back pain (≥3 months; ≤2 years; onset < 45 years) from the SPondyloArthritis Caught Early cohort with a rheumatologist’s diagnosis of axSpA after two years of follow-up were included. MRIs and radiographs of the sacroiliac joints (SIJ) and spine obtained at baseline, 3 months, 1 and 2 years of follow-up were scored for inflammatory and structural lesions by ≥2 readers in two reading rounds: in round A, baseline, 3 months and 1 year were scored; in round B, baseline, 3 months, 1 and 2 years were scored. Change of each imaging outcome over time was analyzed with multilevel generalized estimating equations (considering the reader level), with time as explanatory variable. Two approaches were used: i) ‘integrated analysis’ (patients with ≥1 score from ≥1 reader from ≥1 reading round); ii) ‘completers-only analysis’ (patients with ≥1 score from ≥1 reader from round B at 2-year follow-up). The second and commonly used approach was considered the reference. We tested different time transformations to investigate which yielded the lowest quasi-likelihood under the independence model criterion, and the best model fit. In cases of comparable fit, the model with the simplest time format was chosen.
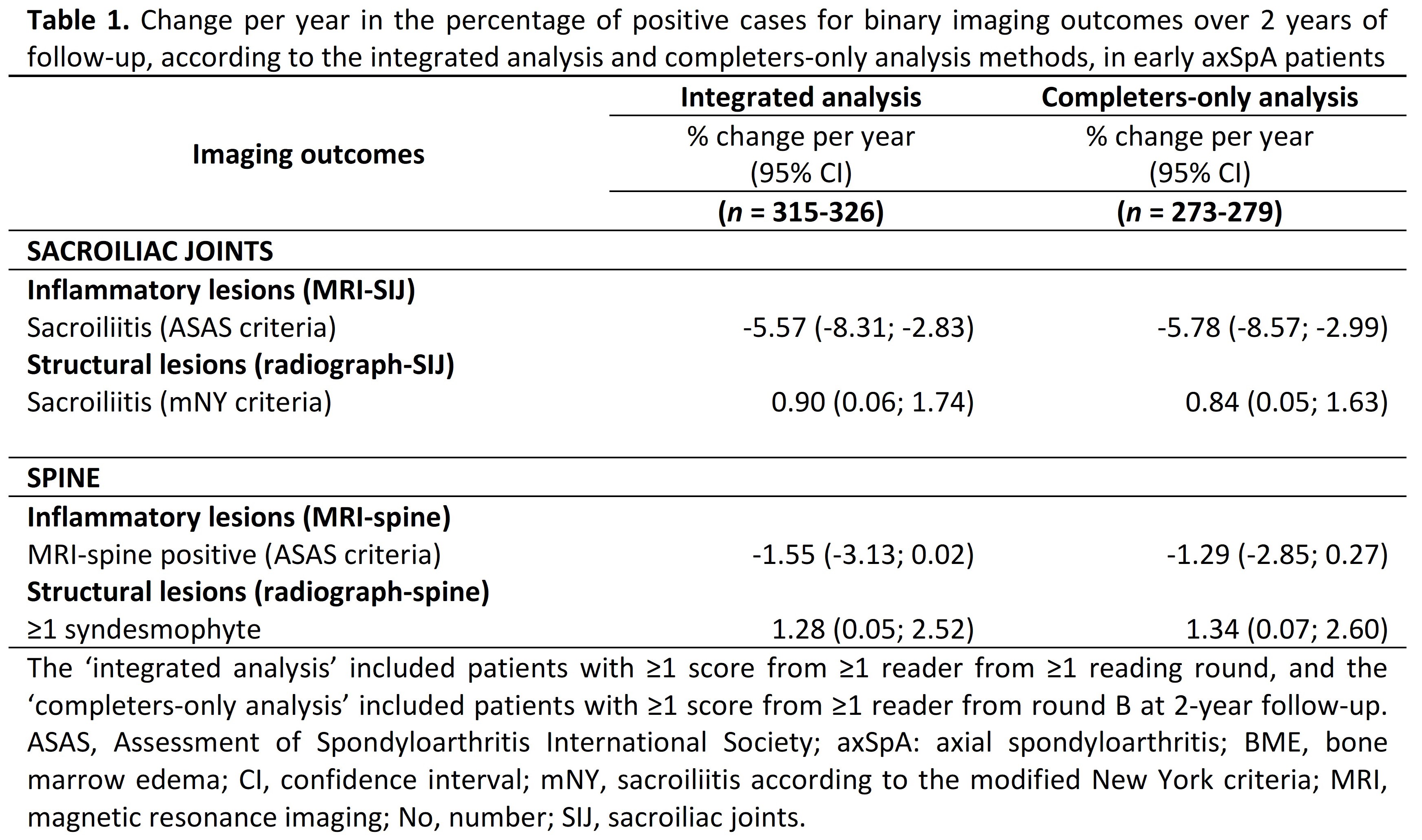
Results: In total, we analyzed 332 patients with axSpA (mean age 30 (SD 8) years; 53% males) of which 279 (84%) patients were included in the completers-only analysis. Binary and continuous variables for inflammatory lesions decreased over time in the MRI of the SIJ and spine, while structural lesions increased (Tables 1 and 2). Due to the best or very comparable fit, models with a linear time representation were used for all outcomes.Comparing both analyses, the integrated analysis included more patients but with similar levels of precision of the change estimates as the completers-only analysis for both the binary and continuous variables. Particularly for binary outcomes, a similar change was found by the integrated analysis with more precision compared to the completers-only analysis, e.g. sacroiliitis according to the ASAS criteria [estimated yearly % change (95% CI): -5.57 (-8.31; -2.83) vs -5.78 (-8.57; -2.99)].
Conclusion: In this longitudinal study, the integrated analysis was shown to allow for the inclusion of all available data, thereby reducing selection bias in determining the population for analysis, while maintaining precision of change estimates in patients with early axSpA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
de Bruin L, van Gaalen F, de Hooge M, van Lunteren M, Marques M, Reijnierse M, Ramonda R, Berg I, Turesson C, Landewé R, Van Der Heijde D, Ramiro S. Reducing selection bias while maintaining precision through an integrated analysis: 2-year longitudinal analysis of imaging outcomes in the SPondyloArthritis Caught Early cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reducing-selection-bias-while-maintaining-precision-through-an-integrated-analysis-2-year-longitudinal-analysis-of-imaging-outcomes-in-the-spondyloarthritis-caught-early-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reducing-selection-bias-while-maintaining-precision-through-an-integrated-analysis-2-year-longitudinal-analysis-of-imaging-outcomes-in-the-spondyloarthritis-caught-early-cohort/

.jpg)