Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Erosive osteoarthritis (EOA) is characterized by osteoarthritic findings with central erosions and collapse of the interphalangeal joint subchondral bone plate. A number of studies indicate that there is an inflammatory component but the pathophysiology of the erosions is not known. Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand (RANK-L) is involved in the erosive process of inflammatory arthritides and we hypothesized that it would be involved in the erosive process of EOA. We therefore compared the RANK-L levels in histological specimens of EOA with non-erosive hand OA specimens and compared the bone mineral densities (BMDs) of a cohort of EOA patients with those of OA patients.
Methods: This was a single center retrospective, observational study. Histological tissue from EOA (n=8) and hand OA (n=15) patients who underwent surgery between 2005 and 2015 were retrieved and stained with an antibody to RANK-L. The diagnosis of EOA was defined by OA based on American College of Rheumatology (ACR) clinical criteria with erosions in at least two interphalangeal joints, as well as a negative rheumatoid factor, anti-citrullinated antibody, and anti-nuclear antigen without personal or family history of psoriatic arthritis or crystal-induced arthritis.
RANK-L+ cells were counted in two to five random 200x fields and RANK-L area was measured in 200X pictures with Image J NIH software. Morphometric analysis was performed in a blinded fashion by two independent evaluators.
A retrospective chart review, of diagnostic codes for EOA and OA from 7/1/2009-7/1/2019 was conducted. EOA diagnosis was confirmed either by radiologic evidence of characteristic erosions in at least two interphalangeal joints or diagnosis by a rheumatologist. Patients with crystalline arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and psoriatic arthritis diagnoses as well as those with a family history of psoriasis were excluded. Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scans for 23 EOA and 50 randomly selected OA patients from the University of Rochester Medical Center were reviewed. Data on age, sex, race, smoking history, height, weight, and osteoporotic medication use was collected. Patients on high doses of steroids were excluded.
Results: There was a significantly larger area of RANK-L staining found with Image J NIH software area calculations for EOA (3773.24 ± 2372.35 microns2, p< 0.0001) compared to OA (1102.32 ± 606.91 microns2, p< 0.0001) (Table 1). There was also a higher number of RANK-L+ cells in the EOA samples compared to the OA samples (Table 2).
DEXA comparison between OA and EOA patients showed a lower median BMD and T-score in the EOA group (0.79 g/cm2, -1.5) compared with the OA group (0.85 g/cm2, -1.35). Demographics between these groups were also compared and were relatively unremarkable (Table 3).
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated that EOA patients had higher levels of RANK-L in synovial tissue and were with lower BMD scores than patients with OA. We therefore propose that RANK-L activity promotes the osteoclastic driven erosive changes in EOA and also results in systemic bone loss.
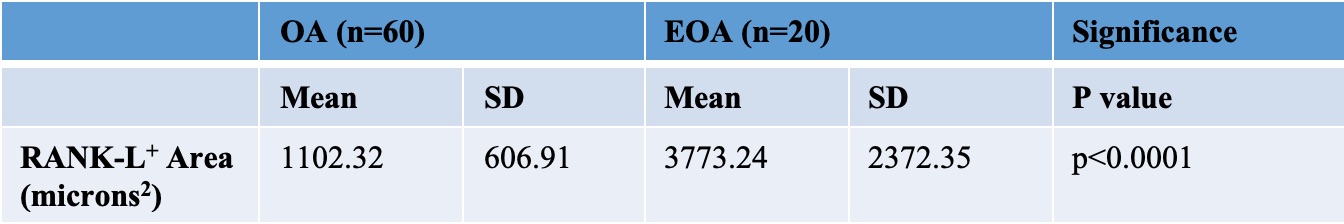 Table 1. RANK-L signal area per 200x field of synovial tissue
Table 1. RANK-L signal area per 200x field of synovial tissue
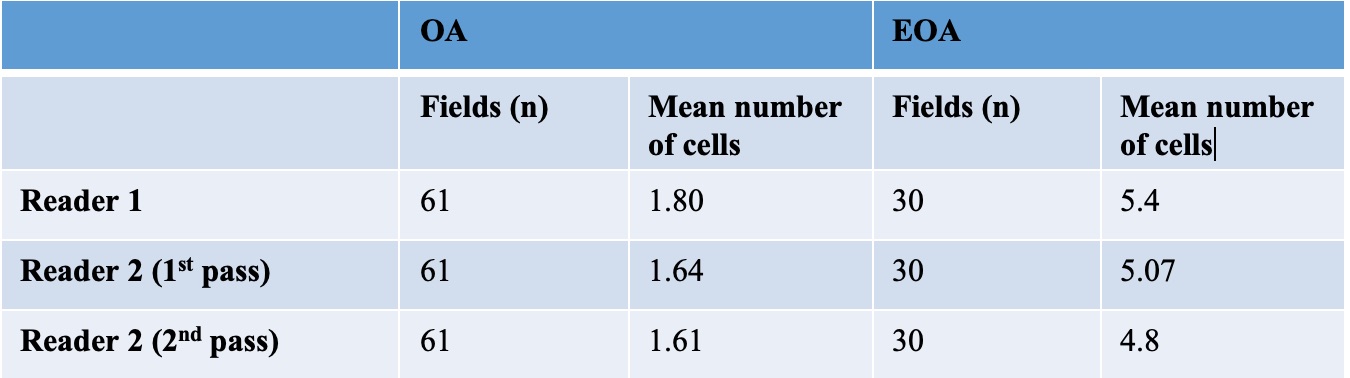 Table 2. RANK-L+ cells counted per 200x field of synovial tissue
Table 2. RANK-L+ cells counted per 200x field of synovial tissue
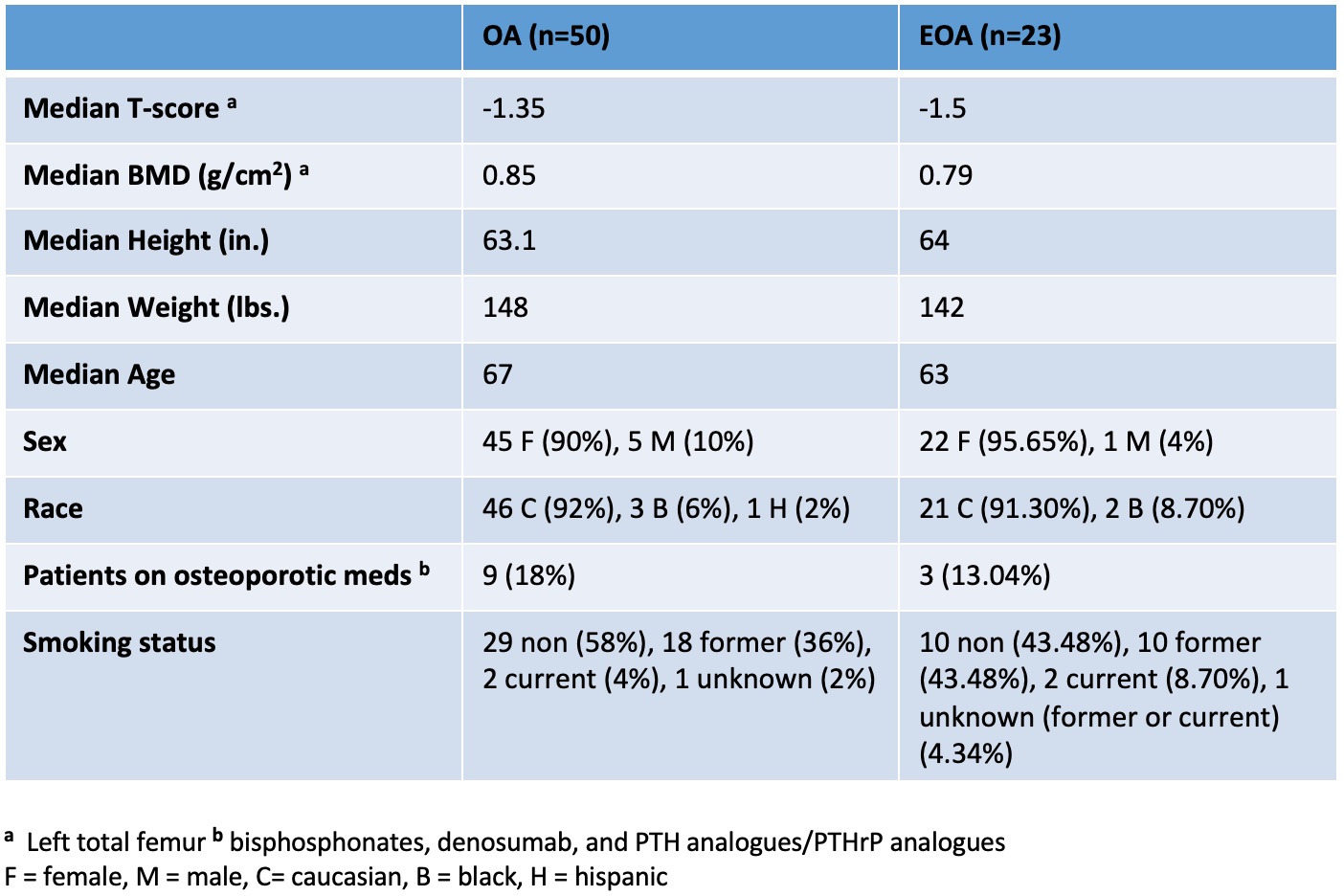 Table 3. DEXA measurements with group demographics
Table 3. DEXA measurements with group demographics
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jakibchuk K, Rangel-Moreno J, Marston B, Anolik J, Anandarajah A. RANK-L Activity: Understanding the Pathogenesis of Erosive Osteoarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rank-l-activity-understanding-the-pathogenesis-of-erosive-osteoarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rank-l-activity-understanding-the-pathogenesis-of-erosive-osteoarthritis/
